What is a Wake-on-LAN tool?
Wake-on-LAN (abbreviated as WoL) is an industry-standard network protocol that is used to remotely bring a computer out of low-power modes – that is, Sleep or Hibernate modes.
A Wake-On-LAN tool, therefore, is a network administration tool that is used to wake machines on a local area network (LAN) by sending the WoL protocol or “magic packet” to select machines that have the Wake-On-LAN feature enabled in their BIOS configurations. Of course, as we are just about to see, the Network Interface Card (NIC) should also support the feature and have it enabled.
See also: The Best LAN Monitors
Here is our list of the best Wake-on-LAN tools:
- ManageEngine OpUtils EDITOR’S CHOICE A collection of network management utilities that includes a Wake-on-LAN function. Installs on Windows Server and Linux. Get a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Remote Access Plus (FREE TRIAL) This remote connection manager for IT support teams provides remote access and remote control and includes a Wake-on-LAN function in its toolkit. Offered as a SaaS package or for installation on Windows Server.
- Aquila Technology Wake-on-LAN Provides access to the WoL feature in an intuitive GUI which lists network-connected PCs and status by MAC address.
- SolarWinds Wake-on-LAN with Engineer’s Toolset Generates magic packets for waking remote network-connected computers from sleep or hibernate mode. One of 60 networking tools in the set.
- NirSoft WakeMeOnLan Can scan sections of a network and detect computers with WoL feature enabled and display MAC and IP addresses.
- Wake on LAN X Includes batch reboot capabilities which is great for working with updates.
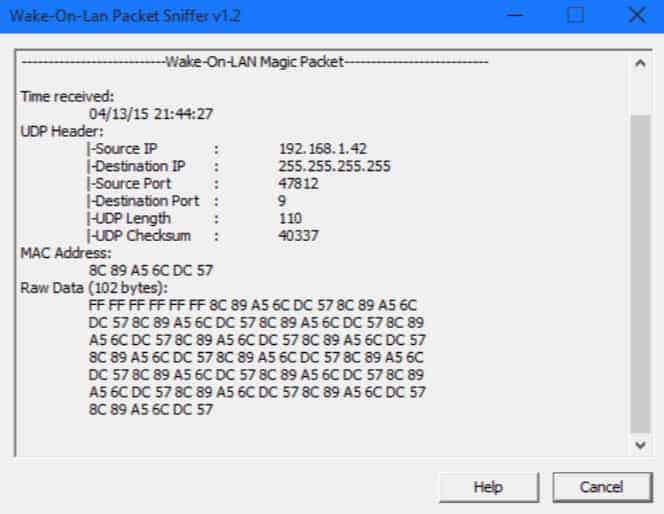
Meanwhile, the magic packet is a simple, light broadcast frame that holds in its payload of 102B: 6 bytes of all-255 subnet mask (FF FF FF FF FF FF in hexadecimal) and the target computer’s 48-bit MAC address repeated sixteen times.
The above image is a diagram representation of a WoL Magic Packet being sent from 192.168.2.26 to 255.255.255.255:9
Setting up Wake-on-LAN on a PC
Let’s take a look at how you can enable WoL on a PC computer and make it available for remote booting:
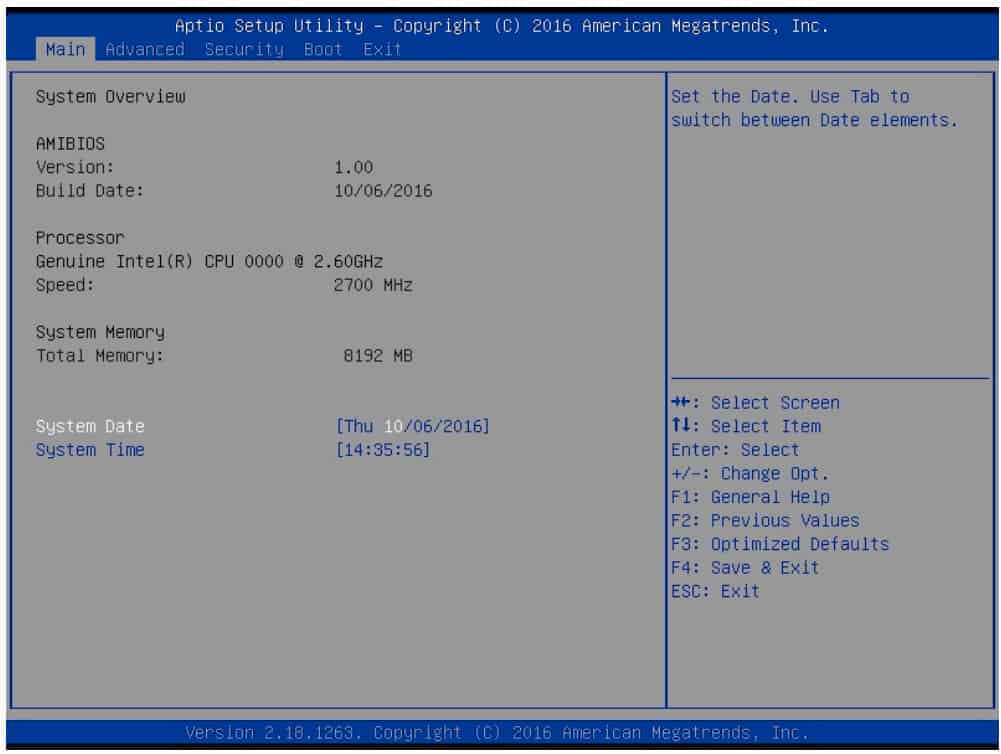
- Enter the BIOS – sometimes known as the setup menu – using the method that is specific to your computer.
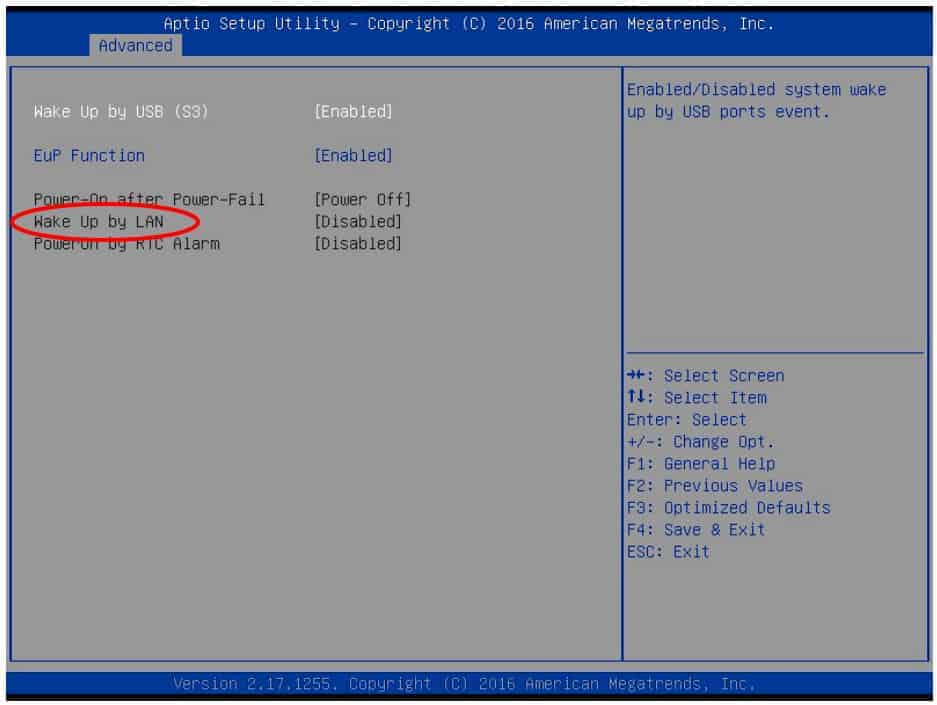
- Enable WoL– you will probably have to dig a little deeper to find the exact sub-menu that holds the options (it is usually under advanced power options and the default setting is “Disabled”).
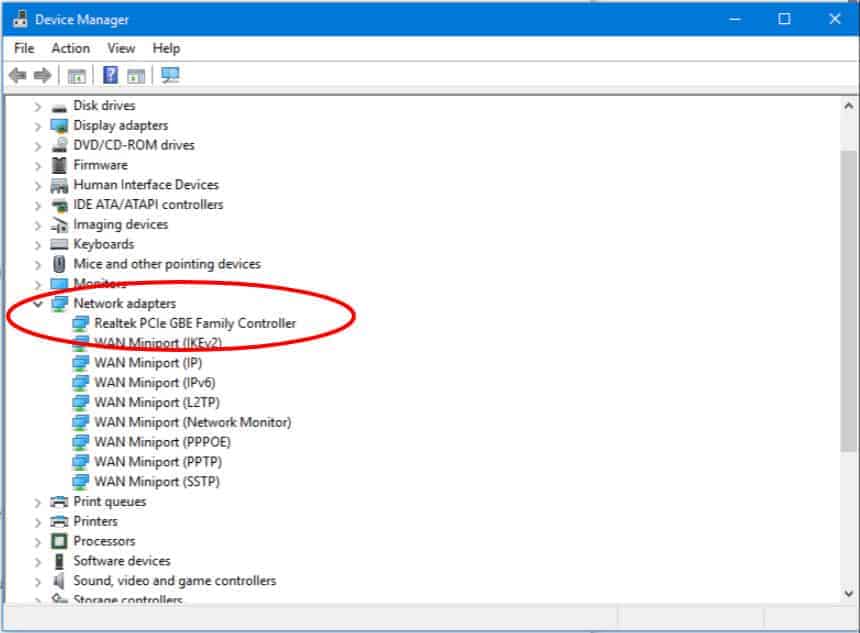
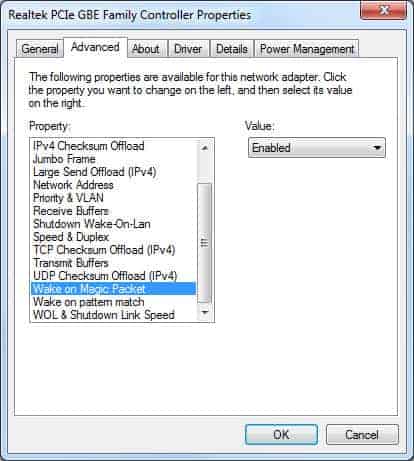
- Next, enable the NIC’s remote awake options – go to the Device Manager, expand “Network Adapters,” right-click on your NIC, go to Properties, click on the “Advanced” tab, and enable “Wake on Magic Packet”.
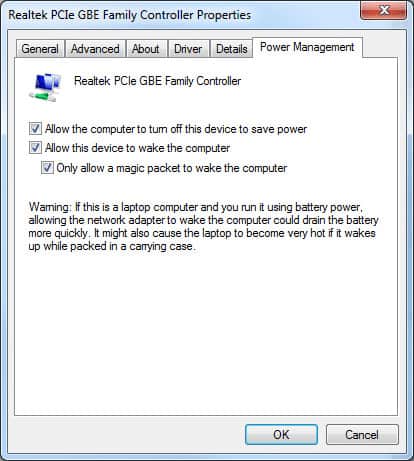
- The OS should also be configured to only allow WoL – On the “Power Management” tab enable “Allow this device to wake the computer” and “Only allow a magic packet to wake the computer.”
And that’s it; your PC is now ready to accept WoL packets and power on or off depending on the instructions. Don’t forget, the settings on MAC or Linux machines are a bit different from what we have seen here. And also, remember to enable broadcast packet handling on your routers.
NOTE: You can install a third-party WoL packet sniffer on your computers to keep track of WoL packets.
Why would you need Wake-on-LAN tools?
Here are two scenarios that would require the services of a WoL tool:
- Perhaps, you can’t come into the office, but need some data from your computer; the easiest way around this issue would be to turn it on using a WoL tool, and then access it remotely.
- Administrators can work on a computer or server that is in other location as if they were next to it – even if they were on another continent.
All it takes in both instances is to wake the computers up with a few clicks on a good WoL tool.
So, what are the best Wake-on-LAN tools?
Our methodology for selecting a Wake-on-LAN tool
We reviewed the market for WOL utilities and tested tools based on the following criteria:
- A system linked to a list of endpoints on a network
- A tool that can easily generate and send a WOL magic packet
- An option to target one machine or wake up many
- Nice to have an integration with software update and patch management systems
- Nice to have related network management tools
- A free trial, a free tool, or a utility that is part of a wider system management package
- Value for money from a useful tool within a package of system administration tools or a free tool
Below, we have the tools we have found to be the best-in-class WoL tools that are effective, easy-to-use, and have a light footprint.
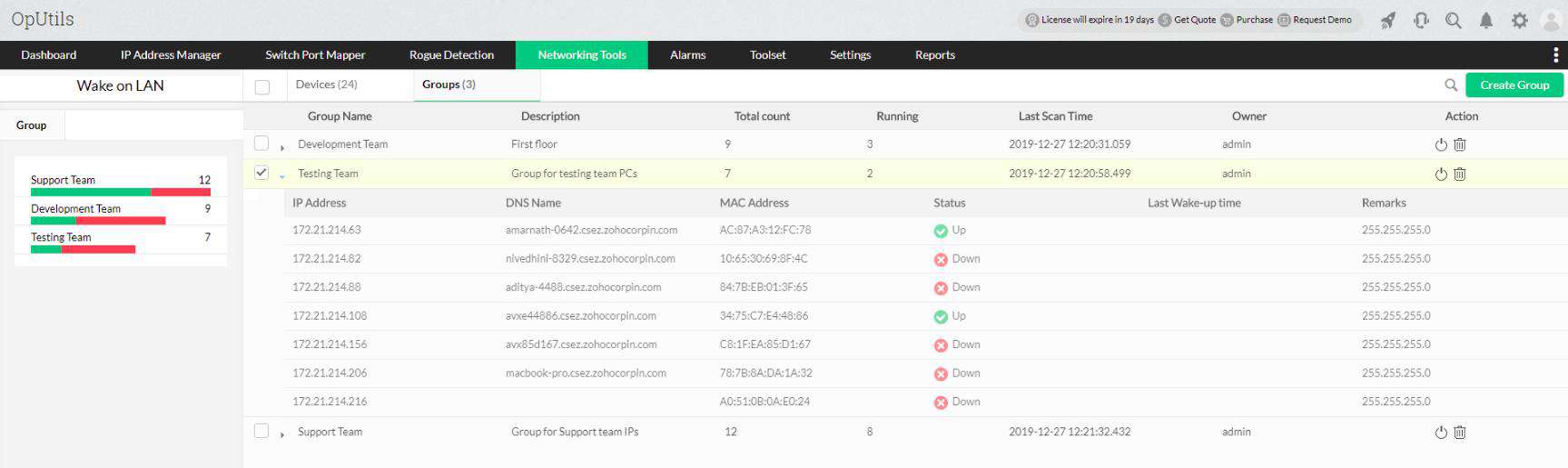
1. ManageEngine OpUtils (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine OpUtils is a bundle that includes an IP address manager, a switch port mapper, and other useful network management tools. One of those other tools is a Wake-on-LAN utility. ManageEngine offers a Free edition of the OpUtils package. That provides 11 of the 30 tools in the paid Professional edition, including the WOL feature.
Key Features:
- Secure WOL: Provides a secure Wake-on-LAN service.
- Local and Remote Operation: Capable of performing WOL actions both locally and remotely.
- Integrated Network and Server Monitor: Part of a comprehensive network and server monitoring suite.
- Scheduling: Allows scheduling of WOL commands.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine OpUtils is a package of monitoring and management tools for networks and servers. There are many little extras in this software bundle and the Wake-on-LAN utility is one of them. The use of this tool is eased by the OpUtils autodiscovery and hardware inventory service, which lists the MAC addresses of all your devices.
The ManageEngine Wake-on-LAN system is a lot more secure than typical WOL implementations. The service is able to startup endpoints that are fully turned off, as long as they are plugged into a power supply. The WOL message can be sent to specific machines, to groups of endpoints, or the entire network, turning everything on.
The ManageEngine Wake-on-LAN records each remote WOL action. The command can also be issued on a schedule. The OpUtils interface will automatically scan the network and list all the devices on the network, showing the MAC address for each. This enables the network manager to monitor the actions performed on all equipment without forgetting to register some of the devices.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine OpUtils provides a useful combination of server and network monitoring systems and the inclusion of a Wake-on-LAN utility in the package means that network administrators have all the tools that they need from one console. This is a software bundle that runs on Windows Server, Linux, and AWS.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Tool Suite: Includes WOL, IP address management, and switch port mapping tools.
- Scheduled WOL Commands: Can send WOL commands to specific groups and schedule them for specific times.
- Autodiscovery: Identifies new machines automatically, ideal for large network deployments.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Available for Windows Server, Linux, and AWS.
Cons:
- Complex for Home Users: Designed for sysadmins, making it complicated for casual or home users.
The ManageEngine OpUtils package installs on Windows Server and Linux. ManageEngine offers the package on a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine OpUtils is our top pick for a Wake-on-LAN tool because its WOL implementation is enhanced by a reliable and intuitive interface that simplifies the deployment of the service. The package provides the ability to schedule WoL tasks, enabling administrators to automate device wake-ups at specific times. This is particularly useful for routine maintenance, updates, or ensuring devices are ready for business hours without manual intervention. OpUtils also supports bulk wake-ups, making it efficient for managing large networks. The tool offers detailed insights into network health, combining WoL capabilities with advanced monitoring features like IP address management (IPAM) and switch port mapping. This holistic approach helps IT teams track device statuses, ensuring that WoL operations target the correct systems. Security is another key advantage. OpUtils provides multi-subnet support, ensuring WoL commands can traverse complex network environments securely. Additionally, its detailed logs allow administrators to track wake-up requests and troubleshoot issues. With its user-friendly interface, comprehensive feature set, and reliability, ManageEngine OpUtils is an essential tool for any organization seeking to streamline device management through Wake-on-LAN. Small businesses that don’t require an extensive network address management feature can just settle for the Free edition, which includes IP scanning and connection troubleshooting tools as well as the WOL utility.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/products/oputils/download.html
OS: Windows Server, Linux, and AWS
2. ManageEngine Remote Access Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Remote Access Plus is a package for IT support teams that provides WoL and remote shutdown utilities as part of its remote device access facilities. This system allows a fleet of devices to be accessed on a regular basis both for unattended access and for remote desktop control during an attended support session.
Key Features:
- WoL and Remote Shutdown: Includes utilities for Wake-on-LAN and shutting down devices remotely.
- Connection Settings Storage: Saves connection settings for easier future access.
- System Health Checks: Provides system health status updates for remote devices.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Remote Access Plus is a package for the management of a fleet of endpoints. One of the tools in the package is a Wake-on-LAN utility. This is a supplement to the WOL that is included with OpUtils because you don’t need to be running OpUtils in order to operate the Remote Access Plus system.
The Remote Access Plus system allows a technician to turn a computer on for maintenance with WoL. Whether the remote device needs to be turned on or if it is already up, Remote Access Plus will scan the computer and provide a status summary to the technician. The interface also provides troubleshooting tools and a file transfer utility.
Remote control sessions are supported with a chat panel that includes options for voice and video chat. This mode gives the technician a full view of the remote desktop.
Who is it recommended for?
Remote Access Plus can operate across a network and also over the internet to manage devices on distant sites. The package also includes a remote shutdown utility, which has a restart option for ensuring software installation completes properly. Access the system as a SaaS package on the cloud and it can also be downloaded onto Windows Server.
Pros:
- Remote Access and Desktop Control: Allows technicians to access and control remote desktops for support and maintenance.
- Comprehensive Troubleshooting: Offers tools for troubleshooting and system health checks.
- Voice and Video Chat: Facilitates communication with users during support sessions through voice and video chat.
Cons:
- No Ticketing System: Lacks an integrated ticketing system for managing support requests.
Remote Access Plus is a cloud-hosted SaaS package but you can opt to download the software and run it on Windows Server. There is a Free edition that enables the regular support of 10 computers and the two paid versions can be accessed on a 30-day trial.
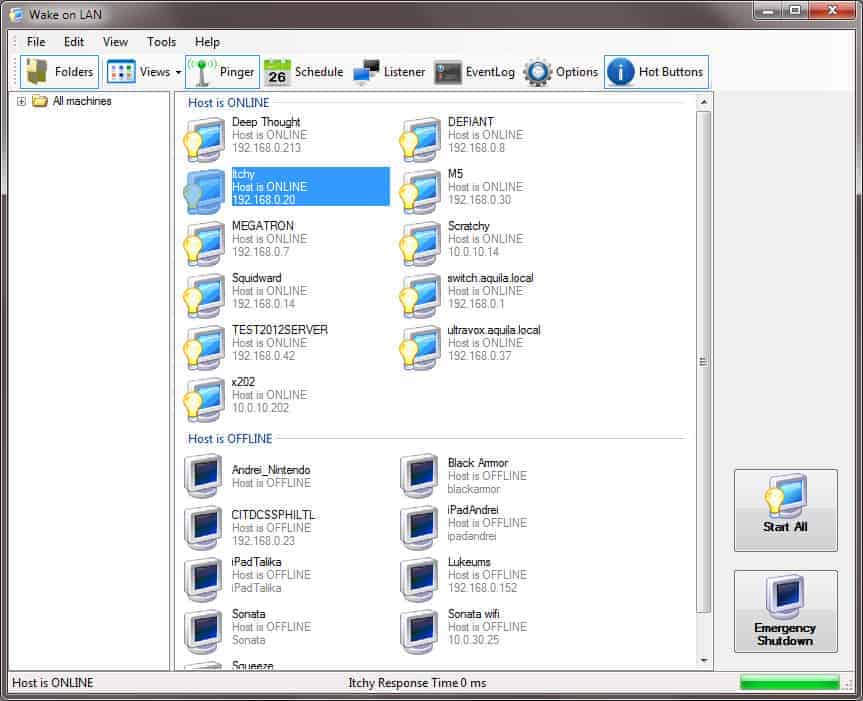
3. Aquila Technology Wake on LAN
From Aquila Technology we get a WoL tool that is rich with features that can really help administrators by, for example, pinging computers and performing remote desktop access, and emergency shutdowns.
Key Features:
- Easy-to-Use Console: Simple and intuitive interface for managing WOL tasks.
- Device Discovery: Automatically detects and adds devices to the tool’s directory.
- Emergency Shutdown: Includes functionality for remote shutdown and reboot.
Why do we recommend it?
Aquila Technology Wake on LAN is a free tool that is part of a GUI tool along with a few other useful utilities. The Wake-on-LAN feature logs all of its activities, so you get a history of WOL actions. The bundle also includes a remote shutdown tool that has a reboot option.
With the help of its simple GUI, administrators can also send out WoL packets to MAC addresses via broadcast IP or to a fully qualified domain name. The reply received can then help discover and add computers to the tool’s directory, and it can also listen for WoL packages – meaning there is no need for additional software to keep track of the packages.
The configuration can be exported and stored offline for future use, while Aquila’s event logs can help with troubleshooting issues.
Who is it recommended for?
This free utility is available for Windows. It is a handy tool to have on the computer and any system administrator with a fleet of endpoints to manage will benefit from using it. The tool has a speedy “Start All” option and the WOL can be set to launch on a schedule.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Displays each machine and its state clearly, making it easy to manage multiple devices.
- Basic Troubleshooting: Supports basic network troubleshooting features like ping and remote shutdown.
- Configuration Export: Allows saving and exporting settings for easy reinstallation.
Cons:
- Limited for Large Networks: Not designed for managing very large-scale networks.
- Interface Scalability: The interface may not handle a large number of devices efficiently.
Aquila’s WoL allows both CLI (Command Line Interface) and GUI interfaces and can be used on both DHCP and static IP address networks, and can even be used to shutdown Linux machines.
4. SolarWinds Wake-on-LAN with Engineer’s Toolset

SolarWinds Wake-on-LAN is one of the most popular WoL tools out there and is constantly given great reviews by satisfied network administrators. Perhaps what makes it appealing to most of its fans is the fact that it delivers on what it is supposed to do – remotely power on a networked PC; no muss, no fuss.
Key Features:
- Network Tools Suite: Part of the comprehensive Engineer’s Toolset with 60+ tools.
- Windows Server Compatibility: Runs efficiently on Windows Server.
- User-Friendly: Intuitive and easy to use interface.
- Magic Packet Sending: Sends multiple magic packets to ensure successful delivery.
- Local and Remote Operation: Controls both local and remote networked devices.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Wake-on-LAN is one of the 60 system monitoring and management tools bundled into the Engineer’s Toolset. This utility will send out several magic packets rather than just sending one and hoping it will get through. Even if there are no traffic problems on the network, a single packet can always get lost.
But, one thing is for sure, the tool takes its job seriously: it sends out multiple WoL packets – at intervals – to make sure they reach their destination. This can be appreciated on larger networks or those with high traffic where the administrator can even create batch files that automate the job.

SolarWinds Wake-On-LAN is a pleasant tool to use with an easy-to-navigate interface that can be used to control the computers that are on the same LAN as the administrator’s computer. It can work as well as remote ones that can be accessed remotely – even over the Internet.
Who is it recommended for?
This utility is a competent implementation of Wake-on-LAN and it is very easy to use. The system is just one of many useful system administration services in the Engineer’s Toolset. The package installs on Windows Server and should be run on a computer that is connected to the network.
Pros:
- Multiple WoL Requests: Quickly sends multiple Wake-on-LAN requests to ensure successful activation.
- Comprehensive Toolset: Comes with a suite of other useful tools designed for network administrators and technicians.
- Scheduled Packets: Allows scheduling of Wake-on-LAN packets at specific times and intervals.
- Network Functionality Verification: Helps verify DNS and DHCP functionality for different devices.
- Import/Export Results: Easily export or import results from previous scans.
Cons:
- Short Trial Period: Could benefit from a longer trial period than 14 days.
This WoL tool can be downloaded as part of SolarWinds powerful premium suite of tools: the Engineer’s Toolset and is available on a 14-day free trial for download and evaluation.
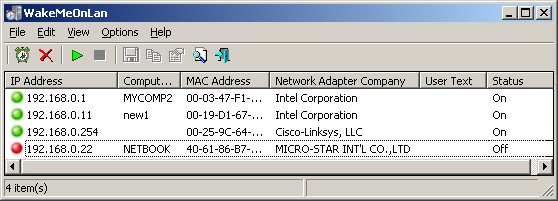
5. NirSoft WakeMeOnLan
With NirSoft’s WoL, administrators have the power to choose what section – or subnet – of a network they want to scan and then work with. This is because the tool allows for ranges of IP addresses to be set before scanning begins.
Key Features:
- IP Scanner: Scans specified IP address ranges for devices on the network.
- WoL Function: Sends Wake-on-LAN packets to devices.
- Free to Use: Available at no cost for users.
Why do we recommend it?
NirSoft WakeMeOnLan is a handy tool that includes a discovery phase. You start a network scan during a period when all of the endpoints that you manage are turned on. This creates a list of devices, which you store. Later, you can launch the WOL service, specifying one of the MAC addresses in that list.
Once done, the result of the scanned network can then be saved in a list that holds relevant information like MAC and IP addresses. It is with the help of this list that the tool sends out WoL packets the next time its services are required – all it takes to wake computers up is a click of a button. Of course, there’s also the option of running it from a CLI.
Who is it recommended for?
Any network administrator would need this tool. The network discovery service is a nice extra and a very useful feature, given that this is a free utility. The software package installs on Windows and provides a GUI window but you can also run it at the command line.
Pros:
- Easy to Use: Simple tool with an intuitive interface.
- Lightweight: Uses minimal system resources.
- Informative: Provides additional information such as hostname, MAC address, and device status.
- Command Line Option: Can be run via CLI for added flexibility.
Cons:
- Limited Visualization: Lacks graphical reporting or visualization features.
- Not Ideal for Large Networks: May not be the best choice for managing large-scale networks.
- Basic Features: May not meet the needs of enterprise networks requiring advanced features.
NirSoft makes sure it regularly updates its tool which is available for Windows 8 and Windows 10 and is also absolutely free.
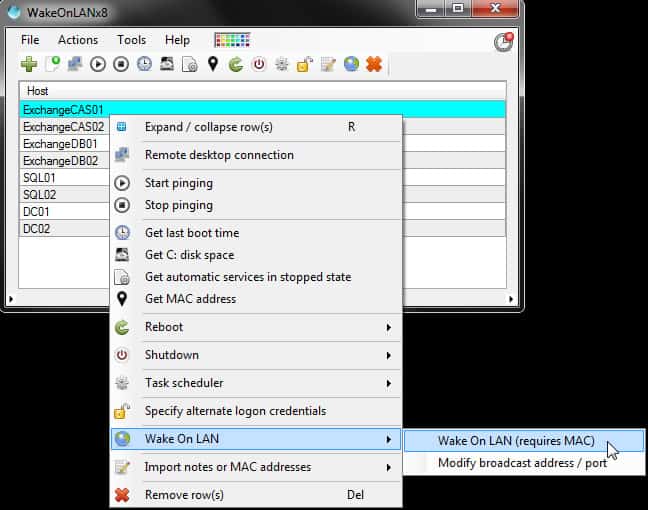
6. WakeOnLANx
WakeOnLANx is a tool designed with administrators in mind and is quite a robust suite of features that let you perform tasks like turning PCs on or off, and even reboot them in batches if need be.
Key Features:
- Local and Remote Operation: Capable of performing WOL tasks both locally and remotely.
- Scheduled Activity: Allows scheduling of WOL, reboot, and shutdown tasks.
- Bulk Actions: Supports bulk actions for managing multiple devices simultaneously.
Why do we recommend it?
WakeOnLANx provides a number of useful tools, not just the WOL. The Wake-on-LAN can be issued in bulk for all devices on a network and it can also be run on a schedule. The tool includes a Ping system to discover devices and an IP address mapper that gets the MAC address for each discovered device.
This is a WoL tool that can be run using GUI and CLI modes which can easily be configured for better performance and in-depth results.
A unique feature that comes with courtesy of this tool is that it can tell administrators the last time a computer was booted. If that doesn’t impress you, how about the fact that it can tell how much disk space is available on a computer and also what system services on it have been set to “Automatic” or are simply idle.
Still not impressed? Well, how about the fact that it can be used for remote access? All this, for free, and you get the picture of why it is on this list.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is available to run on Windows and it is free to use. The software includes network discovery., MAC address recording, and availability testing. The system also offers a reboot and shutdown function for remote computers. The tool can also be run at the command line.
Pros:
- Dual Interface: Available as both a CLI tool and a standard GUI for flexibility.
- Detailed Stats: Provides comprehensive details such as hostname, current status, MAC address, and last boot time.
- Remote Commands: Can send remote commands for rebooting, checking disk space, and performing ping checks.
Cons:
- Limited Visualization: Lacks graphical reporting or visualization features.
- Challenging for Large Networks: GUI may struggle with managing and viewing large numbers of devices.
- Interface Usability: The interface, especially the toolbar area, could be more user-friendly and intuitive.
Although we promised to give you five of the best Wake-On-LAN tools, we have a couple more “goodies” for you:
Best CLI WoL
For those of us who prefer to do things by solely using command-line interfaces we have:
MatCode MC-WOL – this one is for administrators who want a no-nonsense WoL tool that can turn PCs on even if they are on the same or different LAN segments.
Gammadyne WOL – this WoL tool can be used on computers that require passwords before they can be switched on and can be accessed via a specific port.
Wake-on-LAN from your smartphone
Apart from using a computer or laptop to send out WoL packets, administrators can also use their phones to control the machines on their network. The following video will demonstrate how that is possible while also showing how to configure a computer to work with WoL packets.
Things you need to take into consideration with the best Wake-on-LAN tools
Before we leave you with our choice of the best Wake-on-LAN tools, let’s go over some important points to consider before you start using them:
A WoL packet is uniquely “addressed” to each computer and can only wake a single machine. The payload of the packet is deliberately kept light with brief instructions so it can be easily executed by the circuitry present on the NIC – which usually runs on minimal power requirements. This means you may need to send out more than one packet to ensure it is delivered and executed.
The minimum requirement for sending a WoL packet is the target MAC address. In fact, IP addresses and DNS names aren’t as important as the packet operates at a level that is independent of protocol layers.
Since the WoL packet is basically a UDP packet there are no delivery confirmations sent back after delivery; in fact, there is no guarantee that the packet is delivered at all. This, therefore, requires multiple packets (with the help of batch files) to be sent out to ensure that the target computer is indeed up – by, perhaps, using the ping command.
WoL magic packets are broadcast packets (due to the ‘FFFFFFFFFFFF’ node number) which are usually frowned upon a LAN. In larger, routed networks, it is, therefore, configurations that need to be made to allow UDP packets to cross over routers and wake computers in other segments.
Once these points have been taken into consideration, it is just a matter of choosing any one of the best Wake-on-LAN tools listed above and implementing it.