The modern business environment usually consists of several productivity applications. And depending on the size of the company, there could be a large number of instances, or installations, of each application. Now, making sure that every single one of these installations is patched and updated could prove to be a daunting task – in some cases, it might even be impossible to accomplish accurately. Fortunately, we have the best application patch management tools to make this task a breeze for administrators of even the largest of networks.
Here is our list of the best application patch management tools:
- Atera EDITOR’S CHOICE A patch management tool that gives administrators the flexibility to micro-manage their patch management processes; they can even create custom patch bundles and automation to meet specific requirements or entirely exclude patches they don’t need. Start a free trial.
- NinjaOne Patch Management (FREE TRIAL) An endpoint patch management tool that is easy to use and yet, lets administrators take control over patching – right down to selecting and declining individual patches; great for network security, resource conservation, and end-user experience during patching. Get the 14-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL) A wholly automated patching tool for almost any device that connects to a network; administrators have complete control over the process and have detailed reports for deep insights. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Heimdal Security Patch & Asset Management This SaaS system is delivered from a cloud platform of cybersecurity tools and it generates a software inventory, supports software deployment, and runs patches.
- Syncro This SaaS package includes an automated patch manager for Windows and third-party applications in its remote monitoring and management (RMM) module.
- SolarWinds Patch Manager A corporate-level tool for more extensive infrastructures; it is a powerful tool covering endpoints regardless of location and integrates with Microsoft Update systems for an even more secure patching experience.
- SecPod SanerNow This cloud-based system provides a vulnerability scanner that feeds through to its own patch manager to update macOS, Linux, Windows, and software packages.
- Syxsense A cloud-based tool for patch management of endpoints on any networking environment; health reports that calculate the impact of each vulnerability to get a better sense of the severity of each oversight.
- Kaseya VSA A tool for the administrator who wants to have a powerful patching tool and then much more; it is a suite of administrative tools for remote control, endpoint discovery, network monitoring, etc.
- Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager A tool for automatically evaluating, testing, and deploying the operating system and application patches; this tool can reach endpoints wherever they may be – behind firewalls, remote locations, virtualized – it doesn’t matter, it will find it and patch it.
How do you choose the best application patch manager?
Before we can call it the best in the market, we need to make sure that an application patch management has the following characteristics and features:
- Easy to use – the tool should also be easy to install, configure, and administer.
- Extensive patching capabilities and support should work with a large selection of everyday third-party business and productivity applications.
- Instant vulnerability discovery and identification – constant scanning for instant vulnerability spotting, identifying the issue, and then detecting the correct updates from a well-stocked inventory is expected. Better yet, the system should assess vulnerabilities to offer guidance on which patches to install and in what sequence.
- Automation – any patching tool should automate the process of simultaneously installing multiple patches for numerous applications, even if they are running on various platforms.
- Low bandwidth consumption – patching shouldn’t hog the network bandwidth or even slow it down.
- Agents – another feature that contributes to low bandwidth usage is the use of agents to establish endpoint-to-server connections and communications; optimal polling and connection times make a tool efficient.
- Patch testing and rollback – administrators might need to test the effect of patches before deployment. Also, in case of unforeseen errors, the tool needs a rollback feature to return the endpoints to their prior status.
- Cloud functionalities – patching tools should, at the very least, be cloud-enabled, if not fully cloud-based.
- Cross-platform support – a good tool that can manage all endpoints, including cross-platform support for Windows, macOS, and the many flavors of Linux.
- Insightful reporting – reports are a critical feature in application patch management tools because that is the only way administrators can have insights into compliance while keeping an eye on the overall health.
- Great price – a good solution shouldn’t be expensive, and a cheap (or free) one shouldn’t be assumed to be inefficient; the trick is in finding the optimal solution in terms of price and performance.
The Best Application Patch Management Tools
Our methodology for selecting the best application patch manager
We’ve broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- Coverage and Compatibility: The tool should support a wide range of applications and operating systems, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Automation and Scheduling: Offers robust automation features for patch deployment, including the ability to schedule patches for minimal disruption.
- Security and Compliance: Prioritizes security by quickly addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides detailed reports and analytics to track patching status, vulnerabilities, and compliance levels.
- User Experience and Management: Features an intuitive interface and management dashboard, simplifying the patch management process for IT teams.
OK, let’s jump straight into it; here are the seven best application patch management tools.
1. Atera (FREE TRIAL)
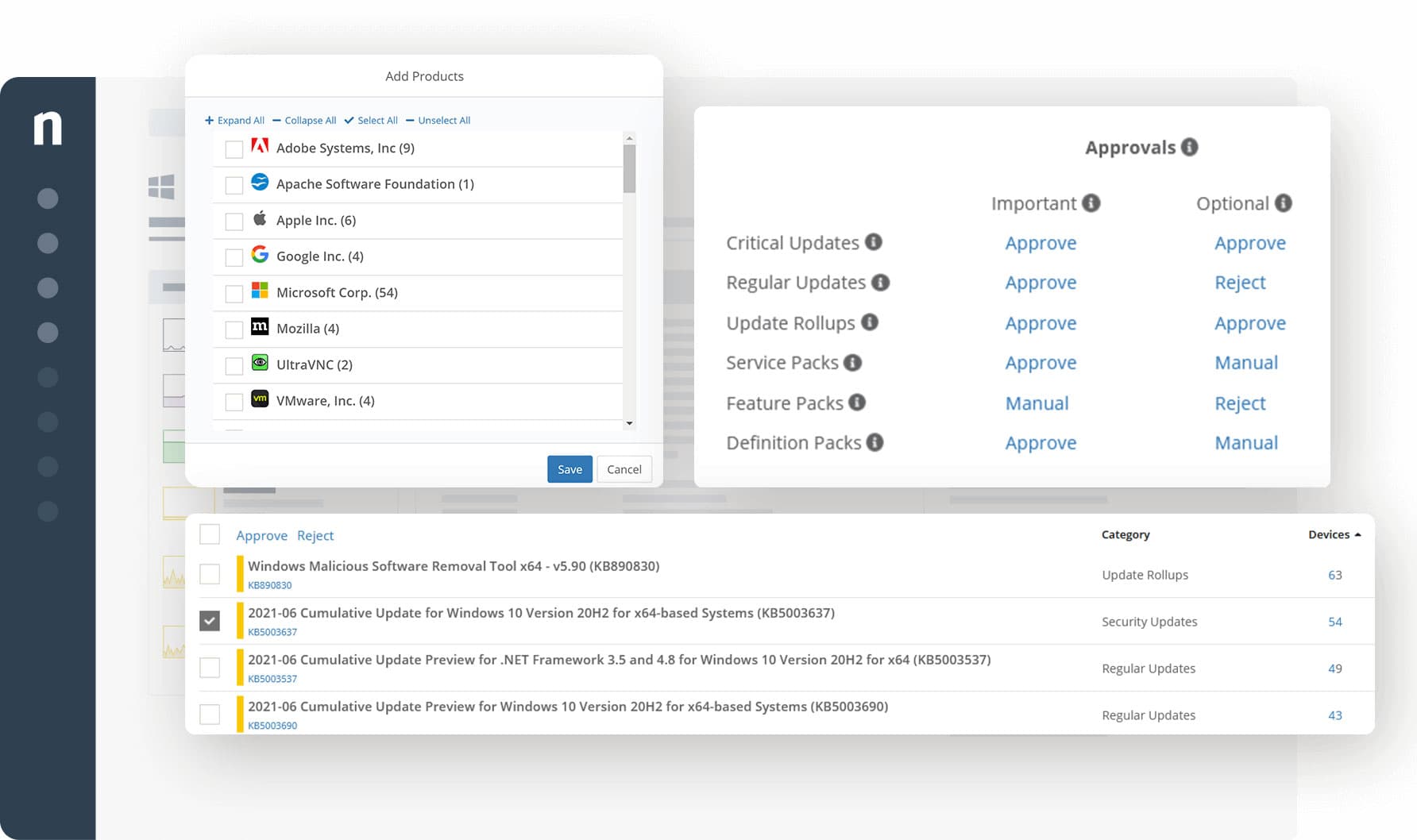
Atera’s Patch Management Software is a tool that gives complete control of patching across entire networks. It offers automatic patching of endpoint operating systems, applications, and hardware – all of which can be overseen from a central location with every agent being tracked to ensure continuous watertight security.
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform Patching: Provides patch management for both Windows and macOS, ensuring broad coverage across devices.
- Cloud Software Patching: Capable of updating cloud-based software packages, keeping all applications current.
- Software Distribution Capability: Allows for the distribution of software across networks, simplifying deployment tasks.
- Automated System Workflows: Features automation for routine maintenance tasks, including patch deployment and script execution.
- MSP-Friendly Options: Offers tools and configurations tailored to the needs of managed service providers, including multi-tenant architectures.
Why do we recommend it?
Atera is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) package that includes a patch manager for operating systems and software for computers running Windows and macOS. The tool is also able to install software. The patch manager is an automation console that provides a list of system maintenance tasks and it can also run scripts.
Atera can be configured to meet custom preferences for patching of endpoints that, themselves, handle critical driver updates; it has automatic patch management for Windows and macOS operating systems via integrations with Chocolatey and Homebrew.
It can patch most of the common business productivity software solutions found in every office like Zoom, Java, Dropbox, and Chrome.
It offers flexibility by allowing administrators to create software bundles or custom automation to meet their specific endpoint requirements or exclude sure patches they deem unnecessary, for example.
Even better, Atera offers a Shared Script Library with scripts that can be cloned and automatically added to automation profiles; these scripts are shared by the user community and are checked for quality by the in-house team allowing for a secure and customized patching experience.
Insightful and shareable reports are also part of Atera’s features that allow for better control and oversight of the patching processes; examples include a Patch Search and Deploy report for Microsoft KBs that would enable installing patches directly from the report.
Atera is a cloud-based service that is able to patch any endpoint anywhere. The system can monitor and manage endpoints on remote sites and there is a multi-tenant architecture available that enables the management of the systems of multiple clients. This version is ideal for use by managed service providers and it keeps the data of each client completely separate. This service is able to patch endpoints running Windows and macOS.
Who is it recommended for?
Atera produces its cloud-based system in two versions. One of them is for IT departments and the other is for managed service providers. Each flavor has four plans and they are tailored to the requirements of the supported business type. Charges are levied per technician with no minimum order size.
Pros:
- Cloud-Based Flexibility: A lightweight, cloud-based platform that ensures ease of access and management from any location.
- Comprehensive RMM and PSA Integration: Designed with managed service providers in mind, including integrated Remote Monitoring and Management and Professional Services Automation tools.
- High Customizability: Offers a highly customizable framework, providing flexibility to meet various operational needs.
- Scalable Multi-Tenant Support: Capable of supporting multiple client databases in a secure, segregated environment, ideal for MSPs.
- Cost-Effective Pricing Model: Accessible to businesses of all sizes due to its technician-based pricing structure, without a minimum requirement.
Cons:
- Target Audience Limitation: Primarily aimed at IT departments and MSPs, which may result in underutilization of features by smaller organizations or those not requiring multi-tenant capabilities.
Pricing starts at $129 per technician. Try Atera on a free trial!
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Atera is our top pick for an application patch management tool due to its comprehensive features, ease of use, and scalability for businesses of all sizes. Designed with IT professionals in mind, Atera offers an all-in-one solution that combines remote monitoring, management tools, and patch management in a single platform. This makes it a highly efficient tool for managing and maintaining the security and performance of both software and applications across a network. Automated patching in the package allows businesses to schedule and deploy patches across multiple endpoints with minimal manual intervention. This automation ensures that systems are always up-to-date, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities from unpatched software. Atera integrates with a wide range of applications and operating systems, providing a centralized dashboard that allows IT teams to manage and monitor updates, installations, and configurations seamlessly. Atera also offers real-time alerts, ensuring that businesses are notified immediately about patch failures or issues, which enhances proactive management. Atera supports growing environments with its cloud-based infrastructure and flexible pricing. The platform is user-friendly, requiring minimal training to get started, and its comprehensive support ensures that technical issues are quickly resolved. This makes Atera a reliable, efficient, and secure solution for patch management.
Download: Get a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.atera.com/signup/
OS: Cloud based
2. NinjaOne Patch Management (FREE TRIAL)
NinjaOne Patch Management is a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool that gives administrators complete visibility and control over end-users applications running on managed endpoints. In addition, it has a third-party patching engine that can keep over 135 typical applications up-to-date – without the users’ input being required.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive OS Coverage: Offers patch management for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems, ensuring a wide range of devices are covered.
- Extensive Software Patching: Capable of keeping over 135 commonly used software packages up to date automatically.
- MSP-Designed: Specifically tailored for managed service providers, offering tools and features that streamline MSP operations.
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne Patch Management is delivered from a cloud platform of remote monitoring and management services. This package is similar to the Atera system because as well as the RMM system, it includes a remote access tool and a ticketing service. It can patch Windows, macOS, and Linux plus hundreds of well-known applications.
The tool offers more. It makes it easy to monitor and control application-related vulnerabilities with its detailed software inventory and built-in tools for deployment, removal, and blacklisting applications.
This tool covers the entire IT infrastructure and keeps them secure and updated using patch deployments for devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems and the applications that run on them.
NinjaOne supports the patching of many of the most commonly used applications like Microsoft Edge, MS Office, Office 365, and much more.
The patches can be sent out to endpoints singularly, in groups, or broadcasted across the whole infrastructure.
A central dashboard gives insight into the patch status of all endpoints and displays details like successfully deployed patches, those that are still pending, as well as those that have failed to install correctly.
End-users don’t need to be joined to the domain, be on the company network or use a VPN for their endpoints to be patched; what’s even better is that there is no complex and expensive patching server to set up and maintain – a win-win solution for both administrators and the end-users user experience (UX).
The tool has aesthetic and insightful reports on patch compliance status, security vulnerabilities, and much more – accessible at a click of a button – and which can be used as reference or proof of compliance.
It has automatic patch approval settings for each patch type and criticality and can be configured for complete control over scanning times, updating schedules, reboot options, and more; administrators also have complete control over how each endpoint is patched with the capability of patch identification, approval, and deployment schedules.
Administrators can use patch policies to optimize and automate the deployment process across the infrastructure while also using manual, ad-hoc management in case there are individual critical updates that need to be deployed immediately.
Patches 140+ Windows applications and 100+ MacOS applications.
Who is it recommended for?
The most likely buyers of NinjaOne Patch Management those businesses that want the Ninja RMM system to support IT technicians. The entire platform is constructed with a multi-tenant architecture that enables MSPs to keep the data of their clients separate but IT departments could also use it.
Pros:
- Silent Application Management: Allows for the silent installation and uninstallation of applications and patches, minimizing disruptions to end-users.
- Flexible Scheduling: Automated maintenance tasks, including patch management, can be scheduled for convenience and efficiency.
- Web-Based Management: Provides a platform-agnostic, web-based management console for ease of use across different operating systems.
Cons:
- Limited Mobile Device Support: Does not offer patch management support for mobile devices, which could be a limitation for organizations with a significant mobile workforce.
You can start a 14-day free trial.
3. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is an application patch management tool available as an on-premises or cloud solution. It supports Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems.
The tool supports automated patch deployment of over 900 updates for over 500 third-party applications that include Adobe, Java, WinRAR, and more.
Key Features:
- Broad Application Coverage: Manages patches for over 500 third-party applications, including widely used software like Adobe, Java, and WinRAR.
- Virtual System Patching: Extends its patching capabilities to virtual environments, ensuring all virtual systems are up-to-date.
- Patch Rejection Feature: Allows administrators to decline specific patches, offering flexibility and control over the update process.
Why do we recommend it?
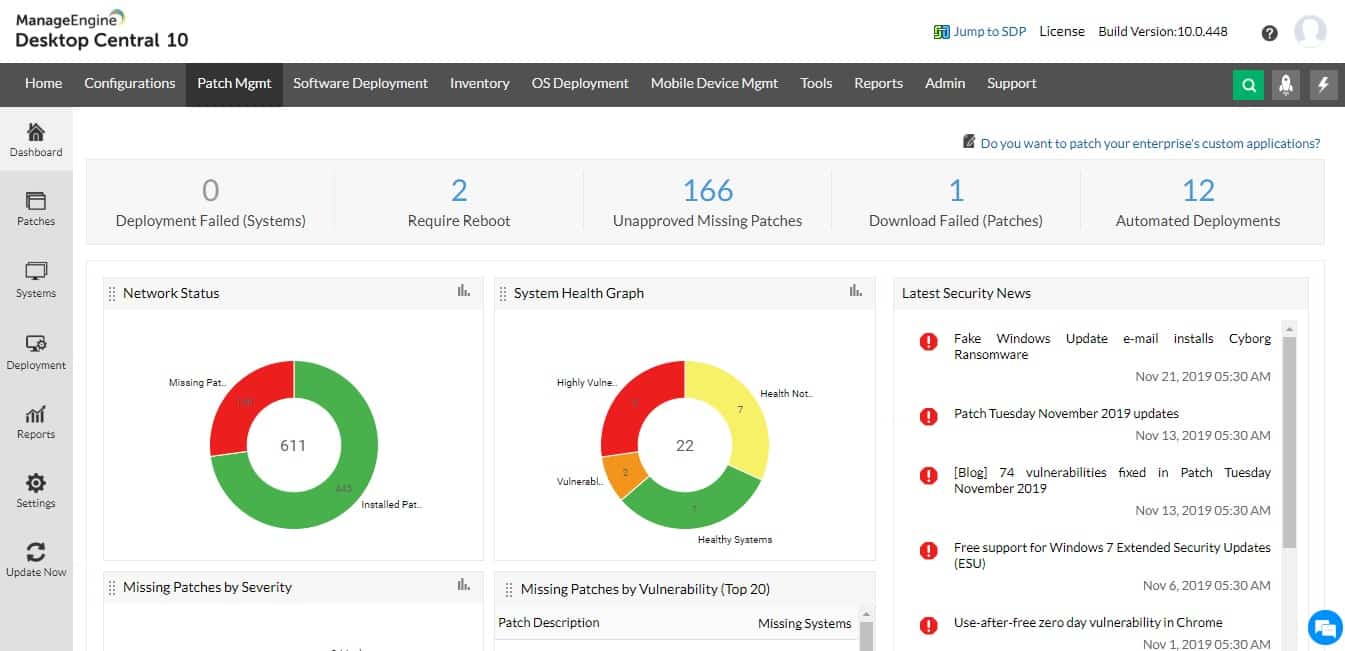
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus compiles a software inventory for all of your endpoints and notes the version numbers of each. ManageEngine maintains a library of the latest patches available for Windows, macOS, Linux, and well-known applications. Your patch manager downloads from this source when it sees a mismatch in version numbers.
Patch Manager Plus automatically spots which applications need to be patched, and the process of acquiring third-party application patches is also completely automated and controlled from a central point.
Administrators can also spot missing patches by manually scanning the endpoints; they can then test available deployable patches to ensure they resolve the vulnerabilities without causing further complications.
They can also track the availability of new patches and have the flexibility of synchronizing patches as per preferred schedules or perform selective deployment of sensitive patches depending on their compliance needs – the tool offers complete flexibility.
It can cover almost any device type on a network: desktops, laptops, servers, roaming devices, and virtual machines (VMs).
All patch deployment processes can be monitored and controlled using robust audits and reports.
An essential feature in this tool is the ability for administrators to decline patches should they be found to be disruptive until the software or hardware vendors have come up with a better patch.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is a good fit for any business. The central patch library creates an efficient local service and enables daily patch availability checking a low overhead process. ManageEngine offers a Free edition of the package, which will cover 20 workstations and five servers.
Pros:
- Extensive Platform Support: Provides comprehensive patch management solutions for Windows, Mac, and Linux systems.
- Automated Patch Deployment: Facilitates automatic detection and deployment of patches, simplifying the patch management process.
- Flexible Patch Synchronization: Enables scheduled synchronization of patches or selective deployment based on compliance and security needs.
- Robust Monitoring and Reporting: Features detailed audits and reports for effective monitoring and management of the patch deployment process.
Cons:
- Complexity and Learning Curve: The feature-rich platform may require a significant amount of time to fully explore and understand.
- Flexible yet Complex Deployment Options: While it supports a wide range of platforms, navigating through the various deployment options can be challenging for new users.
Try the cloud or on-premise version of ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – FREE for 30 days.
4. Heimdal Security Patch & Asset Management

Heimdal Security Patch & Asset Management provides software management for endpoints running Windows and Linux. This is a cloud-based system that accesses devices through the installation of a local agent. This agent program is available for Windows and Linux.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Software Inventory: Compiles detailed hardware and software inventories for effective license and asset management.
- Software Deployment Capabilities: Facilitates both the deployment of new software and the updating of existing applications.
- Automated Patching System: Offers automated patching for devices running Windows and Linux, including third-party and proprietary software updates.
Why do we recommend it?
Heimdal Security Patch & Asset Management provides a system scanner that compiles hardware and software inventories. The software records form the basis of a patching system, which will operate on computers running Windows and Linux. The tool is also able to update third-party applications and bespoke, proprietary software.
Heimdal Security’s package creates a company-wide software inventory. This is a useful service for software license management and it also details the versions of operating systems and software packages. This asset inventory forms the basis for the automated patch manager.
The patch manager includes a scheduler. This can also be used to deploy new software as well as for updates. The scheduler requires a calendar to be input that details timers and days when devices are not in use. The scheduler will roll out patches at the next available maintenance window.
The automated patch installer can activate computers that are turned off in order to install software. It will also order update installations according to patch dependencies. The tool is able to restart a computer when a patch installation requires it.
The scheduler is intended for use during unsociable hours and technicians are not expected to attend to the system while patching is in progress. This, the patching service documents all of its activities, including the completion status of each patch. These records, together with the initial findings of the software scanner provide documentation for compliance reporting.
The Heimdal system provides a number of patching scenarios, One of these is a user-approved patch run. In this case, the device’s user is notified that patches are available and can then command the installation or specify a later time for the patching to occur.
The Heimdal Security platform offers a number of packages of security tools. For example, the Heimdal Security EDR includes the Patch and Asset Management module. So, you can choose to subscribe to just the patching tool or take it as part of a wider package.
Who is it recommended for?
The Heimdal platform offers many security and compliance tools, so potential customers of the patch management service should take an interest in which of those other services they might find useful. The platform doesn’t offer a multi-tenanted architecture for managed service providers.
Pros:
- Automated Unattended Patch Rollouts: Enables patches to be installed automatically during non-business hours, without the need for technician oversight.
- Compliance Reporting: Provides documentation suitable for NIST CM-7 compliance, assisting in regulatory adherence.
- Global Application: Designed to cater to the needs of multinational organizations, ensuring consistent patch management across all locations.
- Patch Dependency Management: Effectively handles patch dependencies to ensure updates are installed in the correct order and systems remain stable.
Cons:
- Focus on Patch Dependencies: While managing patch dependencies is crucial, it may require additional configuration to ensure all dependencies are accurately identified and managed.
- Designed Primarily for Direct Use: Lacks a multi-tenant architecture, which might limit its appeal for managed service providers looking for a solution to offer their clients.
Heimdal Security offers consultation to potential new customers, which provides an assessment of security software needs, matching the company’s products.
1. Syncro (FREE TRIAL)

Syncro is a cloud platform of software for use by managed service providers. Its package of tools for supporting client sites is called the remote monitoring and management (RMM) system and it includes an automated patch manager. This tool keeps Windows up to date and also patches the third-party applications that run on Windows PCs and servers.
Key Features:
- MSP-Oriented Design: Specifically tailored for managed service providers to efficiently manage and support client networks.
- Comprehensive Software Inventory: Automatically compiles detailed inventories of software installed across client endpoints.
- Windows and Applications Patching: Ensures up-to-date security by managing patches for both Windows operating systems and third-party applications.
Why do we recommend it?
Syncro is a platform of tools for managed service providers. This package includes remote monitoring and management tools plus a remote access utility for technicians and professional services automation systems for MSP managers. The RMM’s feature includes a patch manager for Windows. The patching service will also update applications.
The Syncro system’s automated patch manager is resident in the cloud along with the rest of the Syncro platform. This cloud system accesses local networks and their endpoints through the installation of agent programs. These agents gather intel on each endpoint, which includes the version number and edition of its Windows operating system. This information is uploaded to the Syncro system.
The agent also scans each endpoint for all of the software that is installed on it. This process results in a profile for each package on each device and this information is also uploaded to the Syncro system.
One account on the Syncro platform applies to one MSP and its charge rate is per technician. This allows the MSP to manage an unlimited number of endpoints on an unlimited number of client sites.
The technicians of the MSP set up a sub-account for each client. This keeps the data of each client completely separate and enables the technician team leader to control which technician gets access to the data of which clients.
The software data that is uploaded to the Syncro system by the site agents goes to a specific client sub-account. The Syncro service then compiles a software inventory per endpoint and that data is consolidated into a client-wide registry. The version number of each recorded operating system installation and application instance indicates its patch status. The Syncro system is then able to check with software providers for the latest version number and download the patches needed to get each installation up to the current version.
The console of Syncro needs to be set up for each client, giving the system a maintenance calendar. The Syncro patch manager will then queue all available patches and trigger their installation at the next available patch window. Technicians do not need to attend the patch run and will be able to look through event logs the next morning to see which patches succeeded and which failed.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is designed for managed service providers. There isn’t an option to get just the RMM package and IT departments don’t need the utilities of the PSA part of the Syncro platform. The tool is only able to update computers running Windows. Subscriptions are leveled per user.
Pros:
- Automated Patch Management: Facilitates the automated deployment of updates, requiring minimal technician intervention.
- Patch Dependency Handling: Smartly manages patch dependencies to ensure smooth and successful updates.
- Automated Rebooting: Capable of automatically rebooting endpoints as needed after patch installation, minimizing downtime.
Cons:
- Limited OS Support: Focuses on Windows environments, excluding Linux, Unix, or macOS systems from its patch management capabilities.
The event logging feature of the Syncro patch manager provides documentation for SLA compliance reporting and billing. It is also useful for data standards compliance auditing. You can assess Syncro with a 14-day free trial.
6. SolarWinds Patch Manager
SolarWinds Patch Manager is a patch management solution developed by leaders in the application and server monitoring and management tools market. It is an on-premises patch management software solution designed to quickly and efficiently address software vulnerabilities.
Key Features:
- Windows Patching: Specializes in patching Windows operating systems for comprehensive coverage.
- SCCM Integration: Seamlessly integrates with System Center Configuration Manager to enhance its patching capabilities.
- Third-Party Software Patching: Extends patch management beyond Microsoft products to include updates for popular third-party applications.
- Customizable Patch Routines: Allows for the creation of pre and post-patch routines to ensure system stability and compliance.
Why do we recommend it?
The SolarWinds Patch Manager adapts the SCCM process for updating Windows computers. While SCCM can update Microsoft applications, the SolarWinds adaptation enables third-party software packages to be updated as well. You don’t use the SSCCM console but access the automated patch manager through the Solarwinds console.
It simplifies many of the steps in the patch management process, including the research, scheduling, deployment, and reporting on patching and vulnerability issues.
Administrators have a central dashboard from which they can stay on top of security updates, track patch versions, and even be notified of failed patch deployments, thus avoiding security issues before they occur.
It integrates well with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and the Microsoft update agent to update Windows patches automatically, allowing it to automatically update Windows patches.
It also has software deployment tools for Windows to extend the System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM).
Of course, Patch Manager also helps with the deployment of updates for third-party applications; it offers pre-built, tested, and automatically delivered packages for commonly used applications like Adobe, Google, and Oracle
Administrators can create custom patching schedules to meet requirements that are unique to their networks.
They can even get a heads-up to proactively identify servers and workstations that need to be patched, after which the tool allows them to build patch deployment packages to meet these specific demands.
These customizations include control and scheduling of software patching for endpoints based on their operating systems, IP ranges, custom device groupings – or even individual device selections.
This is an ideal solution for businesses with a more extensive installation containing thousands of endpoints. In addition, it can handle the deployment of large numbers of devices – custom or otherwise – with ease.
Apart from patching customizations, administrators can also specify reboot preferences, force updates, or define specific group updates overriding the end users’ preferences.
In the meantime, administrators keep track of the whole process via a patch status dashboard and confirm compliance later through various insightful reports that Patch Manager offers.
These reports are fully customizable and can be sorted, filtered, scheduled, exported, and emailed – enhancing the administrators’ ability to stay on top of their network’s security.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a solution for large organizations because its price puts it out of reach of small companies. The software for the Patch Manager runs on Windows Server and the tool can update other Windows computers across the network. You can’t update software on computers running macOS or Linux with this system.
Pros:
- Intuitive Dashboard: Offers a simple yet powerful dashboard for easy tracking and management of patches across large networks.
- Enhanced SCCM Deployment: Direct integration with SCCM facilitates smoother and more efficient patch deployment processes.
- Extensive Third-Party Support: Provides robust patching options for a wide array of third-party software, ensuring a secure and up-to-date environment.
Cons:
- Enterprise-Oriented: Primarily designed for large organizations, potentially making it less accessible for smaller networks or home labs.
Try SolarWinds Patch Manager with a fully functional 30-day free trial.
7. SecPod SanerNow
SecPod SanerNow is a SaaS package that is called the SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform. The modules in this package provide asset discovery, vulnerability scanning, patch management, and compliance management. The vulnerability scanning part of this system has processes for on-site systems and cloud platforms.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Asset Discovery: Automatically identifies and catalogs all devices on a network, creating a detailed hardware inventory.
- Advanced Vulnerability Scanning: Utilizes a vulnerability scanner that checks against a database of over 160,000 known vulnerabilities for on-site and cloud platforms.
- Cross-Platform Patching: Provides patch management solutions for Windows, macOS, and Linux, including updates for over 400 third-party software applications.
Why do we recommend it?
SecPod SanerNow is a cloud platform of security systems that includes a vulnerability scanner and a patch manager. This system will watch over computers running Windows, macOS, and Linux. It will update third-party software as well as operating systems. The platform also provides compliance management.
The vulnerability manager operates through an agent that needs to be installed on an endpoint on your network. This first discovers all devices and creates a hardware inventory. It then installs an agent on each endpoint, which reports back with a software inventory. The network agent uploads all of that data to the cloud-based console.
The vulnerability management system then instructs all agents to perform system scans. These work through a list of 160,000 known vulnerabilities. If you use cloud-based services, the SanerNow service installs an agent on each of those as well to perform scans. The results of these scans create a list of problems to fix.
While the local agents are working, the central server processes the uploaded list of software on each device, which includes operating systems. The version number of each package indicates its patch status.
The service acquires the installers for the patches issued by the creators of more than 400 software packages plus operating systems. It verifies them and then stores them in its own library. This is where the individual patch manager for each client gets its patches.
You set up a maintenance calendar in the SanerNow console and the patch manager will launch at the next available window. The SecPod philosophy is to run patches as soon as possible. However, you can intervene in the process and manually test or hold individual patches. All vulnerabilities are logged and the patch run completion status is also recorded. These records are preserved for compliance auditing.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is a good option for business managers who don’t have the time to research all of the different types of security systems that are available. It provides system hardening services that reduce the chances of being the victim of a malware or hacker attack.
Pros:
- Integrated Compliance Management: Offers compliance management features for standards such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, NIST 800-53, NIST 800-171, and ISO, aiding in regulatory compliance.
- Pre-Verified Patch Library: Maintains a library of pre-verified patch installers, ensuring reliability and security of patches deployed.
- Automated Patch Deployment: Facilitates unattended patch rollouts, allowing for efficient and timely software updates without manual intervention.
Cons:
- Limited Software Patching List: Patches are available only for an approved list of software, which may not cover all applications used by a business.
You can assess the SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform with a 30-day free trial.
8. Syxsense
Syxsense is a tool with IT management, security vulnerability scanning, and patch management capabilities – all packed into one powerful suite. In addition, it is a cloud-based tool that is hosted in Microsoft Azure. This makes it the ideal tool for cloud-based or hybrid networking environments, but it would still be a practical application patch management tool even if used on LANs.
Key Features:
- Multi-OS Patching: Supports patch management for Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring comprehensive coverage across diverse IT environments.
- Patch Prioritization: Employs a system to prioritize patches based on severity and impact, optimizing the patching process.
- Compliance Assurance: Facilitates compliance with standards such as SOX, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, enhancing security and regulatory adherence.
Why do we recommend it?
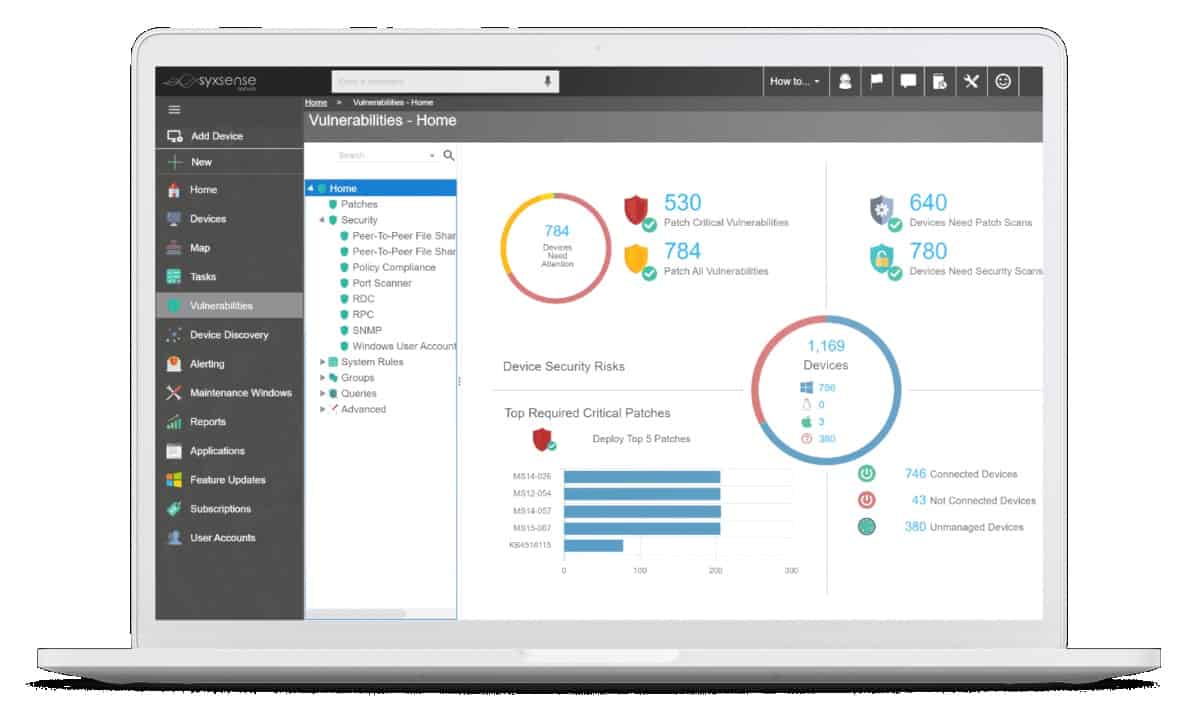
Syxsense is a cloud platform that hosts three packages, called Manage, Secure, and Enterprise. The patch manager is part of the Syxsense Manage module. That plan also provides a remote control feature for manual access to remote devices. The patch manager can watch over computers running Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Syxsense monitors desktops, laptops, and servers running Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems; the endpoints’ location doesn’t matter – they can be roaming devices that are not connected to the administrators’ domain all be patched and updated.
Apart from updating the operating systems, this tool can automatically deploy patches for third-party applications like Adobe, Java, and Chrome; it can also check for hotfixes, bug fixes, and any other patches or updates that application vendors send out.
Administrators can set the patch deployment times for when they won’t interfere with productivity hours; they can also be scheduled for standing times – think Microsoft’s Patch Tuesdays – when they are sure there will be critical updates being sent out.
The tool has a device health monitor that shows where immediate patching is required or if any patches are missing, for immediate action to be taken; the impact of these vulnerabilities is calculated using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to give a better indication of the severity of the oversights.
The tool has a list of detailed reporting tools that give insights into the whole patching process and can be further adapted depending on custom requirements through parameters and filtering.
The resulting reports can be used as executive overviews or finely detailed audits; examples of such reports are those having titles like Security Risk Assessment, Most Vulnerable Devices, and Task Summary – all of which can be scheduled for automatic receipt, exported for further analysis or used as proof of compliance to HIPAA, SOX or PCI.
Who is it recommended for?
Syxsense doesn’t publish a price list, which makes it difficult to assess whether the Manager package would appeal to small businesses. All of the Syxsense units are available as a managed service – in the case of Syxsense Manage, this is called Syxsense Manage Plus.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Offers an intuitive and visually engaging dashboard that simplifies monitoring and management tasks.
- Cloud-Based Flexibility: Being hosted in Microsoft Azure, it provides a robust and flexible platform for managing cloud-based or hybrid networks.
- Adaptable Pricing Model: Offers flexibility in pricing, making it suitable for networks of any size, from small businesses to large enterprises.
- Device Configuration Profiles: Enables efficient device onboarding and management through customizable configuration profiles.
Cons:
- Trial Period: A longer trial period would provide potential users with more time to explore the full capabilities of the platform.
Try Syxsense Manage FREE for 14 days.
9. Kaseya VSA
With the Kaseya VSA Patch Management Software, we get a suite of tools for remote control, IT automation, network monitoring, endpoint discovery and inventory, and application patch management. It is used to install, deploy, and update software across endpoints. But, that’s not all; it also has various add-ons for office productivity and data security features.
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform Patching: Enables patch management for both Windows and macOS, ensuring a broad range of endpoints are kept secure and up-to-date.
- Comprehensive Completion Reports: Offers detailed reports on the completion status of patch deployments, enhancing visibility and control.
- MSP-Oriented Design: Specifically tailored for managed service providers, providing tools that streamline the management of client networks.
Why do we recommend it?
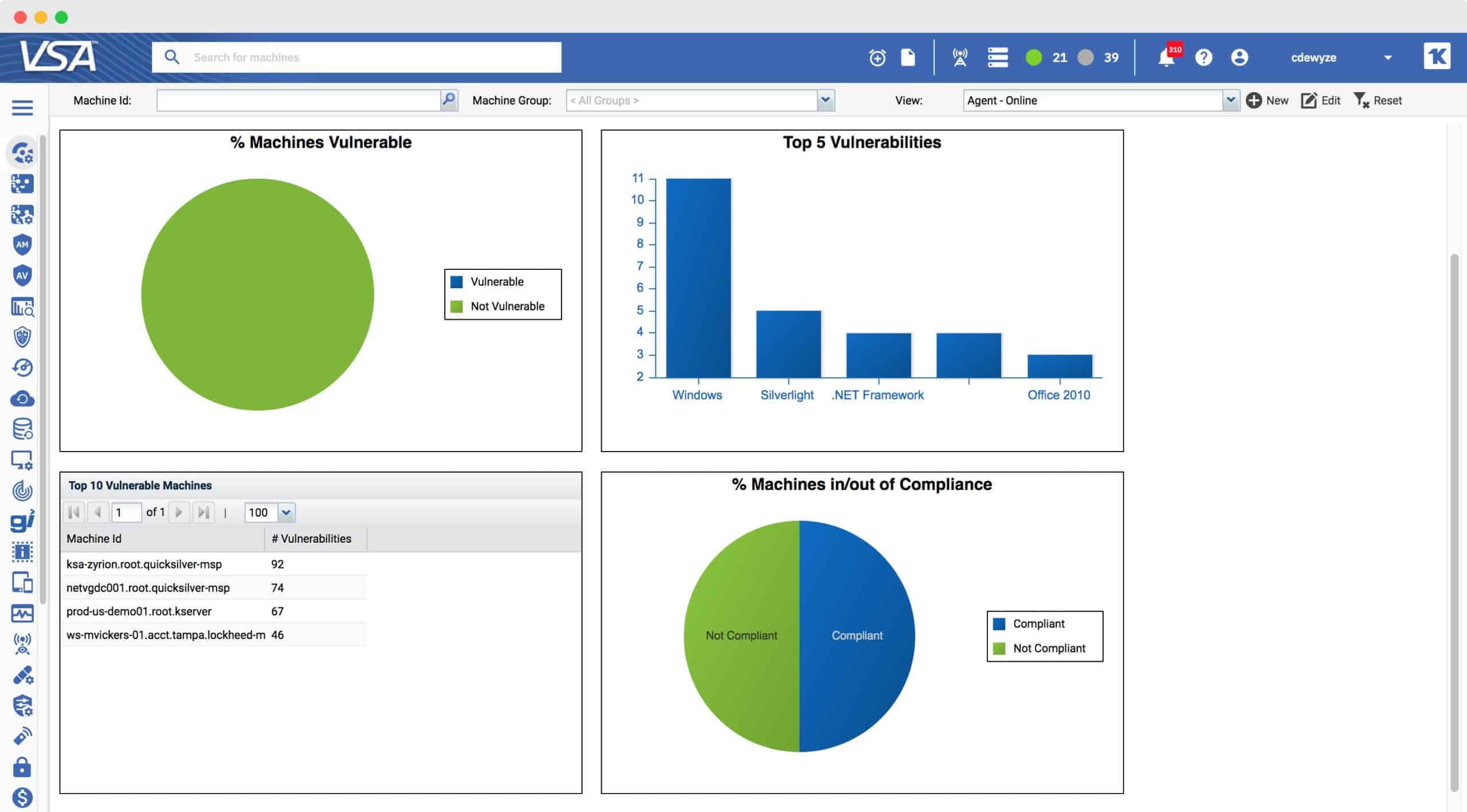
Kaseya VSA is a remote monitoring and management system that is delivered from the cloud. The platform includes a patch management function and that service will operate on endpoints running Windows and macOS. As well as patching operating systems, this tool will update applications. The monitoring service also covers Linux computers.
With Kaseya VSA, administrators have complete control over their patching processes, including running scripts to exclude patches that may have issues or cause conflicts when installed.
The tool intelligently manages software for Windows, macOS, and the third-party applications that run on them.
A central dashboard allows for central monitoring of the patching process and gives insights into vulnerabilities by gauging the health status of the entire infrastructure; administrators can also easily install, uninstall, update, repair, and modify software from there.
On the other hand, Patch reports can be easily configured to monitor compliance across the network or spot operating systems, third-party applications, and endpoints that need immediate remedial actions.
Kaseya helps avoid any complications during patch deployments with the help of its native and easy-to-use policy profiles for managing patch approval, scheduling, and installation; administrators can use the VSA agent endpoint fabric to optimize the delivery of installation packages further and avoid the need for a centralized File Share or LAN Cache.
Administrators can schedule their network scanning and analysis for after-hours and also use Blackout Windows to completely stop processing during peak hours – both of which ensure a more excellent UX on the endpoints.
They can also override default patching policies by skipping specific patches, KBs, and updates – from being sent out to a single endpoint, a subnet of them, or the network as a whole.
Who is it recommended for?
Although Kaseya VSA can discover and monitor computers running Linux, it can’t patch them. So, if you have Linux computers on site, this tool wouldn’t be the best for you. This package is suitable for managed service providers that look after computers running Windows and macOS.
Pros:
- Automated Software Deployment: Simplifies the process of adding new devices to a network, making it easier to expand and maintain IT infrastructure.
- Effective Health Monitoring: Offers robust monitoring capabilities for tracking the overall health and resource usage of devices.
- Customizable Interface: Features a user-friendly and customizable dashboard, allowing users to tailor the interface to their preferences.
Cons:
- Limited Free Trial Duration: A longer trial period would provide potential users with more time to evaluate the software’s full capabilities.
- Remote Control Delays: Users may experience delays in starting remote sessions, potentially impacting the efficiency of remote support.
- Complex Patch Management: The patch management process can be intricate and may require a learning curve to navigate effectively.
Try Kaseya VSA FREE for 14 days.
10. Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager
Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager is a tool for automatically evaluating, testing, and deploying the operating system and application patches. It also manages patch deployment for third-party applications.
Key Features:
- Wide OS Compatibility: Supports patch management for Windows, Linux, Unix, and macOS, providing extensive coverage across diverse IT environments.
- Active System Patching: Capable of patching systems that are currently in use, minimizing operational disruptions.
- Device Wake and Reboot: Offers the functionality to wake up and reboot devices as part of the patch deployment process.
Why do we recommend it?
Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager has probably the widest capabilities of all the patch managers in this review because it can patch Unix as well as Windows, macOS, and Linux. You can also use this package to patch virtual servers. The tool will update applications running on those computers as well.
Ivanti can patch physical or virtual Windows servers and workstations and Linux, UNIX, and macOS devices; it will also patch the third-party apps running on them – it doesn’t matter how heterogeneous the network is.
It offers remote patching that extends to endpoints located beyond the network, regardless of where they are – they could be behind firewalls, roaming, at remote sites, or even asleep – Ivanti can reach them all.
This reach also extends to virtual machines – it can patch both online and offline VMs and hypervisors.
Ivanti supports application patching of the most vulnerable apps like Adobe Acrobat Flash, Java, and Internet browsers.
A centralized console makes it easy to perform all tasks – managing updates and patching of native and third-party applications and securing and managing endpoints – everything is controlled from a Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM) console.
The tool allows for the packing and pre-caching of multi-application patches – which can also be tested beforehand – for quick deployments with zero downtimes; alternatively, patch rollouts can be done in stages to minimize the impact performance of networks and endpoints.
Administrators can take advantage of insightful, consolidated, and detailed reports on security and vulnerabilities. These reports can serve as proof of compliance or serve as audits for quick actions against critical vulnerabilities.
Finally, administrators can also interact directly with the endpoints and send out commands for Wake on WAN (WoW), device booting or rebooting, exclusions from patching, and scheduling after-hours patching times.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is a good fit for businesses that run a central IT support department for multiple sites because it is a remote patching service. This isn’t a service that would appeal to small businesses because its capabilities would be more than they need. The service integrates with Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Platform Support: Its ability to patch a variety of operating systems, including Unix, makes it exceptionally versatile for managing complex networks.
- Remote Patching Capability: Extends patch management to endpoints beyond the corporate network, ensuring that remote, roaming, and even offline devices stay updated.
- Virtual Machine Patching: Includes the capacity to patch both online and offline virtual machines and hypervisors, enhancing virtual environment security.
- Centralized Management Console: Integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Endpoint Manager for centralized control over updates and endpoint security.
Cons:
- Pricing Transparency: Potential users must contact the company directly to obtain pricing information, which may delay decision-making processes.
- Complexity for Small Businesses: Its extensive capabilities and integration requirements may be more than what small businesses need, making it less suitable for smaller environments.
Try Ivanti for FREE.
Would like to hear your thoughts on them. Perhaps, you have a patch management tool you think needs to be on the list. Either way, please let us know; leave a comment below.
Application patch management FAQs
What is a patch management process?
Patch management is a process that involves updating operating systems and software packages. The process involves checking on the current version number of a software package and then checking with the software producer for the current version. If the two numbers are different, the running software news to be patched and then it will be up to date.
What are three types of patch management?
There are three types of patches:
- Feature updates
- Bug fixes
- Security updates
While the security update is the most important of these, it is advisable to install all patches to get the latest version – patches are free, so why not make sure your software is running the latest version?
What is good patch management?
A good patch management solution automates the whole process, including discovering all software on a system and creating a software inventory, checking for updates and copying over the installers, and running those patches when the target system is not in use.