While the evolution of networking has helped companies reach new customers, it has also opened up many vulnerabilities. Now that more enterprises are using applications, it is vital to secure these entry points against the next generation of threats. Static Application Security Testing, or SAST, has become an important weapon in the fight against the next generation of threats. But what is SAST exactly?
SAST Explained
SAST or static analysis is a white box testing methodology where the user can scan through source code, byte code, and binaries to find vulnerabilities. The static analysis takes place when the application isn’t running. After finding vulnerabilities, the user can take steps to remediate the problem.
SAST takes place early in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) to identify vulnerabilities before an application is released. In most enterprises, when an issue is found inside the application source code, the developers then start to correct the code to eliminate the vulnerability.
Combatting vulnerabilities in the SDLC early is beneficial because it is more cost-effective to make improvements ahead of release. Trying to fix applications after a release costs more because small code changes could affect the performance of the entire application.
What do SAST Tools Do?
The main goal of a SAST tool is to give the user guidance on how to write code with integrity from the outset of the SDLC so the developer doesn’t have to redo everything after the release. SAST tools automate scanning code and help to find vulnerabilities during development.
When using a SAST software platform, the user can view real-time feedback as they code. For example, a developer could use the software to scan for vulnerabilities, which would highlight problematic code onscreen for the user to address. Showing the user bad code helps them to build a secure application fast and efficiently.
These tools also provide wider monitoring features like dashboards and reports so users can monitor security issues found. These features help during remediation so that developers have the necessary information to follow up after finding faulty code. Faster remediation means less exposure to threats.
Why is SAST Important?
Static analysis is important in any organization where applications are widely used or are a key business enabler. Over the past few years, many cybercriminals have started to exploit vulnerabilities in applications to gain access to private data. Using SAST and other models of application testing is as important as deploying an antivirus solution.
Without a SAST solution, an enterprise has no way of knowing if application source code is secure. A cybercriminal could easily use insecure source code to gain access to your network and cause thousands of dollars worth of damage. Testing reduces the likelihood of an attacker breaching an application.
While SAST is not the only necessary form of application testing (see SAST vs DAST further below), it is vital to check that the application code is secure. A SAST tool makes it easier for developers to fix coding issues and reduces potential entry points to the network.
SAST is also important from a pragmatic perspective as well. If issues are found and addressed early in the SDLC, then there will be no disruption to the application after release. Static testing helps a developer build a secure application from day one so that it doesn’t have to be rewritten at a higher cost after release.
The Benefits of SAST
SAST solutions and static testing offer a range of benefits to modern organizations. In this section, we’re going to look at some of the main benefits of SAST including the following:
- Detect source code vulnerabilities
- Early diagnostics!
- See the exact segment of code that’s causing problems
1. Detect source code vulnerabilities
The chief benefit of SAST solutions is the ability to identify coding vulnerabilities in source code. With a SAST tool, you can discover issues such as SQL injection and buffer overflows, which could disrupt the service of the application. Catching these issues helps you to minimize exposure to external risks.
Having a SAST platform to find these source code vulnerabilities ensures your applications are available when you need them to be. Other tools that don’t have the means to access source code can’t discover these flaws, leaving the door open to cyberattacks and disruption.
2. Early Diagnostics
SAST grants users the ability to view code before it has been compiled, which makes it ideal for running diagnostics early in the SDLC. SAST solutions can look at the code before it is compiled and give a developer guidance on improvements well ahead of release.
Finding issues early increases productivity and reduces the cost it would take to fix the issues after the application has been deployed. In addition, there is less exposure because the application doesn’t get released until the source code has been polished and perfected.
3. See the exact segment of code that’s causing problems
SAST solutions not only notify you that there is faulty code but also highlight which segments are causing the issue. Highlighting is user-friendly and makes it easy for a developer to improve code. Other testing solutions might tell the user there is a problem but they won’t always show the root cause of the problem.
Highlighting helps the user identify problem areas from a distance without having to sift through code manually. It also makes remediation more convenient and keeps developers productive throughout the SDLC. That means less time looking for issues and more time creating fixes.
SAST vs DAST: Which is Better for Application Security?
There are two dominant methodologies for application security testing: SAST and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST). Each of these takes a different approach to diagnose vulnerabilities.
The main difference is that SAST takes place at the beginning of the SDLC and DAST takes place while an application is running. DAST solutions attempt to penetrate applications to discover vulnerabilities located outside of the code or inside third-party interfaces.
The advantage that DAST tools have is that they can test the security of applications without needing to use the source code or a particular application framework. A penetration test finds vulnerabilities like validation issues that cybercriminals are most likely to target (because most attackers won’t have access to the source code).
These tools also tend to be less expensive to use because they don’t need to be compatible with the programming language of an application. However, the accessibility of these tools comes at the cost of not being able to identify specific coding issues. A DAST solution can’t highlight a specific code fault the way a SAST can.
In contrast, SAST tools have one main limitation compared to DAST; they can’t identify vulnerabilities outside of the application code. The National Security Agency’s Center for Assured Software found that the average static analysis tool covers 8 of the 13 weakness classes. This means that SAST tools can miss important vulnerabilities that attackers are on the lookout for.
SAST tools can also be difficult to use because they require access to application source code. It’s not uncommon for organizations to be hesitant to give third-party testers access to the code they rely on for daily operations! DAST is thus easier to deploy in most enterprises.
The limitations of each tool do not mean they work well together. By combining the two, enterprises can test for an even wider range of vulnerabilities. If you combine SAST and DAST, these two approaches can maximize your coverage.
SAST vs IAST
As security methodologies, SAST and DAST aren’t the only options you have for application testing. There are hybrid solutions such as Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST), which many regard as the future of SAST. IAST combines elements of SAST and DAST together to address security threats.
IAST solutions work by deploying a software agent or sensor inside an application to listen for activity during dynamic testing. An IAST tool measures the application interactions triggered by automated tests and manual tests to identify vulnerabilities in real time.
Like SAST, IAST tools can also detect bad lines of code. The automated capabilities of
IAST means it fits naturally into the CI/CD pipeline and helps to speed up the software delivery process. Automated testing allows companies to find issues and make fixes quickly. In other words, IAST reduces the manual administration tasks of developers and gives them time to focus on more important concerns.
IAST also enables enterprises to start testing earlier in the SDLC during the test/QA stage. Catching problems earlier means lower costs and higher productivity.
IAST also has two significant advantages over DAST, with speed and code highlighting. It takes a long time to scan for vulnerabilities with DAST and even when you do, these solutions can’t highlight faulty code. That leaves it to developers to run detective work!
As a result, many companies are transitioning to using IAST instead of DAST. Still, there are many vulnerabilities that only SAST and dynamic testing can detect. So, while some vendors have suggested that IAST is a replacement for SAST, it is best used as a complementary tool.
SAST Tools
There are many different types of SAST tools on the market. In this section we’re going to look at three popular SAST tools:
1. Synopsis Coverity
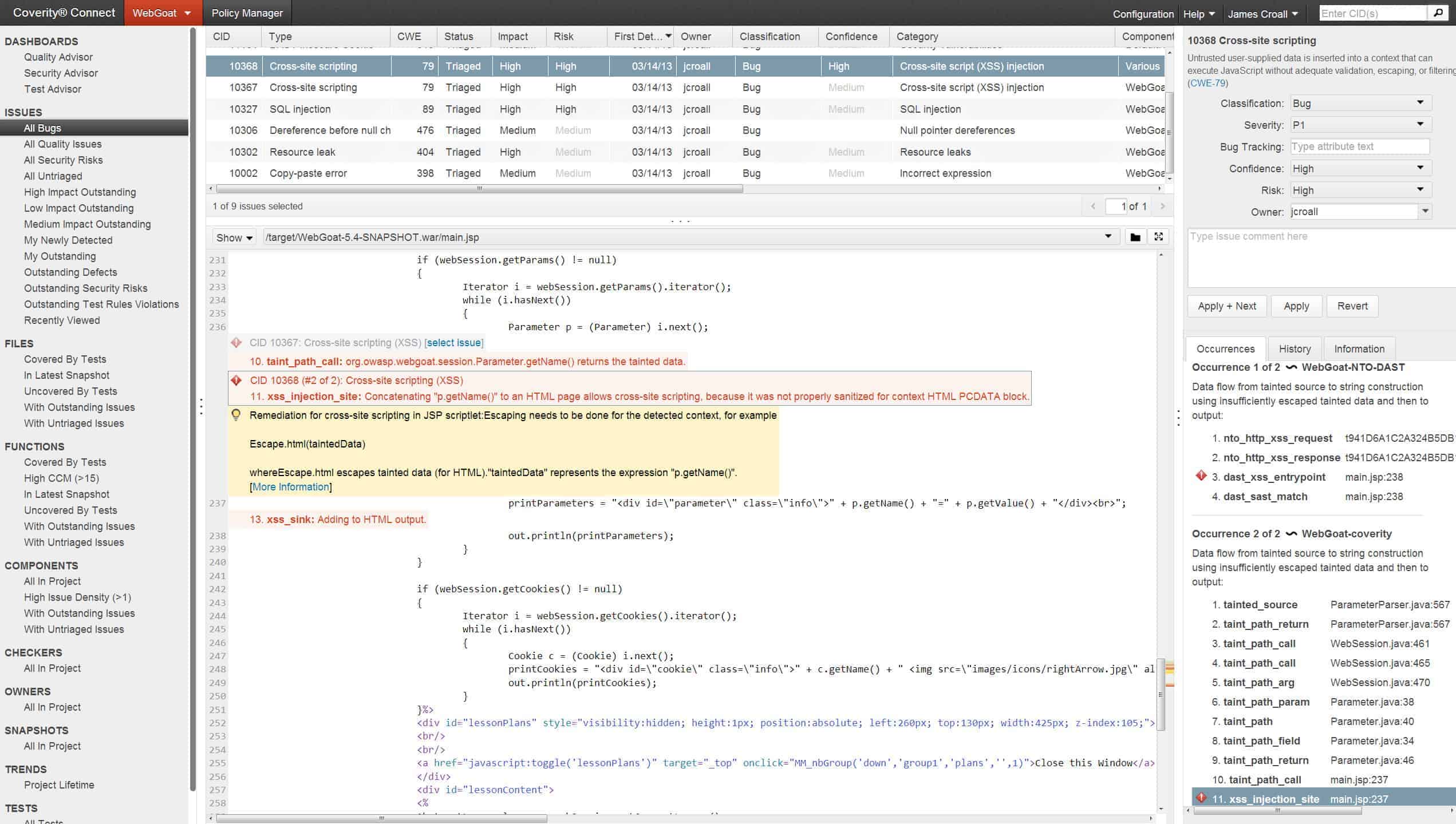
Synopsis Coverity is a piece of SAST software designed to help developers build secure applications. Synopsis Coverity is available on-premises and in the cloud, so you can choose precisely how you manage your application testing. To find bad code the program has a Code Sight IDE plugin that highlights code problems and provides additional information that can be used to find a fix.
Key Features:
- Application security testing
- Code quality assurance
- IDE integration
- Programmer education
- Continuous tester
Why do we recommend it?
Synopsis Coverity scans application programs under development to identify security loopholes and also poor-quality code. This system highlights incorrect lines in a program, recommending changes. This is a good way to improve the skills of a programming team and provides assurance that the finished program is of a high standard.
There are even eLearning lessons to help developers fix any issues they’ve found. The tool also has integration with other IDEs and source code management tools so it can fit well within your application security plan.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a good choice for any development company but particularly important for companies that provide contract programming services – they will be able to present code to their clients of the highest possible standard. DevOps teams that also manage Web applications can periodically rescan live applications to check that code has not been adulterated.
Pros:
- Highly detailed tool available on-prem or in the cloud
- Builtin systems can highlight syntax, functions, and identity problems in bad code
- Integrates well with other source code management software
Cons:
- Must contract sales for a demo
If you’re looking for a SAST solution with a low false-positive rate with a scalable cloud platform then Synopsis Coverity is a solid choice. However, to purchase a copy of Synopsis Coverity you will have to contact the sales team directly. You can also sign up for a demo.
2. Checkmarx SAST (CxSAST)
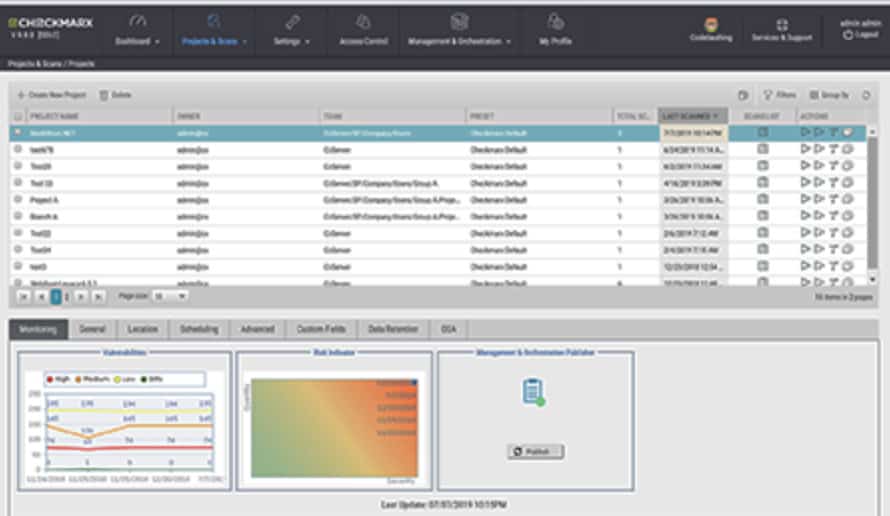
CheckMarx CxSAST is a SAST tool that can monitor custom and open-source code. It can scan over 20 coding and scripting languages and requires no configuration to scan any language. Supported languages include Java, C#.net, PHP, Python, Android, C++, JS, Microsoft ASP.net, Perl, and more.
Key Features:
- Code repository scanner
- Unit tester
- Checks APIs and frameworks
- IDE plug-in
Why do we recommend it?
Checkmarx SAST is provided on a platform that includes many code security testing strategies, including dynamic and interactive application security testing as well as static application security scanning. You can get all of the facilities with a platform account called Checkmarx One.
The software is efficient and only scans new or edited code during scans, dramatically reducing the overall scan time. The Open Scan Engine also helps to highlight the root cause of code issues so that the developer can correct them. There is also the option to integrate with other IDEs.
Who is it recommended for?
The SAST package is most appropriate for use by developers because it requires access to source code. Operations teams can use the tool to scan Web applications that are written in plain text programming languages and not compiled, such as JavaScript, Python, and PHP.
Pros:
- Offers modular visualization options as simple widget add-ons
- Easier to use than most SAST tools
- Includes root cause analysis for advanced troubleshooting
Cons:
- Must contract sales for pricing
CheckMarx CxSAST is a tool that’s easy to use and can reduce the amount of leg work your developers need to complete. If you want to know the price you will have to contact the sales team directly. You can request a demo of CheckMarx CxSAST.
3. SonarCloud

SonarCloud is a cloud-based code quality and security tool that analyzes code for bugs, vulnerabilities, and code smells. It integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, providing detailed insights and metrics to improve code maintainability and team collaboration. A valuable resource for developers.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based code analysis
- Supports multiple programming languages
- Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) integration
- Real-time code quality insights
- Customizable quality gates
Why do we recommend it?
SonarCloud is a solution for maintaining code quality across projects. Its comprehensive analysis and real-time feedback empower teams to identify and resolve issues quickly, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. The intuitive interface makes it accessible for both seasoned developers and newcomers alike.
SonarCloud is an essential tool for teams looking to enhance their code quality and security. By leveraging advanced static analysis, it helps developers catch potential issues early in the development lifecycle, reducing technical debt and improving overall software reliability.
Who Is It Recommended For?
SonarCloud is ideal for software development teams, DevOps professionals, and organizations focused on improving code quality and security. It suits both small startups and large enterprises looking to streamline their development processes and foster collaboration among team members.
Pros:
- Easy integration with existing workflows
- User-friendly interface
- Regular updates and feature enhancements
- Detailed vulnerability and bug reports
- Developer collaboration tool
Cons:
- Requires internet access for cloud features
SonarCloud offers a 14-day free trial that allows users to explore its features without commitment. This trial includes access to basic functionalities, making it easy for teams to assess its impact on their coding practices before deciding on a paid plan.
What is SAST?: Essential to Application Security!
Protecting applications from attackers is not easy. The trend of sophisticated attacks targeting the application layer to breach networks has shown that companies need to start updating security measures. Application testing methodologies like SAST and DAST are essential for ensuring the integrity of applications.
Just one breach can not only make an application unavailable to users but result in the loss of customer data and revenue from potential downtime. Purchasing the right SAST will reduce the chance of an attack compromising your network and protect your reputation from irreversible damage.
Companies that deploy SAST should do so in the infancy of the SDLC for the best results. Doing so will enable developers to code with the support of automated suggestions to make sure there are no glaring security issues to address further down the line.