N-able N-central (formerly SolarWinds MSP N-central) is a comprehensive remote monitoring and management platform. However, no one should plump for one tool without checking out the alternatives, so we have lined up some really strong RMM systems for you to consider.
Here is our list of the best N-central alternative RMM software:
- Atera EDITOR’S CHOICE This cloud SaaS platform offers a bundle of remote monitoring and management systems plus professional services automation tools in one deal. This package is suitable for use by independent support technicians and large MSPs and IT Departments alike. Start a free trial.
- NinjaOne (FREE TRIAL) – formerly NinjaRMM – a SaaS platform that offers the typical complement of RMM tools plus a ticketing system. Access a 14-day free trial.
- Paessler PRTG (FREE TRIAL) A comprehensive system management tool that can be deployed for remote monitoring. Runs on Windows Server. The tool has excellent mapping and tracking capabilities, which enables you to manage traffic for your customers. Start a 30-day free trial.
- N-able N-sight (FREE TRIAL) This RMM is available in the Cloud or on-premises.
- ManageEngine RMM Central (FREE TRIAL) A self-hosted bundle of MSP tools that is offered in free and paid versions. Installs on Windows Server or on AWS and Azure accounts.
- Domotz This network RMM service is delivered from a cloud platform and includes a multi-tenanted account structure for MSP use.
- OpenRSM Free, open-source RMM that can be extended by plug-ins or customized in-house.
- OpenNMS Open-source RMM available in both free and paid versions.
- Nagios Core Free and open source network monitoring system that can operate remotely. Installs on Windows and Linux.
- ITarian This cloud platform offers RMM plans for IT departments and managed service providers and there is also a free version.
- Microsoft Configuration Manager This cloud-based tool is the replacement for Microsoft SCCM. It is a module of the Microsoft Intune platform but is charged for separately.
- ConnectWise Automate Network management system that can operate remotely. Includes a high degree of task automation.
- Pulseway Cloud-based network management platform charged on a subscription per operator.
- Kaseya VSA Comprehensive package of all the functions an MSP needs and with an attractive console.
About N-able N-central
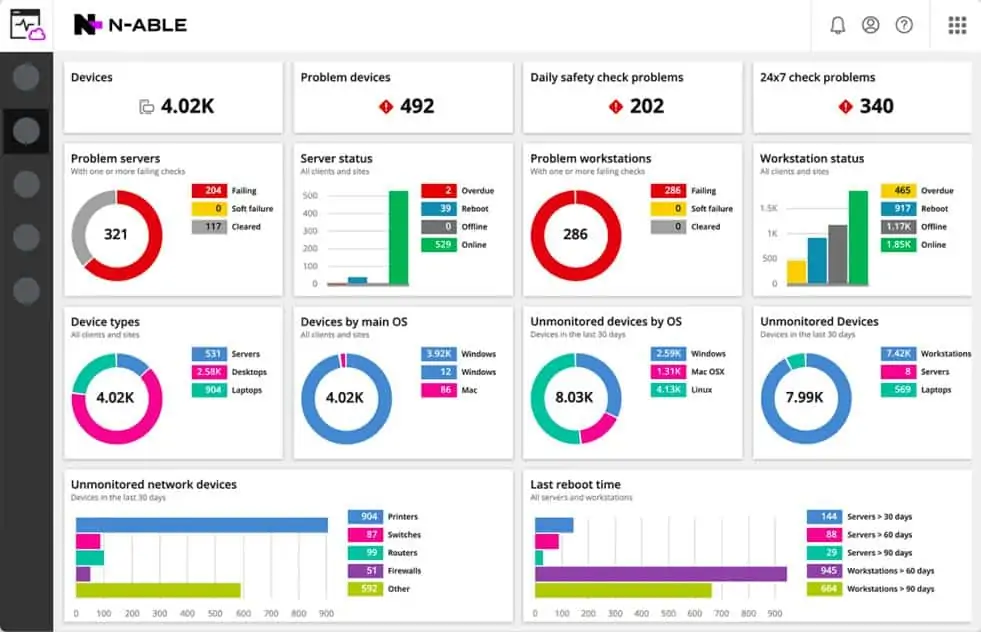
N-able N-central was designed with managed service providers in mind. However, it could also be used by the central IT department of a large multi-site business. The core of the service is a Remote Monitoring and Management platform (RMM). The N-central system can be downloaded and installed on-site or used as a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model.
N-able N-central includes all of the software that an MSP needs to support clients. Not only does it center on RMM tools, such as a remote access system and task automation, but it also includes an endpoint detection and response (EDR) package to keep client devices secure. Another great security feature is the disk encryption manager, which protects storage from tampering. The N-central system can also be combined with N-able Cove Data Protection to provide extra security to clients.
The bundle also includes a patch manager, an automated configuration manager, and a system for managing a fleet of mobile devices. The service is able to interface through to your PSA of choice with its integrated ticketing service.
Related post: The Best RMM Software Solutions
N-able N-central
The N-central system includes team management functions that support the allocation of work between multiple technicians. The workspace of each technician also allows multiple client devices to be supported simultaneously. Tasks can easily be re-routed through the team manager dashboard. Other team management features include the option to create shared tasks.
Although each technician in the team is able to access any device on any client site, there are controls over how access is implemented and automated logging of technician actions. A credentials manager stores access usernames and passwords and makes those available within the technician dashboard when needed. This removes the need for passwords to be passed around on paper and no individual technician would be able to access client devices outside of the supervision of the N-central system.
The reporting module of the package included SLA goal reporting, and other performance monitoring formats. Although there are no PSA functions within the N-central system, it integrates with third-party systems, such as ConnectWise Manage, HaloPSA, and TopDesk for ticketing.
The technician dashboard also includes live network performance monitoring and NetPath, which enables traffic flows to be monitored end-to-end between any given nodes on the network. The network monitoring module starts with an autodiscovery service that automatically generates a network inventory and spots any changes during ongoing monitoring. The system is able to supervise cloud resources as well as the infrastructure on the client’s site.
Network device and endpoint performance monitoring are standardized by templates that set performance expectation thresholds. These can be tied into SLAs and they automate capacity monitoring. Alerts draw the attention of the technicians when problems arise, so operators can get on with other tasks, knowing that no news is good news. Alerts are set at levels that give technicians time to head off problems before they become noticeable by users.
N-able offers two options for hosting N-central. It is available as a hosted system on a SaaS model or it can be self-hosted. The on-premises software package includes its own operating system. This is a version of CentOS. Some features, such as NetPath, require a separate host running Windows or Windows Server. N-able offers a 30-day free trial of N-Central.
RMM options
Even though you now know that N-central does still exist, you might be interested in exploring other RMM software. All of the alternatives to N-central that we have researched are free to use or offer you a free trial.
The next section of this guide gives you details of each of these alternatives.
The best N-central alternative RMM software
By continuing the service life of N-central N-able actually ensured the longevity of one of the rivals to its own RMM tool. This is the leading alternative to SolarWinds N-central and it is the number one option detailed in your list below. However, we give you descriptions of 14 other RMM tools that would work as an alternative to N-Central.
Our methodology for selecting alternatives to N-able N-central
We reviewed the market for remote monitoring and management packages like N-able N-central and assessed the options based on the following criteria:
- Technician tools to support remote systems
- Secure password management and distribution
- A multi-tenant architecture that keeps the data of MSP clients separate
- Automated monitoring for networks, servers, and applications with performance alerts
- Automated system administration tools, such as a patch manager
- A free trial or a demo option for a no-cost assessment opportunity
- Value for money from remote monitoring and management package that is offered at a fair price
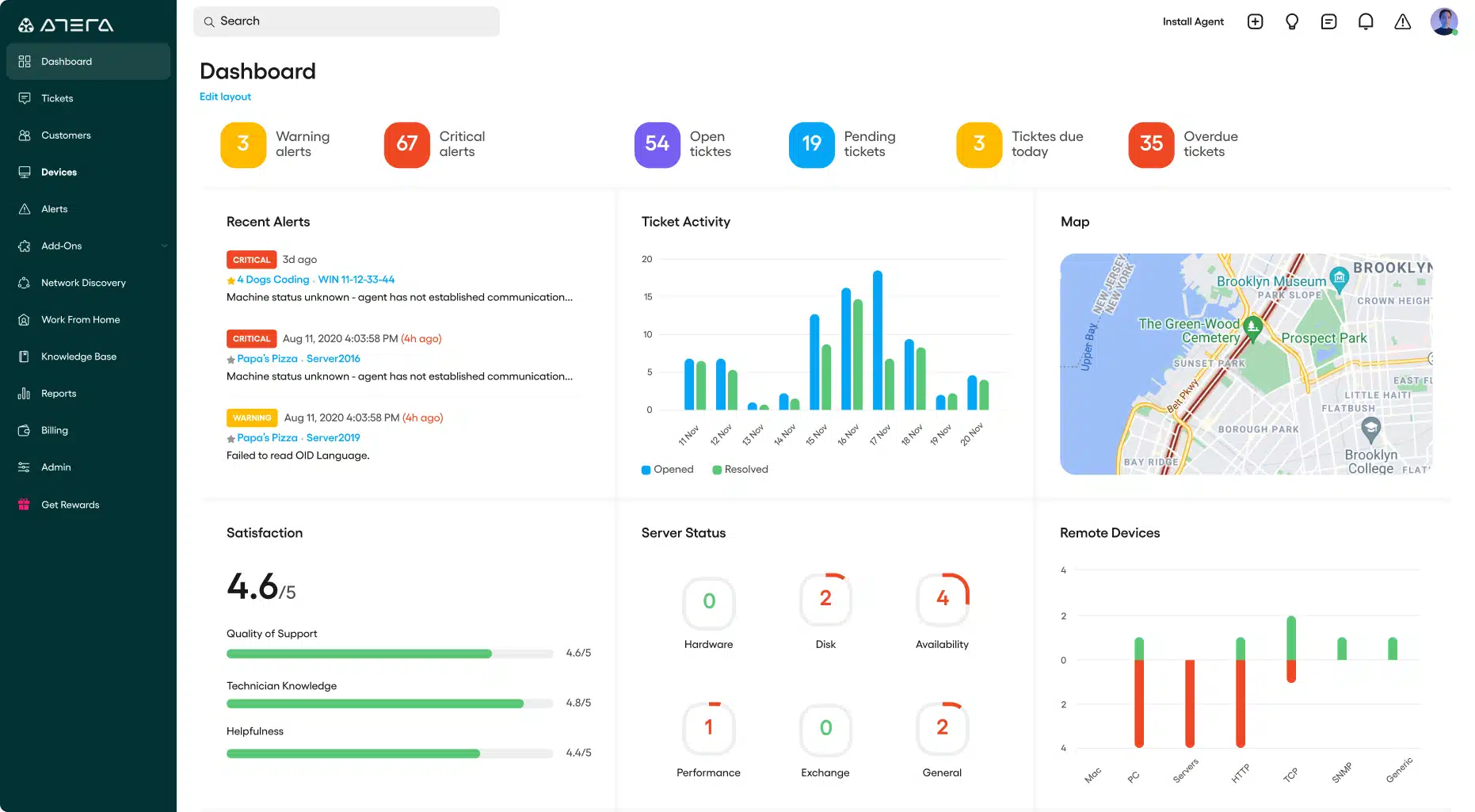
1. Atera (FREE TRIAL)
This cloud-based platform provides professional services automation (PSA) systems as well as RMM tools so you get all of the systems you need to run an MSP and you don’t have to host the software.
Key Features:
- Versions for in-house or MSP use
- Ticketing system included
- Software deployment and patch management
- Monitoring automation with alerts
- Remote access
Why do we recommend it?
Atera is a close competitor of the N-Able N-central package. This is a cloud platform with tools that service support technicians and also includes a ticketing system. The Atera package doesn’t have a parallel PSA package but services such as timesheet generation and billing calculations are included.
The Atera system includes storage space and a multi-tenanted architecture so all of your work is kept on the Atera servers and you don’t need to keep any information about your clients on your own servers – this is a great data security feature. Each account on the Atera platform is protected by encryption and so are the connections between that system and the users that access it.
The RMM provides a system scan to track down all endpoints and devices on the network. The system requires endpoint agents to be installed in order to monitor the software that they hold. These agents are available for Windows, Windows Server, and macOS.
The system scans each endpoint and compiles a list of installed software. This is the basis for the automated patch manager built into the Atera package.
Atera includes a ticket management system. This automates work allocation and the team manager console shows which technician is working on which tickets. Tasks can be escalated, split, merged, shared, and re-routed. The technician console also gives access to Splashtop, which gives access to remote endpoints. This can be performed both when the device is attended by the user or unattended. The package includes a Wake-on-LAN routine to enable devices to be accessed even when they are turned off.
Atera includes an alerting system that provides automated monitoring and enables a few technicians to look after many client systems because they only need to pay attention to each of them if a problem is detected.
Who is it recommended for?
There are two versions of Atera. One of those is designed for use by managed service providers and the other is for IT departments. Each version includes four plans, which have parallel services except that the MSP version has a multi-tenant architecture and client management features that aren’t in the IT department version.
Pros:
- A cloud platform that can be accessed from anywhere, tying distributed teams together
- Network, server, and application monitoring across the internet with endpoint agents for Windows, Windows Server, and macOS
- Dashboards for technicians and team managers that include ticket distribution functions and task management services
- A password locker and remote access tools plus activity logging for technicians
- MSP administration functions that ensure contract compliance with SLA tracking
- Automated processes including performance threshold alerts and a patch manager
Cons:
- There is no endpoint agent for Linux
The Atera system is offered in three plans that suit businesses of different sizes. You can assess the Package on a free trial.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
Atera offers both RMM and PSA services in one, cloud-based package. This service includes storage space for all client data so there is no risk of remote workers leaving client data on a lost device. The system can be accessed from anywhere, so your team isn’t limited to working together in one office. You can manage the technician team’s workload through the ticketing system and give them secure access to remote endpoints.
Start a free trial: atera.com/signup/
OS: Cloud-based
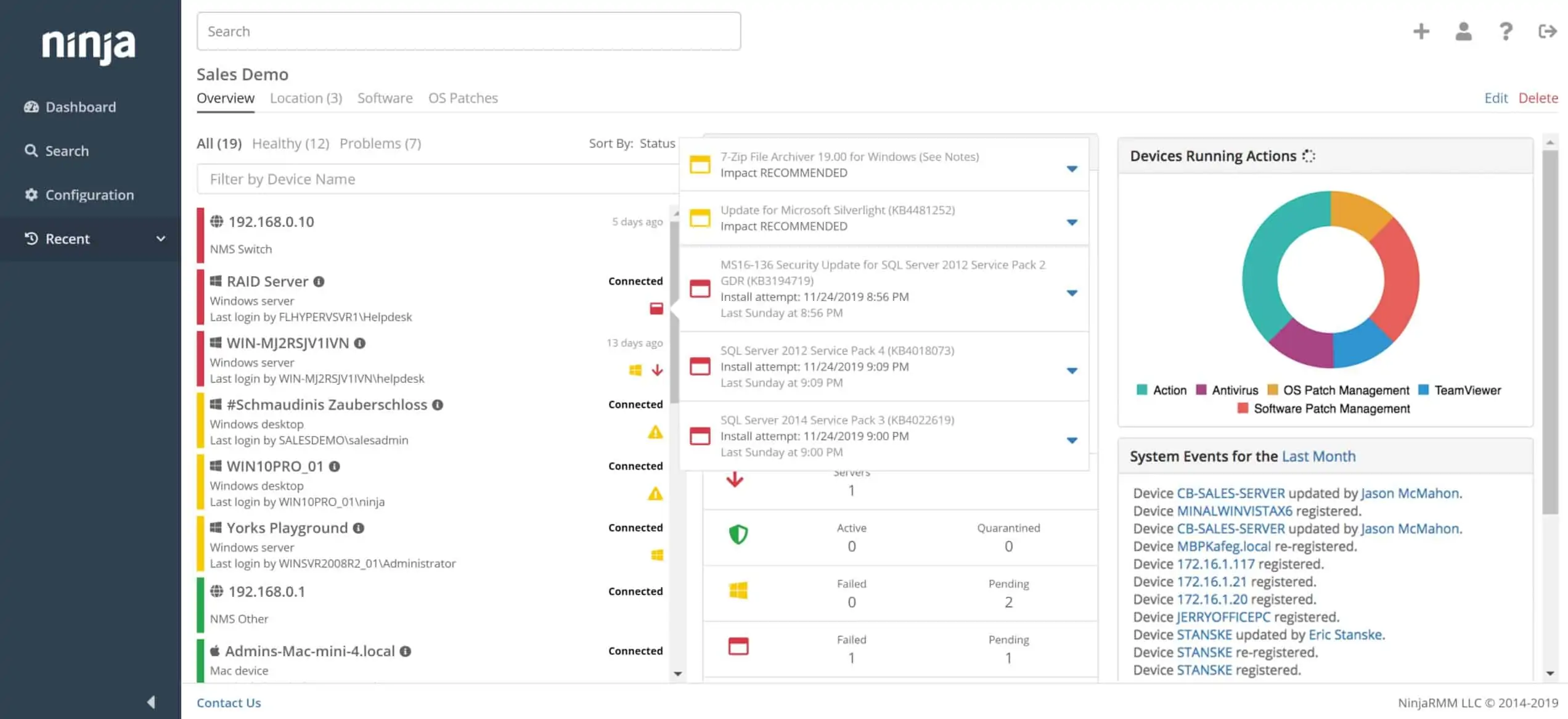
2. NinjaOne (FREE TRIAL)
NinjaOne (formerly NinjaRMM) is a close competitor to N-able N-central. While most RMM providers also offer a professional services automation (PSA) package, NinjaRMM doesn’t have an in-house companion. It is possible to add on a third-party PSA – the system integrates with eight PSA systems, including ConnectWise Manage and Accelo.
Key Features:
- Network monitor with performance alerts
- Endpoint management for Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Software management includes a patch manager
- Ticketing system
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne is another cloud platform that is a good alternative to N-able N-central. This package is much closer to Atera than to N-central because these two packages include ticketing systems, which N-central does not. The NinjaOne platform offers a patch management service and there is also a Backup option available.
One of the main tools that an MSP would want from a PSA is a ticketing system – NinjaOne includes that. By integrating its own ticketing system, the NinjaOne service is able to use that platform as a team management system, not just for Help Desk tasks. The NinjaRMM service is able to cater to Help Desk scenarios and it provides a task dashboard for use by technicians to queue allocated tasks and mark progress.
The ticketing system acts as a scheduler, automatically channeling through tasks raised by the automated monitoring system’s performance alerts and also scheduled maintenance tasks.
The monitoring service that is built into NinjaOne offers automated processes that track performance on networks and endpoints. This service includes endpoint agents for Windows and macOS and it monitors Linux devices across the network. The tool includes a discovery system that logs all of the devices connected to the network. It also scans each endpoint to create a software inventory. These information bases underpin configuration management and patch management services in the bundle.
The patch manager scans through the software inventory and notes the version numbers of operating systems and software packages. This scans software suppliers for new versions and then copies over patch installers when they are available. The system will then install those updates at the next available maintenance window. These updates are performed unattended – remember that the MSP will be managing several different clients simultaneously. All actions taken through the system, either manually or through automated processes, are logged.
The NinjaOne SaaS package includes storage space on the cloud server for those installers and log files. In fact, an MSP doesn’t even need any of its own infrastructure in order to serve clients – the technicians can work from home. No matter where technicians are based, the system channels performance and progress reports through to the team manager.
Who is it recommended for?
NinjaOne is designed for use by managed service providers and it has a multi-tenant architecture. However, IT departments can also use it – they just wouldn’t need to set up sub-accounts. NinjaOne doesn’t publish a price list, which makes it difficult to compare the package to N-central for price-sensitive small businesses.
Pros:
- A support infrastructure for managed service providers
- Automated processes and tools for manual intervention
- A ticketing system for work scheduling and team management
Cons:
- Not very strong on supporting Linux devices
There is no published price list for NinjaOne – you need to contact the Sales Department to request a quote. NinjaOne is available on a 14-day free trial.
3. Paessler PRTG (FREE TRIAL)
 Paessler’s network monitoring strategy is unique. While other software houses produce specialized modules, Paessler markets one sole product, which is PRTG. The package contains a large number of sensors. A sensor monitors one specific aspect of infrastructure or performs a service, such as Ping. The system is capable of monitoring networks, servers, and applications. However, you can tailor the tool by choosing the number of sensors to activate. The system is completely free to use if you only activate up to 100 sensors.
Paessler’s network monitoring strategy is unique. While other software houses produce specialized modules, Paessler markets one sole product, which is PRTG. The package contains a large number of sensors. A sensor monitors one specific aspect of infrastructure or performs a service, such as Ping. The system is capable of monitoring networks, servers, and applications. However, you can tailor the tool by choosing the number of sensors to activate. The system is completely free to use if you only activate up to 100 sensors.
Key Features:
- Customizable package
- On-premises or SaaS
- Automated asset discovery
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler PRTG is strictly a monitoring system, so it doesn’t compete with the system management tools in the N-able N-central package. However, its automated monitoring modules cover every aspect of system monitoring, including asset discovery, mapping, and inventory documentation. The package is customizable so any buyer can adapt the extent of the system.
Although the PRTG strategy is one of applying a general WAN monitoring tool to MSP scenarios, the package does include tailored dashboards and account management. This allows you to allocate different capabilities to different team members.
One weakness of PRTG for MSPs is that it is purely a monitoring tool. Although those monitoring functions are very comprehensive, the PRTG system doesn’t include any infrastructure management functions, such as Help Desk ticketing or patch management. PRTG would probably be better suited to a corporate IT center that operates as a cost center rather than to outright independent MSPs.
The tool has excellent mapping and tracking capabilities, which enables you to manage traffic for your customers. The capabilities of PRTG extend into Cloud and wireless network elements as well.
Paessler offers PRTG as on-premises software and also as a Cloud service. The rate you pay for the tool depends on how many sensors you want to activate. The company runs a free trial for new customers and that extends to both formats. The software installs on Windows Server and even if you opt for the Cloud-based service, you will still need to install data collectors on your own system which require Windows Server.
The premise of this application of PRTG is that it can monitor networks, endpoints, network devices, operating systems, and software for a WAN from a central location. On that basis, it works perfectly well for MSPs to administer several sites on behalf of clients.
Who is it recommended for?
Small businesses can use PRTG for free if they only activate 100 of the sensors in the package. Larger businesses will use a lot more than the minimum purchase quantity of 500 sensors. There is also a version for MSPs. Deployment options are a SaaS platform and an on-premises software package.
Pros:
- Uses a combination of packet sniffing, WMI, and SNMP to report network performance data
- Fully customizable dashboard is great for both lone administrators as well as NOC teams
- Drag and drop editor makes it easy to build custom views and reports
- Supports a wide range of alert mediums such as SMS, email, and third-party integrations into platforms like Slack
- Each sensor is specifically designed to monitor each application, for example, there are pre-built sensors whose specific purpose is to capture and monitor VoIP activity
- Supports a freeware version
Cons:
- Is a very comprehensive platform with many features and moving parts that require time to learn
The free trial gives you unlimited sensors. You can download PRTG on a 30-day free trial. The trial stops working on its expiry date but you will not be charged after that date.
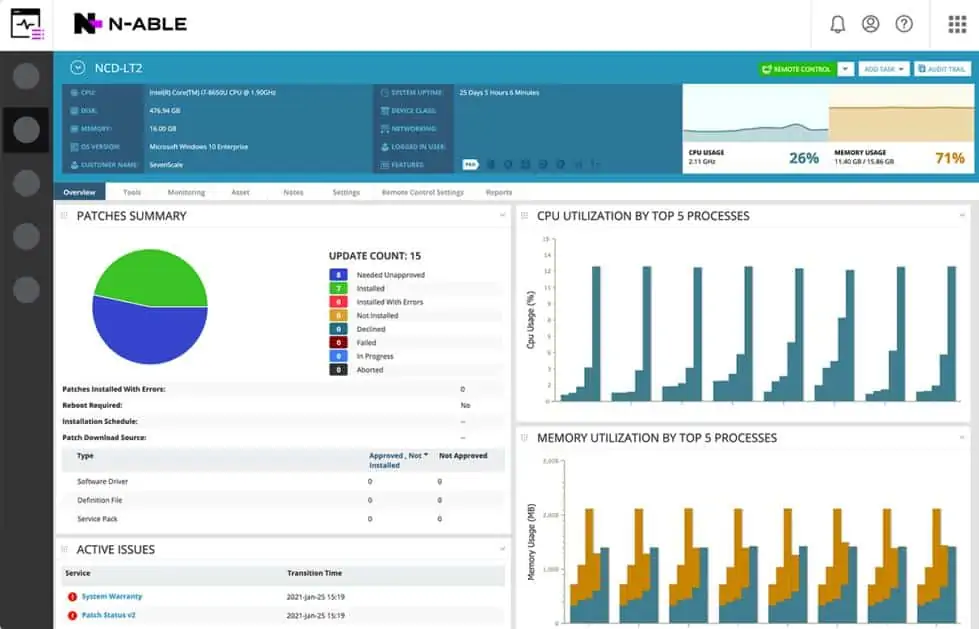
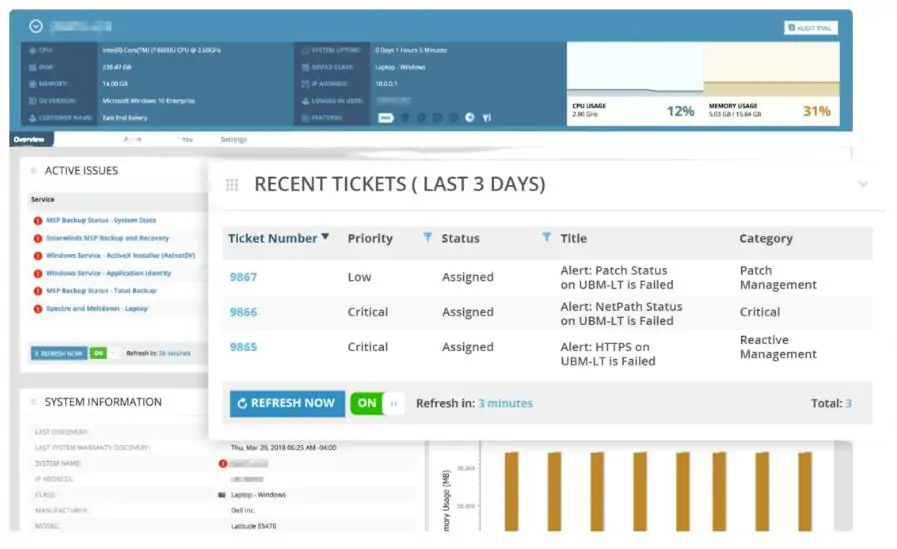
4. N-able N-sight (FREE TRIAL)
N-able N-sight is part of a series of remote support assistants produced by the company. The other MSP-oriented tools that N-able produces are MSP Manager, Cove Data Protection, Mail Assure, Risk Intelligence, and Take Control. All of these tools are designed to work together with the RMM module, although they are sold separately.
Key Features:
- Suitable for IT departments
- Designed for smaller MSPs
- Automated monitoring
Why do we recommend it?
N-able N-sight is a stablemate of N-central. While N-central is purely an RMM system, N-sight includes some extras, such as a ticketing system, which is usually part of a separate PSA package. The N-sight package compares more directly to Atera and NinjaOne and, like those rivals, the package’s subscription rate is levied per technician.
The N-able MSP module that most directly maps onto the functionality of N-central is the N-able N-sight. The company set up two rival RMM packages when it took on N-Central. Its other MSP tools are also able to interact with N-central, so if you choose to get all of your MSP software from SolarWinds, you have two options when choosing software to cover RMM.
The main features of this tool are very similar to those available with N-Central. The system enables you to manage the assets of clients on remote sites, both through direct contact and through automated procedures. Patch management and antivirus update coordination are very strong elements of SolarWinds RMM. The addition of the company’s Risk Intelligence module will greatly enhance the security features of this tool, which include malware protection and website protection. The system also guards against the possibility of infected websites being used as an entry point to the network.
The tool is able to monitor a wide range of devices and can also detect and track the supporting services for virtualizations. The combination of functions built into the RMM enables operatives to keep track of system conditions on client sites from one console. The dashboard includes automation features, such as drag-and-drop activity allocations. The reports that ship with the package will also help you monitor the performance of your staff as well as the conditions of the client’s site. With a combination of the reports of the RMM tool and its dashboard utilities, your team will be better able to identify security and performance threats to your clients’ systems and head them off before they cause damage. The simplicity of the RMM’s interface is one of this tool’s strengths because it enables support staff to get to the most frequently-used tools quickly.
Who is it recommended for?
N-able markets N-sight for established managed service providers, while N-central is packaged for IT departments and growing MSPs. So, there is a little difference in the design of the two services. However, the core monitoring and system management tools are the same. For example, both packages include a patch manager.
Pros:
- Excellent monitoring dashboard, great for MSPs or any size NOC teams
- Scalable cloud-based deployment
- Monitor for anywhere via web browser
- Automatic asset discovery makes inventory management easy, even on busy networks
- Wide variety of automated remote administration options make it a solid choice for helpdesk support
Cons:
- The platform can take time to fully explore all of its features and configuration options
N-able offers a 30-day free trial of its N-sight package. You don’t need to present any payment details in order to receive this offer; therefore, there is no risk at all to trying it.
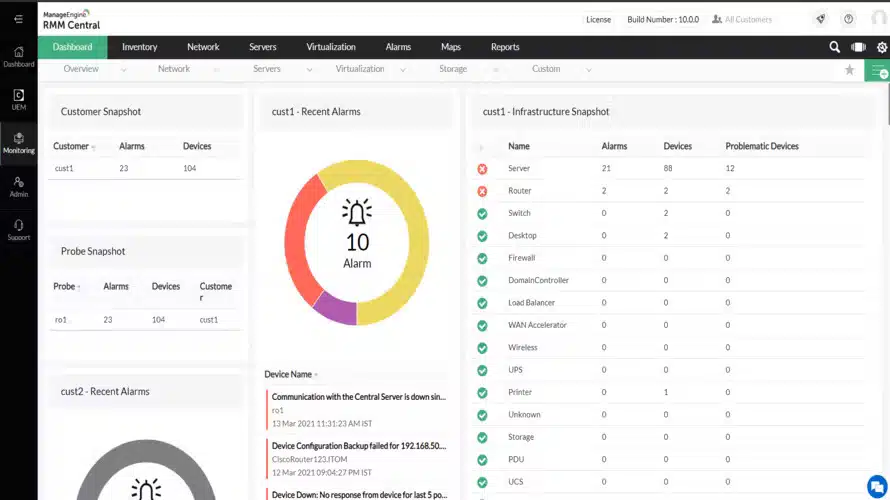
5. ManageEngine RMM Central (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine RMM Central is a package of tools that you host yourself, rather than a SaaS platform. You can run it on your own server with Windows Server or add it to an account on AWS and Azure. The package includes technician tools that automate most of the tasks involved in monitoring and managing an entire IT system.
Key Features:
- On-premises or cloud installation
- Automated discovery and documentation
- Controls desktops, mobiles, and peripherals
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine RMM Central is clearly aiming for N-central’s market – the similarity in the name of the package is an indicator. However, the ManageEngine option is more comprehensive than N-able’s offering. As well as providing system discovery and automated network and endpoint management RMM Central includes a mobile device management module.
On enrollment, the RMM will scan a network and log all of the devices and endpoints in an asset inventory. This scan repeats continuously, so any changes made to the hardware composition of the network are reflected immediately with inventory updates.
The RMM Central package includes a network topology mapper. This generates network maps on access from the data in the hardware inventory, so it always shows the latest state of the network.
The network monitoring functions of the RMM extend to the activities of wireless networks and virtualizations – RMM Central will track events on Hyper-V and VMWare hypervisors.
The package includes an endpoint scanner that logs all of the software that encounters, creating a software inventory. That process provides the base for a patch manager. This system will operate for Windows, Linux, macOS, and software packages. It polls for update availability and also scans for vulnerabilities.
Device monitoring in RMM Central includes a USB device control system that enables you and your clients to set up blocks on USB storage device attachment or define the data types that can be installed on them.
A mobile device management tool helps identify and permit BYOD on your network. However, the tool also operates for devices that are company-owned and intended for use off site. The system includes mobile content management to control where corporate data goes and containerized delivery of applications and data for situations where employees use their own devices to access corporate resources. The mobile device management suite is appropriate for use with devices running iOS and Android.
All of the monitoring systems in ManageEngine RMM Central include performance alerts that automate the monitoring of regular activity. Technicians are only required to get involved when thighs go wrong.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine makes this package accessible to small businesses by offering a Free edition that will monitor and manage 20 endpoints and five network devices. It even includes the MDM package. Both the free and paid editions are software packages that you can run on Windows Server, AWS, or Azure.
RMM Central is offered in two editions, which are called Free and Enterprise. Both versions include the same functions but the Free edition is limited to monitoring 20 endpoints and 5 network devices. You can get a 30-day free trial of the Enterprise edition.
6. Domotz
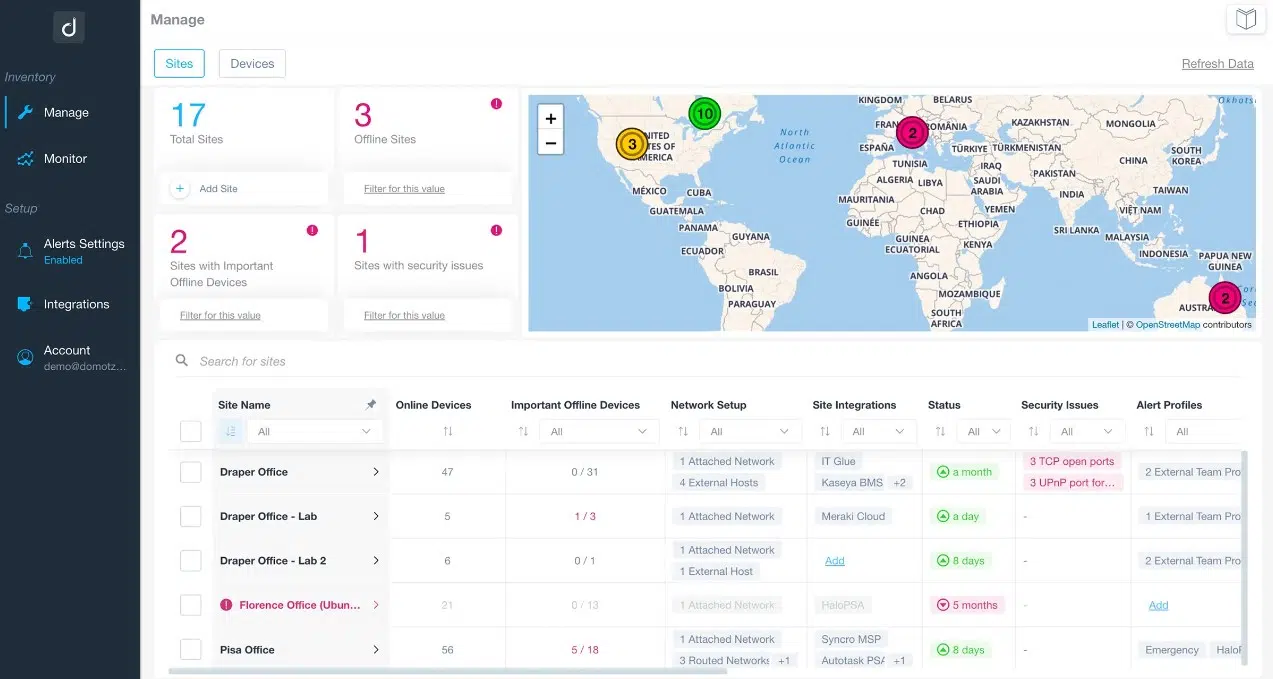
Domotz is a SaaS platform that offers remote monitoring and management services that can access any network anywhere in the world that has an agent installed on it. The most appealing feature of Domotz is its fixed price per site. This really helps MSPs price their services because the price doesn’t change according to the number of devices on the LAN. So, you can cost software for a new client account without even having to quantify the network hardware to be monitored.
Key Features:
- Device discovery and network mapping
- Asset inventory creation
- Automated monitoring with alerts
Why do we recommend it?
Domotz is a network monitoring and management package, so it doesn’t fully compete with N-able N-central, which also monitors and manages endpoints and software. This system implements network discovery and creates an asset inventory. It then implements continuous network monitoring with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). The package also includes a network configuration manager.
The Domotz system includes an autodiscovery service, which documents the network by providing an inventory and a topology map. It is also possible to view multiple sites for each customer on a world map. The Domotz system is multi-tenanted, so you keep all of the data for each client separate. You can enroll multiple sites in each client sub-account.
The platform uses SNMP to provide automated device monitoring and this service includes an alerting mechanism. Alerts are raised if an SNMP device agent reports a status problem and it is also possible to place performance expectation thresholds on any of the metrics that the system gathers to trip alerts.
Ad-hoc investigative tools in the system include a response time and availability test with Ping. This can be set to run periodically on a schedule and can trip an alert if performance dips. It is also possible to store test results to analyze performance over time.
Who is it recommended for?
Domotz has an interesting subscription price because it is levied per network, which, essentially means per site. It doesn’t matter how large that LAN is, so that makes this a very good deal for large businesses. The only problem is that this package doesn’t include software management features.
Pros:
- A fixed price per site for any size of network
- Automated network and endpoint monitoring
- Security monitoring and configuration management
Cons:
- The trial only lasts 14 days
The Domotz package includes system management tools such as configuration backup and monitoring for network devices. Each endpoint gets scanned for OS details and a software inventory. Security tools in the package include connection protection checking, SSL certificate monitoring, and port monitoring.
You can assess Domotz with a 14-day free trial.
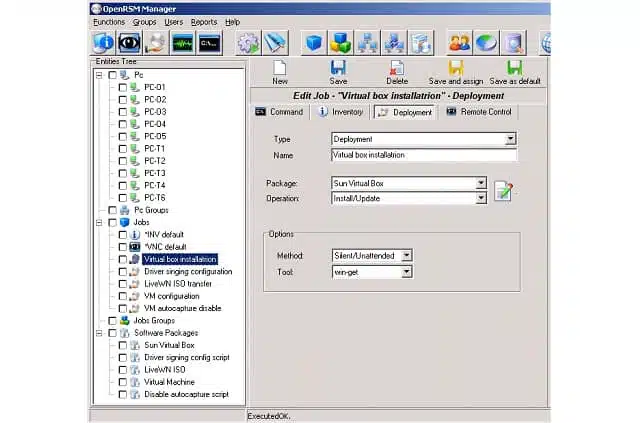
7. OpenRSM Manager
Although PRTG has a free version and both N-able RMM solutions can be had on a free trial, none of those options were planned as free services from the ground up. OpenRMS Manager is an open-source project, hosted by Sourceforge. You can just download the programming code and install the package for free.
Key Features:
- Automated monitoring
- Remote access
- Reporting module
Why do we recommend it?
OpenRMS is a free tool, which is always appealing. The system is quite old now and hasn’t been updated since the release of version 2.2 in April 2011. This gives you an opportunity to scan through the code and even make your own RMM system by rewriting it if you want.
Being a free non-commercial project, OpenRMS isn’t as sophisticated as the top options in this guide and you don’t get any technical support from the company – because there is no company. However, having access to the source code means that you can be sure that there are no hidden tricks. Also, if you have programming resources available to you, there is also the option of customizing the code to get the perfect RMM solution for your organization.
The core of the OpenRMS system is a remote access monitoring service. Plugins to the central module allow all the capabilities to monitor wireless networks and even IoT devices. The system includes agent software that gets installed on the remote equipment. This communicates with a server module, which provides the command center.
The three main tasks categories performed by the remote management console are:
- Asset management
- Network monitoring
- Remote Desktop control
The types of tasks that these facilities can perform include path distribution, user credential management, and status reporting. The software for OpenRSM can be installed on both Windows and Linux operating systems. There are also agents that operate on embedded systems.
If you operate virtualization on your network, or on client sites, the OpenRSM service can manage these services for you. It can also bypass the VM environment whenever queries to the underlying hardware and operating systems are required.
The reporting module of OpenRSM offers the option to create your own reports. The program doesn’t ship with many pre-written report formats and it isn’t specifically designed to serve as an SLA compliance reporter, so you need to set up those categories of reports for yourself.
If you are not attracted to the “cookie-cutter” solutions offered by the big software houses, then a customizable open-source option could be what you are looking for. This software does need work. However, it is completely free to use.
Who is it recommended for?
Open source projects are always interesting and this tool’s development project seems to have been abandoned. So, you won’t get any professional support included for free. However, the creator of the tool now runs OpenRMS as an IT support service, so you could contract that business for professional support.
Pros:
- Completely free and open source
- Can provide asset management, networking monitoring, and remote desktop support in a single tool
- Reports are highly customizable
Cons:
- The interface is outdated making it harder to navigate
- No technical support
- Requires a large time investment into learning the platform and fixes issues manually
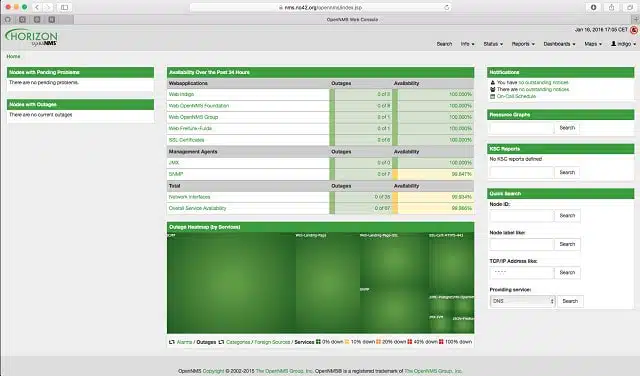
8. OpenNMS
OpenNMS offers you another free, open-source RMM option. This system has a different production format to that of the volunteer-driven OpenRMS. The OpenNMS service is open source and anyone can read the code. However, this is a commercial product and is copyrighted. There is a paid version of OpenNMS as well.
Key Features:
- Remote network monitoring
- Remote access
- Free option
Why do we recommend it?
OpenNMS provides two options with its free Horizon package and the paid Meridian system. This dual strategy is not unique because, for example, systems, such as Nagios also offer that structure. This service doesn’t directly compete with N-able N-central because it doesn’t include system management tools or features to watch over endpoints and software.
The free OpenNMS is called Horizon and the paid version is called Meridian. The Meridian version has more features and is subjected to more vigorous software testing than Horizon. It has technical support, including the release of more regular updates and bug fixes that are available for the free version. Both versions do coordinate over time through updates.
Bug discovery and fixes for Horizon are generated by a user community, whereas a dedicated staff monitors the code for the paid version. So, bug alerts and innovations spotted or created by users eventually get integrated into the paid version, but only once the code is judged to be stable. Basically, by using Horizon, you get the beta version of Meridian.
NMS stands for “Network Monitoring System.” This is a traffic monitor that can be applied to WAN support and so would also be suitable for managed service providers to check on the activities of client networks.
The company behind this service is constantly improving the visualizations that the management module provides in its dashboard. However, the back end remains the same and that is primarily an SNMP-based service. This is a solution for MSPs that monitor network performance and have contracts that revolve around the continual availability of network devices. There aren’t any problem resolution modules included in the package; however, remote access facilities could be used to check on configurations and also to roll out patches.
This is a monitoring system that would be better suited to a back-office system for the IT department of a medium-sized enterprise.
Who is it recommended for?
The free edition of OpenNMS is used as a Beta test for any new features, which, when stable, are released for OpenNMS Meridian users. The service only monitors networks with an emphasis on traffic analysis. Small businesses will like the Horizon version and mid-sized companies will go for the Meridian edition.
Pros:
- Open source projects, lots of room for customization, and personalized add-ons
- Has a large amount of documentation available
- Features two versions, a stable version and a beta test version for new features
- Offers a wide range of monitoring options and flexible alert notifications
Cons:
- Is more complicated to set up than paid tools that focus on streamlining the onboarding process
- Users rely on help documents and forums for support, which isn’t always the quickest way to resolve issues
- It can take a long time to get things working the way you want them on the platform
9. Nagios Core
 Nagios Core is a free open-source network monitoring system. The tool can be extended endlessly by plugins. You can either write your own plugins or get them from the user community. The tool has a very wide user base and there are even other network management systems that are adaptations of Nagios Core. The users of Nagios communicate through a forum and offer their extensions to the basic system for free. You can pick up extensions that will make Nagios Core a great RMM tool to rival N-Central.
Nagios Core is a free open-source network monitoring system. The tool can be extended endlessly by plugins. You can either write your own plugins or get them from the user community. The tool has a very wide user base and there are even other network management systems that are adaptations of Nagios Core. The users of Nagios communicate through a forum and offer their extensions to the basic system for free. You can pick up extensions that will make Nagios Core a great RMM tool to rival N-Central.
Key Features:
- Monitors networks, endpoints, and software
- Automatic discovery
- Free to use
Why do we recommend it?
Nagios Core and its paid counterpart, Nagios XI are well-established system monitoring packages from a highly respected brand. You get network, endpoint, and software monitoring with both of these packages. However, neither includes network traffic monitoring, which is available in a separate tool, called Nagios Network Analyzer.
The basic Nagios Core doesn’t include an interface, but you can browse front ends that are available for free in the user community. The Core package is very widely liked for its flexibility, but its native monitoring messaging standard can overload the system of a large network with extra traffic. However, you can adjust that by including an SNMP monitoring plugin and relying on that protocol instead of the Core monitoring system.
Nagios Core is able to operate on and monitor both Windows and Linux hosts. The system can monitor servers and applications as well as network equipment. The tool can also be set up to focus on Web applications. A paid product, called Nagios Fusion, links different sites together. So if you used Nagios to monitor client sites, you would probably end up installing Nagios Core on each client site and then administering them all remotely from your HQ through this linking system.
Who is it recommended for?
Nagios Core will appeal to small businesses on a tight budget and Nagios XI is a good buy for businesses that can afford it. The XI system can implement sub-accounts, which is a necessary feature for managed service providers. The software is written for Linux but you can run it on Windows over VMware or Hyper-V.
Pros:
- Open-source transparent tool
- Simple, yet informative interface
- Flexible alerting options support SMS and email
- Robust API backend makes it a great option for developers who want to integrate their own custom applications
Cons:
- Open-source version lacks quality support found in paid products
- Installation can be technical and complex
If you want a more sophisticated front end to Nagios and you can’t be bothered to look around all for the community pages for guidance and additions, you can opt for Nagios XI, which is a full infrastructure monitoring system, with an attractive interface and technical support included. Nagios XI has full multi-tenant features, which would make it a quicker solution to set up for MSPs than Nagios Core. You can get the full version of Nagios XI on a 30-day free trial.
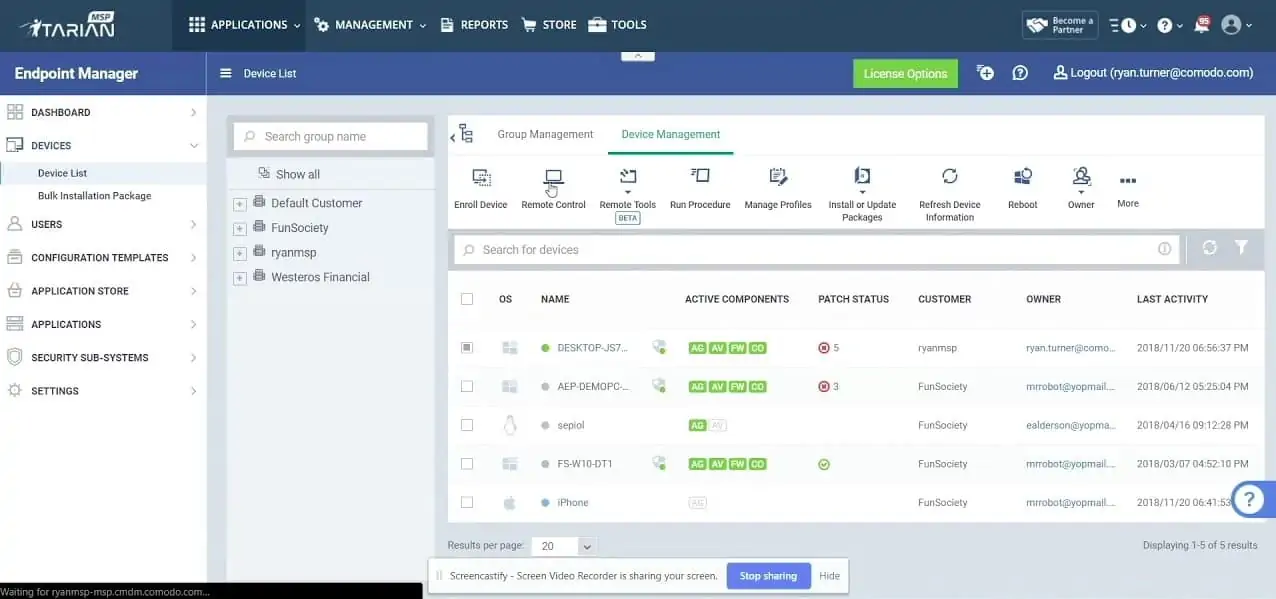
10. ITarian
ITarian is a cloud-based technical support package that includes professional services automation (PSA), service desk, remote monitoring and management (RMM), and remote access tools. The ITarian brand is owned by Comodo and that company recommends this package as a replacement for the free Comodo One RMM package, which has been discontinued.
Key Features:
- Autodiscovery
- Asset management
- Free version available
Why do we recommend it?
ITarian is offered as a replacement for Comodo One and the backing of Comodo is a strong reason to recommend this tool. However, Comodo One offered many more features than the free edition of ITarian, so it is a shame that the free Comodo One is no longer available.
The ITarian system includes a device discovery service. This is central to the RMM module in the platform, which creates an asset inventory, enabling lifecycle management. The package records both hardware and software and the software inventory provides the basis of an automated patch manager.
The monitoring services in the RMM package operate continuously to watch over network devices and endpoints. This system includes performance thresholds and when gathered activity statistics cross these lines, the tool will generate alerts.
The platform also includes a ticketing system. ITarian classifies this as a Service Desk package. However, as all of the asset management functions on the platform are in the RMM module, this is more accurately a Help Desk system. The ticketing service records user requests made by phone and email and it can also channel alerts from the RMM or from third-party tools.
A remote desktop system in the package allows technicians to access endpoints whether or not there is a user sitting at that computer. Facilities in this module include remote control and an option to access the operating system for investigations or to launch maintenance scripts.
It is possible to track mobile devices with the Mobile Device Management service. That service is able to track, lock, and wipe fleet devices. However, it will only control devices running Android.
Who is it recommended for?
The free edition of this platform is called ITarian Basic. However, this doesn’t include the RMM package. You get the Remote Desktop module and the Help Desk ticketing system. The full RMM service is available in the ITarian Device. The MDM is a separate package, called ITarian Mobile. There is also a bundle for managed service providers.
Pros:
- A free Help Desk system and remote desktop service
- A plan for use by managed service providers
- A free endpoint security system
Cons:
- The RMM module is not free
ITarian recommends a free endpoint security tool, called Open EDR from Xcitium. This is available for enterprises and for MSPs. you can get a 30-day free trial of all of the modules on the ITarian platform. At the end of that period, you can keep using the ITarian Basic package for free.
11. Microsoft Configuration Manager
Microsoft Configuration Manager (MCM) is the latest incarnation of Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM). The Corporation has done a pretty poor job in rebranding SCCM, a move that it began because the abbreviation clashed with that of the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The big difference between MCM and SCCM is that the new tool is hosted on the cloud rather than on Windows.
Key Features:
- Updates Microsoft software
- Patches Windows
- Enforces security policies
Why do we recommend it?
Microsoft Configuration Manager is the definitive tool for the management of Microsoft software, including all of the editions of Windows. However, the recent name change has made the tool less attractive. It is part of the Microsoft Intune platform but a separate purchase from the Intune system.
Microsoft originally called this tool the Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager but dropped “Endpoint” from the name in 2023. Up until that point, the tool was part of Microsoft Endpoint Management but that product category was also removed in 2023.
SCCM was able to update software on macOS, Linux, and Unix. However, that capability is integrated into the Microsft Intune interface and not part of the Microsoft Configuration Manager, which only deals with computers running Windows. Confusingly, the endpoint agent for the software update process on macOS, Linux, and Unix is called the Configuration Manager agent. Microsoft advises that the Configuration Manager is also officially known as ConfigMgr.
The console for the Configuration Manager is hosted in the cloud and is part of the Microsft 365 division of the company, along with Microsoft Intune. The service is able to manage endpoints on multiple sites through one account. Each endpoint that is enrolled in the Configuration Manager service needs to have an agent installed on it.
The system can be used to deploy Microsoft software and the Windows operating system and it will also keep track of the version numbers of those installed systems and automatically schedule updates when patches become available. The central cloud-based server takes care of all necessary software transfers through coordination with the endpoint agents.
Who is it recommended for?
Businesses that want some form of control over when their Windows PCs get updated or when Microsoft software packages get updated could benefit from Microsoft Configuration Manager. However, if your endpoints all have access to the internet, the native update system in Windows and all Microsoft software will manage updates automatically by themselves without the intervention of the Configuration Manager.
Pros:
- Gives administrators a central console for managing Microsoft software
- Automatically identifies patch availability
- Automatically schedules updates
Cons:
- Has had a confusing number of name changes
12. ConnectWise Automate
ConnectWise Automate is a network management system that includes a number of remote administration features. These RMM characteristics make this software great as an N-central alternative for MSPs. You can operate system monitoring and alerting, patch management, remote control, scripting, and asset management through the tool.
Key Features:
- Software deployment
- Self-service enrolment
- Task automation
Why do we recommend it?
ConnectWise Automate is an RMM that provides a lot of automated processes. You can write your own task automation scripts and get ConnectWise Automate to run them for you on a schedule or you can select from a list of pre-written automation functions and set them up on a schedule within the Automate console.
The name of this tool shows that its creators particularly wanted to provide a system that is very comprehensively driven by scripts. The automation level of the asset management system can be set on install and can also be enhanced further through a scripting module that lets you create your own automated workflows.
The remote access module of ConnectWise Automate is called Screen Connect and it is a great way for Help Desk technicians to fix problems on individual client computers. So, the blend of the scripting language and the ad-hoc manual access provided by Screen Connect means you can cover the whole spectrum of customer support functions with this tool.
The range of services provided by ConnectWise Automate also gives the tool a very wide client base. It is suitable for remote services conducted by an individual operator, such as training and one-on-one support; it can also cater to MSPs with a large number of clients. Onboarding can be performed remotely by email invite if you need to support a widely-dispersed home-based team, or you can apply group policies, to manage large numbers of similar machines on a site automatically en masse.
Who is it recommended for?
Like most RMM systems, ConnectWise Automate is marketed to managed service providers and also IT departments. It is particularly useful for managing IT assets on multiple sites from one office. The console for this system is based in the cloud but you will need to install agents on all of the endpoints that your team monitors.
Pros:
- Remote management, inventory management, and reporting are all accessible from a single dashboard
- Interface templates can be made for individuals, or entire teams
- Very easy remote access to endpoints through multiple protocols
- Supports automation as well as remote troubleshooting without impacting the user session
- 100+ preconfigured commands and templates to use out-of-box.
Cons:
- Prefer a longer trial period to explore all features
- Interface can be confusing, especially in the reporting and management areas
- User chat function is clunky at times
Access to the ConnectWise Automate is delivered on the Software-as-a-Service model from the Cloud, which makes it easy to add on new technical staff and onboard new clients. The service is completely scalable. You can get ConnectWise Automate on a 14-day free trial. The sales team is happy to extend that trial period up to a month on request. However, ultimately this is a paid service.
13. Pulseway
Pulseway is a Cloud-based network management system that has features that attract MSPs. The scalability of this tool and its per-workstation subscription pricing model makes it very easy to expand the service as you acquire new clients. The mid-market for RMM software is very crowded at the moment and you may find it difficult to tell a number of the services on this list apart. Pulseway is a very similar prospect to both ConnectWise Automate and Kaseya VSA (below), so in all three cases, you will need to assess each option on their free trial offers.
Key Features:
- Remote monitoring with alerts
- Task automation
- Remote access
Why do we recommend it?
Pulseway is an RMM system that is similar to N-able N-central. This package, like N-central, doesn’t include a ticketing system. It is hosted in the cloud and can be accessed from anywhere through a Web browser or through the Pulseway mobile app for iOS and Android. The system manages networks and endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Like ConnectWise Automate, the Pulseway solution for MSPs is not free, but you can get it on a free trial. The company also offers a version of the Pulseway network monitoring system for free to very small businesses. The free Pulseway only allows one user account and gives you the ability to manage just two endpoints. The full Team version is also available as on-premises software.
Pulseway offers a base subscription package to MSPs that provides all of the RMM functions that you will need to support your clients. On top of the standard RMM, there is an extensive array of add-ons available to enhance the system and cover all of your client interactions and in-house systems.
The online Pulseway Dashboard gives access to remote Desktop control, OS patch management, software deployment, update management, and application monitoring. The tools embedded in the Dashboard provide advanced automation, operative monitoring, customer SLA reporting, and custom management information reporting tools.
Teams get multiple logins and group account functions that let you adapt the Dashboard per employee role. You can also adjust system monitoring alert settings and direct those service alerts to different team members by email. You can also allocate automated workflows that get triggered by specific events detected on the networks of your clients.
Additional modules available from Pulseway include Web server protection, antivirus protection, a Cloud data backup service, and a PSA module.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is marketed for use by IT departments and managed service providers. The platform includes a patch manager but that is a paid extra. The system also offers you ransomware detection for an extra free and you can choose to buy endpoint protection from Bitdefender or Webroot along with your Pulseway subscription.
Pros:
- Has a freeware version for small deployments and testing
- Supports multi-platform deployments like Linux, Windows, and Mac.
- Automated patching can run Windows updates as well as updates for common apps such as Adobe or Dropbox
- Custom script library allows you to build and run fixes at will, or through a scheduler
Cons:
- The interface could use improvement
- Pricing information could be a bit more transparent for larger deployments
- File transfer between devices can sometimes cause errors with larger files
14. Kaseya VSA
Kaseya VSA is the third in our choice of mid-market scalable MSP support platforms that excel at task automation. Kaseya also has a remote control module, called Live Connect, so you can implement bulk updates and also give each endpoint one-to-one attention.
Key Features:
- Asset discovery and management
- Remote access
- Knowledgebase templates
Why do we recommend it?
Kaseya VSA is a remote monitoring and management package for networks and endpoints. The system is hosted in the cloud, like N-able N-central. You get all of the regular RMM tools with this package, such as automated network device monitoring with regular discovery sweeps and the endpoint monitor operates through agents for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
As an MSP, you have to get automated network monitoring with built-in alerts, patch management, and service auditing in your support platform. Those are the features that N-central provides and they are also standard with Kaseya VSA.
A key feature that Kaseya VSA offers is a module that is called AssetIQ. This is a contextual documentation management system and it is easy to see how this could lighten the burden of an MSP. The documentation system could work as a substitute for manned Help Desks or could be structured as a script for Help Desk operatives to work through a problem and direct problems to back-office staff. If linked to a workflow, the documentation base could also provide a guide to fix strategies if you want human attendance for a specific category of problems. So the guided documentation option gives you a middle path between total problem resolution automation and personal contact.
A couple of other nice features, including AV and backup integration, will enable you to integrate added-value features into your charge sheet.
Who is it recommended for?
This package was designed for use by managed service providers, thanks to its multi-tenant architecture. However, IT departments can also use the package for their in-house support teams and just ignore the sub-account feature. The package doesn’t include a ticketing system but it does have a patch manager.
Pros:
- Automated software deployments can help streamline adding new machines to the client network
- Does a good job at monitoring overall health and resource consumption of devices
- Interface is simple and customizable
Cons:
- Free trial could be longer
- Remote control agent can take a long time before remote sessions are able to be started
- Patch management can be confusing
Whether you are setting up an in-house network operation center or offering third-party MSP work, you will be able to cover all of your system requirements with Kaseya VSA. The only difficulty you will have is distinguishing between this and the service’s main competitors, which are listed in this guide. The company offers a 14-day free trial so that you can become familiar with the Kaseya VSA utilities.
Choosing RMM software
When you consider an N-central replacement, you also need to look at the boundaries of RMM definition. It is difficult to work out whether a specific tool will fit into the role that N-central could fulfill without considering all of the related services than an MSP needs. If you just narrow your search to straightforward patch management and remote access systems, then the pool of alternatives expands into a lake. However, a great benefit of buying a tool from a comprehensive system provider is that it offers companion products that exchange data with the tool under consideration.
Could you run an MSP with a standalone RMM? No, you couldn’t, so there is no point considering the best RMM in the world if it: doesn’t exchange data with your Help Desk system, doesn’t have a related PSA, and can’t be integrated into an SLA compliance and billing system.
Other RMM options
This review is limited to ten N-central alternatives to save you time. You may wonder why some of the very excellent management tools that you may have heard others rave about do not appear on this list. Particularly, you may have heard about Zabbix and Icinga 2. These two tools are very, very close to Nagios and it seems unfair to include Zabbix and Icinga 2 while including Nagios.
When deciding on tools to include on this list, the need was to present options that were unique. Zabbix is a good option, but Nagios is the leader in the open-source network monitoring category and it has plugins available that tailor it better to MSP usage than Zabbix.
Icinga 2 is a direct clone of Nagios. So, all of the plugins available for Nagios will also work with that network management options. However, in the interests of brevity, all of the Nagios clones are truncated into one entry.
Like Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga 2, Kaseya VSA, Pulseway, and ConnectWise Automate are very similar products. However, each has a focus that makes it more appropriate for a different audience. The Kaseya VSA approach to intelligent documentation management could be regarded as an automated self-service solution that an MSP could set up and run as an ongoing front end to a standard remote network monitoring and patch management system. The scripting capabilities of ConnectWise Automate make it a truly unique tool for MSPs that want to replace as many staff as they can. Pulseway is a rising star that has a very loyal following, and so needed to be included in this list of the best N-central alternatives simply because of its glowing review profile.
Paid & Open-source N-central options
If you are annoyed that N-able’s N-central is no longer available, you should be happy to discover that N-central is now a SolarWinds product. SolarWinds is a very large organization and is able to provide much better technical support to its buyers than N-Able could ever afford.
The SolarWinds re-write of N-central made it compatible with the other MSP modules offered by the company and also brought in interoperability with the wider SolarWinds stable of specialist asset management tools.
You can see from our list that you do not have to limit your options to paid services. There are many open-source, free MSP support systems out there. However, never lose sight of the fact that you get what you pay for, and if your business relies on providing excellence in IT services, you really can’t afford to risk cutting corners for the sake of budget squeezes.
Do you run an MSP? Are you one of the thousands of entrepreneurs around the world that has turned IT skills into a home-based management service? Which RMM package do you prefer? Leave a message in the Comments section below to share your experience with the community.



Have you tried ThreatLocker? It’s really easy to use and quick to setup. It also allows application whitelisting and storage control.
Am using comodo one RMM solution for my business..! It really works very well and monitor clients endpoints and networks efficiently.