On the internet, Google’s reach barely scratches the surface. So, if you want to know how to access the dark web safely, you need to understand that the vast majority of the dark web, or dark net, is only accessible through the Tor browser. Google uncovers less than 0.2% of the entire web. It’s like an iceberg – The visible tip above water, known as the “surface web” represents the familiar, searchable content. But lurking beneath lies the expansive, mysterious “deep web” or“dark net” – the gigantic submerged part that remains invisible to standard searches.
The dark web, an even more puzzling sublayer, exists within this hidden world. Here, stealth and secrecy rule. It’s designed as an environment to elude detection, where site owners and visitors hide their identities. And while the dark web isn’t synonymous with illicit activities, it’s undeniably the breeding ground for the internet’s black markets, hacker forums, malware vendors, and other illegal activity.
Our rigorous research and testing have revealed revealing truths and busted myths. We’ll navigate this intricate maze with you, uncovering its secrets while ensuring your online safety.
What is the dark web?
The dark web, or dark net, is a small part of the deep web that is kept hidden on purpose. Websites and data on the dark web do typically require a special tool to access.
The type of sites most commonly associated with the dark web are marketplaces where illicit goods such as narcotics, firearms, and stolen credit card numbers are bought and sold. The darkest corners are used to hire hitmen, engage in human trafficking, and exchange child pornography.
More than that, though, the dark web contains content and data that can be accessed anonymously. It could be a blog, forum, chat room, or private gaming server.
The beauty of the dark net is anonymity. As long as users take the necessary precautions, no one knows who anyone else is in the real world. Users’ identities are safe from the prying eyes of governments and corporations.
Journalists and whistleblowers, including Edward Snowden himself, often use the dark web and Tor to exchange sensitive information. For instance, the Ashley Madison data dump was posted to a site only accessible to Tor users.
How to access the Dark Web safely
Using Tor is a must. Tor is a network of volunteer relays through which the user’s internet connection is routed. The connection is encrypted, and all the traffic bounces between relays worldwide, making the user anonymous.
Related post: Dark Web Monitoring Tools
How to get the Tor Browser
The easiest way to access Tor is through a special browser known as the Tor Browser. You can download and install it for free. You might want to hide your Tor Browser download using a VPN and your existing browser’s private/incognito mode.
Based on Firefox, the Tor Browser lets you surf the clear and dark web. All your traffic is automatically routed through the Tor Network. Ensure you download the Tor Browser from the official website to avoid downloading malware, spyware, or other viruses to your device.
Officially, the Tor Browser is only available on Windows, Mac, Android, and Linux. Many experts advise against using third-party mobile browsers that utilize the Tor Network. Sorry, iOS users. No standard web browsers can be used to access dark web content.
Added security: Use a VPN
Internet providers and websites can detect when Tor is being used because Tor node IPs are public. Although websites can’t identify you and ISPs can’t decrypt your internet traffic, they can see that Tor is being used. This can raise suspicions and draw unwanted attention.
If you want to use Tor privately, you can use either a VPN or Tor Bridges (Tor nodes that are not publicly indexed). Tor users in the USA, in particular, may want to use a VPN, which will be faster and more reliable.
When using a VPN for the dark web, your ISP will not be able to see that you are connected to a Tor node, only an encrypted tunnel to a VPN server.
WANT TO TRY THE TOP VPN RISK FREE?
NordVPN is offering a fully-featured risk-free 30-day trial if you sign up at this page. You can use the VPN rated #1 for the dark web with no restrictions for a month—great if you want to try this no-log provider's Onion over VPN servers for yourself.
There are no hidden terms or conditions—just contact support within 30 days if you decide NordVPN isn't right for you and you'll get a full refund. Start your NordVPN trial here.
It would also be wise to install antivirus software. Even when using security measures and your common sense, accessing deep web content still poses a risk. Antivirus will ensure that any viruses or malware downloaded from the dark web are removed.
Navigating the dark net
Now that you have Tor, you can access the dark web. Dark net websites are called “Tor hidden services”, and they can be distinguished from normal websites by their URLs.
Instead of “.com” or “.org”, dark web addresses can be distinguished by the top-level domain, “.onion“.
Obviously, finding these .onion websites is the first challenge, as they won’t show up in Google search results. You can’t just Google “Silk Road” and hope to land on the dark website.
A handful of dark web search engines that do index .onion sites include NotEvil, Ahmia, Candle, and Torch. There are also directories like dark.fail.
BUT DON’T TAKE MY WORD FOR IT…
Always exercise extreme caution when using publicly posted onion URLs. If you can’t get a personal recommendation from someone you trust, verify the URL from multiple sources.
The dark web has no shortage of criminal activity, scams, phishing sites, suspicious links, and malware designed to trick newbies. Links posted to the clear web, in particular, are often malicious. And because there’s very little use of HTTPS on the dark net, verifying whether or not a website is genuine using an SSL certificate is not feasible.
Reddit is also a valuable resource for finding the dark net or deep website you’re looking for. Try the /r/deepweb, /r/onions, and /r/Tor subreddits.
Anonymity is in your hands
You can now safely browse dark web websites and hidden wikis, but if you plan to do anything more than that, you’ll need to take several precautions. If you plan to purchase on a dark net marketplace or dark web commerce sites, you’ll need to create a fake identity. That means setting up encrypted email with a new email address, encrypting messages with PGP, using a pseudonym, setting up an anonymous Bitcoin wallet, disabling Javascript in Tor Browser, researching vendors, and more. Remember only to make purchases using digital currencies and never provide any online banking login details.
Again, we can’t emphasize enough that security and anonymity are paramount to those on dark websites. Your ISP and the government might not be able to view your activity when on the Tor Network, but they do know you are on the Tor Network, and that alone is enough to raise eyebrows. In fact, a recent judgment by the US Supreme Court denoted that simply using Tor was sufficient probable cause for law enforcement to search and seize any computer around the world.
Another vital precaution is to ensure that your .onion URLs are correct. Onion URLs generally contain a string of seemingly random letters and numbers. Once you are certain that you have the correct URL, save it in an encrypted note—the Tor browser will not cache it for later. Otherwise, there’s a good chance of falling victim to a phishing scam like this fake Bitcoin mixer.
We highly recommend employing another layer of security via a VPN.
What is the deep web?
The deep web is often confused with the dark net. Put simply, the deep web is all the information stored online that isn’t indexed by search engines. You don’t need special tools or a dark net browser to access most of the deep web; you just need to know where to look. Specialized search engines, directories, and wikis can help users locate the data they’re looking for.
That information is hidden simply because most users won’t find it relevant. Much of it is tucked away in databases that Google is either uninterested in or barred from crawling. A lot of it is old and outdated. The contents of iPhone apps, the files in your Dropbox account, academic journals, court records, and private social media profiles are all examples of data that Google doesn’t necessarily index but still exists on the internet.
Many of the best general deep web search engines, like Alltheweb, DeeperWeb, and CompletePlanet, have shut down or been acquired. Only a couple will offer more complete results than Google, Bing, or Yahoo:
- Dogpile – A metasearch engine that compiles results from several other search engines, removes duplicates and gives results
- The WWW Virtual Library – The original index of the web, but more of a directory than a search engine.
These are okay, but specialized search engines are better than general ones for finding info on the deep web. If you’re looking for a court case, for example, use your state or country’s public records search. If you need academic journals, check out our article on using deep web search engines for academic and scholarly research. The more specific you can be, the better, or else you’ll end up with the same search results you would find on Google. If you need a specific file type, like an Excel file or a PDF, learn how to specify searches for that type of file (e.g., type “filetype:PDF” in your query).
How can I differentiate legitimate services from scams on the dark web?
Here are some tips to help you differentiate between legitimate services and scams on the dark web:
- Research: Before using any service on the dark web, do your research. Look for reviews and feedback from other users to get an idea of the service’s legitimacy. Be wary of services that do not have reviews or feedback.
- Payment: Be cautious of services that require payment upfront or ask for payment through untraceable methods such as cryptocurrency. Legitimate services will usually offer secure payment options. Avoid providing credit card details or anything that can personally identify you.
- Too good to be true: Be wary of services that offer unrealistic deals or prices. If it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
- Communication: Legitimate services usually have a way to contact them for support or questions. If a service does not have a way to contact them or does not respond to inquiries, it may be a scam.
- Reputation: Check the website’s or service’s reputation on the dark web. If it has a bad reputation or is known for scams, it’s best to avoid it. Some of these sites include illegal content and have been known to be monitored by law enforcement agencies.
- Personal Information: Be cautious of services that ask for personal information such as your name, address, or social security number. Sharing this information can put you at risk of identity theft or fraud. Legitimate services will require only minimal information.
- Avoid illegal activity: Although many people use the dark web for legitimate reasons, it is also a hive for unlawful activity. Innocent users may find themselves unknowingly involved in something illegal. Be very cautious before engaging on marketplaces and forums.
VPN over Tor versus Tor over VPN
A VPN allows a user to encrypt all internet traffic traveling to and from his or her device and route it through a server in a location of that user’s choosing. A VPN, in combination with Tor, further enhances the user’s security and anonymity.
While somewhat similar, Tor emphasizes anonymity, and a VPN emphasizes privacy.
Combining them reduces risk, but there’s an important distinction in how these two tools interact. Let’s first discuss Tor over VPN.
If you connect to your VPN and fire up Tor Browser, you’re using Tor over VPN. This is by far the most common method. All your device’s internet traffic first goes to the VPN server, then bounces through the Tor Network before ending up at its final destination. Your ISP only sees the encrypted VPN traffic and won’t know you’re on Tor. You can access .onion websites normally.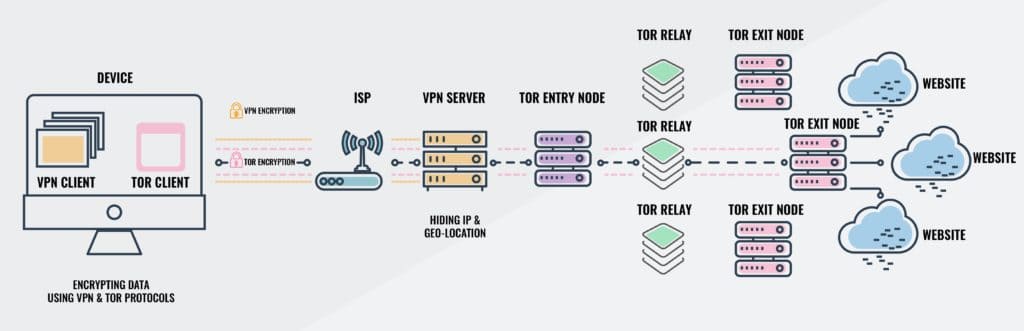 Tor over VPN requires you to trust your VPN provider, which can see that you are using Tor and keep metadata logs, though it can’t actually see the content of your encrypted Tor traffic. A logless VPN, which doesn’t store any traffic logs nor session logs is highly preferable. Traffic logs contain the content of your internet traffic, such as search queries and websites you visited, while session logs contain metadata like your IP address when you logged into the VPN, and how much data was transferred. Traffic logs are a bigger concern than session logs, but neither are good.
Tor over VPN requires you to trust your VPN provider, which can see that you are using Tor and keep metadata logs, though it can’t actually see the content of your encrypted Tor traffic. A logless VPN, which doesn’t store any traffic logs nor session logs is highly preferable. Traffic logs contain the content of your internet traffic, such as search queries and websites you visited, while session logs contain metadata like your IP address when you logged into the VPN, and how much data was transferred. Traffic logs are a bigger concern than session logs, but neither are good.
For built-in Tor over VPN functionality, NordVPN operates specialized servers that automatically route you through the Tor network. You don’t even need to use Tor Browser, but keep in mind other browsers can still pass identifying information through the network. Alternatively, there’s IPVanish who claim to be the world’s number one VPN for Tor and comes highly recommended, you can save 60% on the annual plan here.
DEAL ALERT: NordVPN is running a 2-year deal with a huge 62% discount here.
Tor over VPN also doesn’t protect users from malicious Tor exit nodes. Because Tor nodes are made up of volunteers, not all of them play by the rules. The final relay before your traffic goes to the destination website is known as the exit node. The exit node decrypts your traffic and thus can steal your personal information or inject malicious code. Additionally, Tor exit nodes are often blocked by websites that don’t trust them, and Tor over VPN can’t do anything about that, either.
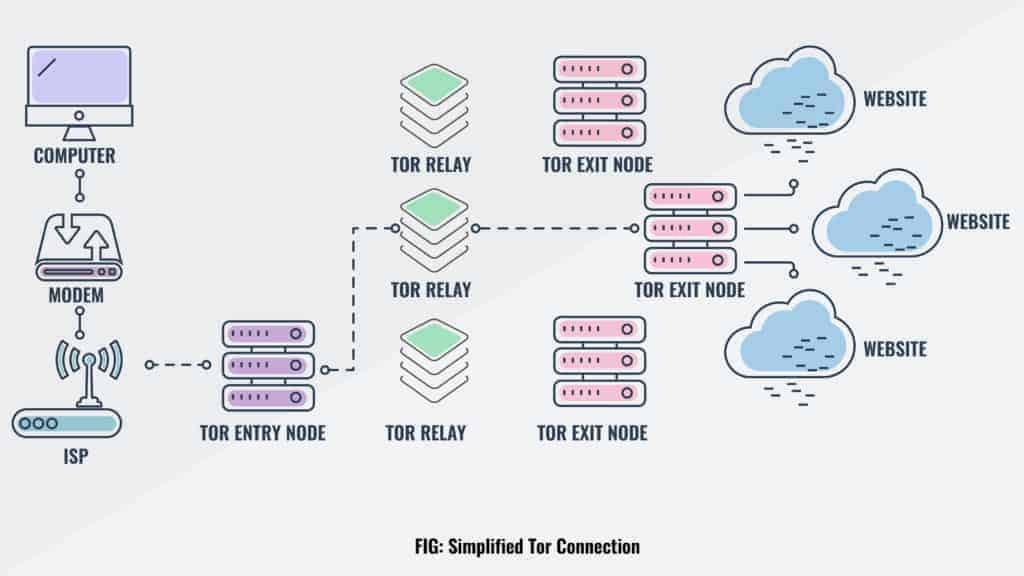
Then there’s the less popular VPN over Tor, which is advised against by the official Tor Project. Only two VPN providers that we know of, AirVPN and BolehVPN, offer this service, although neither of these score highly for speeds. In this case, the order of the two tools is switched. Internet traffic first passes through the Tor Network, and then through the VPN. This means the VPN provider doesn’t see your real IP address and the VPN protects you from those bad exit nodes.
The big downside is that your ISP will know you are using Tor, which is cause for concern in some places and will put many people off using this method. In this instance, too, it is important to use a logless VPN and pay with Bitcoin if you can to stay anonymous. The VPN over Tor technique is also susceptible to an end-to-end timing attack, though it’s highly unlikely.
Tor over VPN requires you to place some trust in your VPN provider but not your ISP, and is best if you want to access .onion websites. VPN over Tor requires you to place trust in your ISP but not your VPN and is best if you want to avoid bad Tor exit nodes. Some consider VPN over Tor more secure because it maintains anonymity throughout the entire process (assuming you pay for your VPN anonymously). Although the official Tor Project advises against VPN over Tor, both methods are superior to not using a VPN at all.
The major caveat is speed. Due to all the nodes that your traffic passes through, Tor by itself significantly limits bandwidth. Adding a VPN to it, even a fast one like IPVanish will make it even slower, so please be patient.
I2P
I2P is an alternative anonymous network to Tor. Unlike Tor, however, it cannot be used to access the public internet. It can only be used to access hidden services specific to the I2P network. I2P cannot be used to access .onion sites because it is a completely separate network from Tor. Instead, I2P uses its own brand of hidden sites called “eepsites”.
So why would you use I2P instead of Tor? After all, it’s much less popular, can’t be used to access normal websites, and isn’t as easy to use, among other disadvantages. Both rely on a peer-to-peer routing structure and layered encryption to make browsing private and anonymous.
I2P does have a few advantages, though. For a number of technical reasons, it’s much faster and more reliable than Tor. The peer-to-peer routing structure is more advanced, and it does not rely on a trusted directory to get route information. I2P uses one-way tunnels, so an eavesdropper can only capture outbound or inbound traffic, not both.
Setting up I2P requires more configuration on the user’s part than Tor. I2P must be downloaded and installed, after which configuration is done through the router console. Then individual applications must each be separately configured to work with I2P. You’ll need to configure your browser’s proxy settings to use the correct port on a web browser.
Freenet
Like I2P, Freenet is a self-contained network within the network that can’t be used to access sites on the public web. It can only be used to access the content uploaded to the Freenet, which is a peer-to-peer distributed data store. Unlike I2P and Tor, you don’t need a server to host content. Once you upload something, it stays there indefinitely even if you stop using Freenet, so long as it is popular.
Freenet allows users to connect in one of two modes: darknet and opennet. Darknet mode allows you to specify who your friends are on the network and only connect and share content with them. This allows groups of people to create closed, anonymous networks made up solely of people they know and trust.
Alternatively, users can connect in opennet mode, which automatically assigns peers on the network. Unlike darknet mode, opennet uses a handful of centralized servers in addition to the decentralized peer-to-peer network.
Configuration is fairly straightforward. Just download, install, and run. When you open your default browser, Freenet will be ready and running through its web-based interface. Note you should use a separate browser than the one you normally use to help ensure anonymity.
Freenet is still an experiment designed to resist denial-of-service attacks and censorship.
Dark Web stats and facts
- The Dark Web, often associated with illegal activities, has seen a surge in activity in 2023.
- Over 2.5 million daily visitors accessed the Dark Web, with more than half involved in illicit activities.
- In April 2023, the number of daily visitors spiked to 2.7 million.
- The Dark Web has become a hub for threat actors, with an estimated $1.5 billion changing hands in 2022.
- Illicit drug sales on the Dark Web are projected to grow by 15% annually.
- Despite the shutdown of Hydra Market in 2022, new darknet markets have emerged.
- The volume of malware on the Dark Web has increased, posing challenges for cybersecurity teams.
- The Dark Web Price Index 2023 shows a decrease in pricing for most items and services due to increased competition.
- Despite efforts to dismantle illegal marketplaces, the Dark Web economy remains robust. No long-term decrease in sales volume has been reported, indicating a strong demand for illicit goods and services.
How to get on the Dark Web safely FAQs
Are sites on the dark web illegal to use and visit?
The dark web contains much of the internet’s illicit content, ranging from drug trafficking to child pornography sites. Accessing such content is illegal and should be avoided.
That being said, not everything on the dark web is illegal. Many dark websites are perfectly legal and safe to use and, in many cases, are better for your privacy than clear websites.
Why was the dark web created in the first place?
The Tor network was created by the US military in the 1990s for anonymous communication between spies over the internet. That effort was never fully realized, but the US military published the code under a free license in 2004. Researchers from the Electronic Frontier Foundation and other groups continued its development and launched the Tor project in 2006 as a tool for journalists, activists, and whistleblowers.
Will visiting the dark web attract attention?
Connecting to the Tor network might raise eyebrows depending on who and where you are. Although data sent through Tor can’t be tracked or decrypted, your internet service provider and network administrator can still see that you’re using Tor. For this reason, we recommend pairing Tor with a VPN. The VPN’s encryption will hide from your ISP the fact that you’re using Tor.
Can I use Tor to browse the surface web?
Yes! One of the great things about Tor is that it can be used to access both the dark and surface web. Just note that although you’ll be anonymous, you won’t have the speed or convenience of a direct connection, and some sites might block you outright.
Is my phone number on the dark web?
Yes, your phone number may be on the dark web. The best way to find out is to check the “Have I Been Pwned” (HIBP) website. This website allows you to type in your email address or phone number and see if it’s been compromised in any data breaches. If your information has been compromised, then it’s likely that your phone number is also on the dark web.
Do I need a VPN if I access the dark web on my phone?
Yes, you definitely need a VPN if you want to access the dark web on your phone. This is because the dark web is full of potentially dangerous content, and a VPN will help keep your identity and personal information safe. Without a VPN, you could be putting yourself at risk of being hacked or scammed.
There are many different ways to access the dark web, but navigating it can be tricky and dangerous if you don’t know what you’re doing. A VPN will give you an extra layer of protection and anonymity, making it much safer to explore the dark web.
Is porn available on the dark web?
There is no doubt that porn is widely available on the dark web. In fact, there is an entire section of the dark web dedicated to pornographic content. However, it is important to note that not all of this content is legal.
The dark web allows people to access and share all sorts of illegal and explicit material without judgment or censorship.
In fact, much of it may be illegal under your jurisdiction. As such, you should exercise caution when accessing any unofficial dark websites.
Why isn't the dark web stopped or shut down?
There are a few reasons why the dark web isn’t stopped or shut down. First, it’s difficult to track and monitor activity on the dark web since much of it is encrypted.
Second, shutting down or controlling access to the dark web would be a huge undertaking and could have unintended consequences. Finally, many people consider the dark web a necessary tool for privacy and freedom of speech.
Can my ISP see that I am accessing the dark web?
Installing the Tor Browser is the best way to access the dark web. Note that your ISP will be able to see you’re connected to Tor. However, your online activity is encrypted and hidden from view thanks to Tor’s onion routing. This means your ISP can’t see that you’re accessing the dark web (or indeed, the specific sites you’re accessing).
You won’t be able to search the dark web with a regular browser (such as Chrome or Firefox). Besides, your online activity on such browsers is visible to your ISP unless you connect to a VPN service.
Can you go to the dark web with incognito mode?
Yes, you can access the dark web in incognito mode. However, this does not provide any extra security for your device or information.
Incognito mode only prevents the browser from storing history and cookies; your IP address and other details are still visible to anyone on the network. Therefore, it is recommended that you use a different browser, such as Tor, to browse safely and securely on the dark web.
Is the dark web actually anonymous?
Yes, the dark web is indeed anonymous. This means that the identities and locations of darknet users are hidden from public view and remain anonymous, even when interacting with other users or engaging in any online activity.
The technology behind this anonymous connection is known as “onion routing,” which utilizes a layered approach to obscure data and protect users’ locations on the network.
Identifying specific individuals who use the dark web can be quite tricky. However, we advise connecting to one of our recommended VPN services to stay anonymous.
See also: The best VPNs for Tor and how to Download the Tor Browser










VPN then startpage then search tor browser and download then search using the tor browser am I missing anything?
VPN start page then tor brower right?
you may want to open your normal browser in incognito mode with the VPN on to get to the Tor Browser download page.
Can anyone say how to enter the dark net
Howvdo I get so the dark web
Read the article.
Assalam o Aleikum
To my fellow brother( ) thanks for the great help you have enlightened us partaining the use of TOR. Could someone help me with links to deepweb markets.
Shukran.
Thank you.
It’s fine if you’re doing it the right way?? Literally read his advice and you’ll be fine if you add a few more safety precautions along side.
Hi Paul. Well thanks for this wonderful article . Hmm is it need to root your android device before downloading tor browser? in-order to use it as availability ?
I think Orbot works without root but not certain
I’d recommend using a pre-built Darknet Box or Darknet Key for maximum security when accessing the darknet. That way there’s no risk by using your own pc/laptop.
Google ‘DarknetBros’ to find them for sale.
paul i need some help …… i need a way to have at least a way of starting up with the dark web did the vpn stuff so waiting for you
Get the Tor Browser and be on your way
Don’t try it plsss I ALMOST DIE
I had my tor browser working just fine until I switched carriers and all of a sudden I have been unable to access my tor browser and I have even tried reinstalling it…but it just keeps coming up with a dialogue box that says I need to close my tor browser before I can open another! But it won’t relaunch even when I select Close Tor Browser..I believe I am being blocked from using this web browser and there is no reason for this as I am NOT doing anything illegal…I JUST WANT MY PRIVACY to be protected because I HATE THE THOUGHT OF BEING MONITORED LIKE I AM SOME CRIMINAL! ISNT IT UNLAWFUL FOR THE ISP OR ANY AUTHORITY TO INVADE YOUR PRIVACY LIKE THIS AND TO FORCE YOU TO USE A REGULAR BROWSER?
what about tails ? VPN -> TAILS -> DARK WEB ? or
VPN -> TOR -> DARK WEB
Great detailed in-depth article…Just the perfect kind of information I was searching for.
Hello Paul,
thanks for your great, useful and precise article.
My question is a theoretical one concerning both possibilities to have the most efficient cover.
“Tor over VPN vs VPN over Tor” issues.
Both systems have advantages and disadvantages that is clear.
Now using : VPN1 over (Tor over VPN2*)
*Using 2 different No log Tier VPN services.
Is that a possibility that could solve both systems disadventages
or is there no solution to that problem?
Thanks for taking time
Hi Vince, I’m not sure it would make a huge difference. The main distinction is more about the entry and exit points you use to get into the Tor network. If you plan on visiting .onion sites, you still need a Tor exit point and not a VPN at the other end of your connection, for example. I imagine double VPN + Tor would be very, very slow.
Hi!, The dark web can be accessed on both computer and android phones or only computers
You can use Orbot on Android to access the Tor network.
So if I go to the deep web and I want to get out I can only do that by exiting tor?
Yep.
Hi Paul
I know you are away at the moment but I need your help in removing all of my data from the onion peel app on the dark Web. Also, any other data that is linked to me, how do I go about doing This?
Urgently need some advice
I’m not sure what you mean by the “onion peel app”. Could you give me some more detail please?
So using the VPN is the must? I thought tor browser is enough since it’s already hide ur ip
VPN is not a must, it’s just an extra layer of protection.
What if i lost my coin? Coz my OS was being upgraded and my old Deep Onion Wallet was totally gone.. and now that i installed it again i have new Deep Onion Wallet address! How am I able to retrieve my coins from my old Deep Onion wallet and/or Deep Onion wallet address?
Cryptocurrency is another topic entirely I’m afraid. I’m not familiar with your particular wallet, but typically if you lose access then it’s gone forever, save for any recovery measures you put in place prior to losing access.
I still want to try. 🙂
Hi,will you get punished from Gov.if you just access the tor browser? Or only if you get into a sensitive behaviours?
Probably not but depends on your govt.
can i use cyber ghost !!!is it good or no
Check out the CyberGhost review on our site.
I’ve used the Tor browser before (a couple years ago), and my computer got wrecked. It froze while I was playing a game, and when I tried to restart it, it gave me an error saying that system32 needed to be repaired. It was my first time using the browser so I didn’t know what I was doing, and I didn’t use a VPN. Is that why my computer broke? Did I get hacked?
Sounds like you may have downloaded a malware or some other form of virus when downloading tor, which could mean you downloaded from the wrong site. System32 is an extremely important asset to windows and is often the go to file to be deleted when an attacker is looking to put you out of comission. Although, it is a very easy fix, you just need to hook the HDD from your computer up to another, and possibly run a repair on your windows. If all else fails, wipe the HDD and reinstall windows, then put it back in your PC. With the second method you WILL lose your files, but at least you will be able to use your computer.
I have no idea.
Desperate for some help! I had to get a new phone and tried to download the tor browser
The old way but can’t figure out how to drag file from folder to Applications folder (I’m seriously probably the dumbest computer/phone person to ever successfully do it but not this time) I have checked time and date and it is fine. I downloaded the app and can use it just can’t get onion sites to load. I could really use some help!!
Depends on your OS and browser app.
I am new to this and don’t know exactly what you mean by malicious exit nodes. Does this mean using Tor over VPN will allow the sites and people and such you visit on tor to see your data such as Ip and other important details that will leave you vulnerable? Thank you in advance for your help.
What is the correct way to leave Tor and the deepweb? I want to use regular internet with my Chrome browser.
Not sure what you mean. Just use your normal browser instead of Tor browser.
WELCOME THE DARK WEB
Et ben sa c’est hyper trop grand
hello, if i got you i have to first connect to tor and after i connect my vpn or i do the contrary? vpn and then tor?
Easiest to turn on the VPN and then open Tor browser, which will run your connection through the VPN server first and then onto the Tor Network.
VPN is like an internet condom; TOR is like an old geezer holding an umbrella while quietly sneaking off.
How can i get into the darknet for my own needs?
… read the guide?
Aaron if you truly say the dark web is over,then why are there continuous bank frauds all over the world with the existence of the NIT(Technologies). Get you facts straight
The main problem with TOR now is that the search engine now works using “default search engines.” When you download the TOR browser, you’ll notice that it is configured with StartPage! You can choose another default ( they have a defaultboot of law enforcement in this. I think that the folks at the TOR administration were “forced” to make this change. There seems to be no way around it. In effect, these default search engines that guard the
entrance way to the Dark Net act like “search nannies” and won’t let you do anything controversial.” Besides, I hear tens of thousands of lawbreakers are getting busted every month by the new global cyber police and their so called “Network Investigative Techniques ( Technologies )anyway. The Dark Web is pretty much “over.”
StartPage is an anonymous, secure search engine that queries Google on your behalf without you having to deal directly with Google. What’s wrong with that?
Hi.i was thinking about doing some dark web searching but i guess i will not after hearing some comments!
So how do I download the VPN anonymously and how do i set up an anonymous bitcoin wallet? I understand the rest and how I can be anonymous downloading tor by using the vpn.
Same i was thinking but not after all what i heard
what are you trying to say?