Cloud Workload Security (CWS) is a new discipline that applies security processes for cloud-based services and software.
The technology behind CWS is complicated and it is based on a new system called Extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF). Think of eBPF as a cross between telemetry systems and containers. We won’t go deep into the methodology of eBPF because, in this guide, we are focusing on cloud workflow security.
Here is our list of the best cloud workload security platforms:
- Datadog Cloud Workload Security This cloud-based platform implements cloud workload protection as an advancement on the parallel distributed tracing system offered by the provider. This service also includes file integrity monitoring.
- Zscaler Workload Communications This platform operates as a secure virtual network across the internet and includes the protection of data in motion between cloud workloads.
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud This is well-known and widely trusted Windows Defender ported to the Azure platform and aimed at protecting cloud-based systems.
- Illumio Core This platform implements “micro-segmentation,” which is a form of cloud containerization that enables the system to guard data exchanges between modules on the cloud.
- Broadcom Carbon Black Workload This is the cloud workload protection module of the VMware Carbon Black brand, which also offers endpoint protection and container security.
- Trend Micro Deep Security This service operates as a cloud vulnerability manager and it includes a virtual patching service to close off security weaknesses in cloud workloads.
This type of service starts with performance tracing because you can’t protect a system unless you know its components as well as its boundaries. As such, CWS is part of the emerging discipline of “observability,” which looks for alternative methods to track activity within cloud-based systems, such as microservices.
Once the CWS system has identified all components of a service, it examines the activities of those modules to spot anomalous behavior that could indicate malicious takeover. Several techniques can be used to perform this detection – both currently implemented by next-gen AV and SIEM systems.
Observability can extend its activities from tracking the performance of microservices to recording those observations and establishing a baseline of normal activity. If that behavior suddenly changes, you might have a security issue. The second method is the use of a signature database. This is almost identical to the Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) that SIEM systems use.
The fact that CWS is a sort of “telemetry plus” package means that the best providers in this field are those cloud platforms that have already perfected a distributed tracing service. Many of the components in Web applications are run by plain-text programming languages that are not compiled. Therefore, the distributed tracing system can acquire the code as it executes and scan it through code profiling.
What is cloud workload security?
A “cloud workload” is a service, an application, a platform, a framework, a function library, or a piece of software that you install on a cloud virtual server. Any software running on a cloud platform is a workload.
As cloud services become more prominent, the need to find new ways to monitor and secure those processes become more urgent.
Cloud workload security is also called a Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP). Just as you need to protect your on-site resources from malware, intrusion, and data loss, you need to secure those resources that you use in cloud computing. Although Amazon and Azure offer secure platforms, there is no way of knowing whether a malicious actor is currently devising a way to hijack cloud-based database systems or Web servers.
Why do you need cloud workload security?
Many applications are now built with the support of third-party development frameworks, APIs, and function libraries. These services provide tested and reliable functions that cut down development time. However, those APIs, functions, and framework services are all calls to little bits of programs that are running elsewhere on servers that you don’t own and don’t have access to. Many of them rely on the support of other services. One API can front many layers of microservices that run on different servers all over the world.
A little tweak in the unknown process could extract all of your clients’ personally identifiable information as it is processed. This would be a severe security breach. A well-meaning provider might implement insufficient security in its service and if hackers spot that weakness, all of your data could be stolen.
You don’t need to be engaged in the development of applications to be vulnerable to cloud workload security vulnerabilities. Many business software packages have been converted into Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings. In this scenario, you get cloud processors and storage space, but you lose control over security.
CWS platforms restore your control over the cloud-based software that your business uses.
The best cloud workload security platforms
The way CWS platforms operate is complicated. However, you shouldn’t need to spend time working out what the security system does, you need to be able to use it in a similar way to the methods you currently use with a SIEM package for your on-premises assets.
What should you look for in a cloud workload security platform?
We examined the market for CWS platforms and analyzed the providers based on the following criteria:
- A dashboard that interprets cloud asset discoveries clearly
- A system that can map application dependencies
- Tools that include security indicators and automate vulnerability identification
- An alerting mechanism that draws attention to cloud workload security weaknesses
- An automated service that enables rapid response to security problems
- A free trial or a demo for a no-cost assessment opportunity
- Value for money, represented by a competent tool at a reasonable price
With these criteria in mind, we identified the most impressive new CWS platforms that are currently coming onto the market.
1. Datadog Cloud Workload Security
Datadog Cloud Workload Security uses eBPF to examine the kernels of cloud platforms and containers. The system also examines files and data exchanges for attacks and it can provide full traces on data access activities.
Key Features:
- Examines all Cloud Processes: Doesn’t monitor on-premises systems
- Uses eBPF to Examine Kernels: Digs into cloud platforms and containers
- Includes File Integrity Monitoring: Adds extra access controls
- Security Alerts: Forward them as notifications by Slack, PagerDuty, Jira, or email
- Combines Strategies: Looks for indicators of compromise and performs anomaly detection
Why do we recommend it?
Datadog Cloud Workload Security provides deep examination techniques to look into the operating systems of your virtual servers on the cloud and also containers. These can be running Windows or Linux. The package provides both a threat intelligence feed and anomaly detection. Alerts can be channeled into collaboration services or project management tools.
Datadog is very good at presenting data in a digestible manner in its dashboard, so you don’t get bogged down with technicalities when using the system. You just need to look at the live reports of activity on the screen that summarizes activity and highlights threats and possible security breaches.
The Datadog detection strategy combines a vulnerability scanning style of detection with an anomaly detection system. The tool will scan through systems and their contributing modules, capture their code and scan it. The system includes an alerting function so you don’t have to sit and watch the dashboard to catch security issues.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is designed for companies that use cloud services rather than those that create and deliver cloud systems to other businesses. The service is delivered from the cloud and maintains constant vigilance without human involvement. The system is suitable for use as a standalone package but it is also an interesting prospect in conjunction with other Datadog modules.
Pros:
- Cutting Edge Technology: This is a recently developed service
- Preventative Scanning as a Companion Module: Look at the Datadog Cloud Security Management package
- Shipped with Out-of-the-Box Threat Detection Rules: Custom detection rules are possible
- Scans Containers and Cloud Platforms: Looks into their Windows and Linux operating systems
- Hosted on the Cloud: Web-based console
Cons:
- Not Suitable for all Cloud Services: Doesn’t monitor AWS Fargate
Datadog is easy to subscribe to and its Cloud Workload Security package is just one of the modules that this platform offers. You can combine this tool with log analysis, a SIEM, and network monitoring to get full control over your entire IT system. Datadog Cloud Workload Security is available for a 14-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Datadog Cloud Workload Security is our top pick for a cloud workload security platform because it offers pre-written threat detection rules and also enables administrators to create their own detection rules. The package gets right down into the heart of the operating systems that are installed on virtual servers and containers to look for intrusion and unauthorized software attacks. This service is part of the Datadog Cloud Security Management division of services. The other option in that stable is a cloud security posture management (CSPM) service. There are two levels available for the CSPM but only one plan level for the Cloud Workload Security module.
Download: Download a 14-Day Free Trial
Official Site: https://www.datadoghq.com/product/security-platform/cloud-workload-security/
OS: Cloud-Based
2. Zscaler Workload Communications
Zscaler Workload Communications provides a Zero Trust Access system that relies on protecting connections to applications and blocking all direct access. The Zscaler service operates in the cloud and forms the endpoint of a series of connections out to different resources. The platform also creates connections to each user. Access by a user travels down the VPN to the Zscaler server where authentication is applied and then access is granted to the VPN that leads to the requested application.
Key Features:
- App-to-App Data Transmission Protection: Focuses on protecting connections
- Virtual Networks: Constructed with VPNs
- Implements Micro-Segmentation: Zero trust access hub
- Data Protection: Operates on AWS, Azure, and GCP
Why do we recommend it?
Zscaler Workload Communications creates a virtual network across the internet to connect functions and elements that are hosted on cloud platforms. This system is an evolution of VPNs. It provides a hub that will form an endpoint for VPNs to each resource, effectively creating a virtual switch.
The Zscaler approach simplifies workload protection because all traffic travels through the Zscaler cloud server. The tool can also establish secure links between applications that are hosted on different platforms. The tool is able to link to AWS, Azure, and GCP.
By forming a series of protected connections that are only open to authorized users, the Zscaler system automatically protects data and workloads without needing to scan them or classify them.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is a little different from the others on this list because it focuses on protection rather than detection. The service is one of a clutch of new VPN-based virtual networks that implement application protection through a Zero Trust Access strategy. The strategy involves adding access rights into the VPN setup, thus, users hub through the Zscaler platform to get access to applications.
Pros:
- Innovative Protection: Effectively fences each application
- Lightweight Security Methods: Security is built into transmission management
- Protection for Data Exchanges: Data moves within a secure tunnel
- Access Controls: Access rights are built into the VPN
Cons:
- Difficult to Conceptualize: Blocks all access except for by authorized users
The Zsaler system can be applied to all processes that are deployed by hybrid networks, this system implements application security across sites and platforms and it doesn’t only apply to cloud workloads. You can ask for a demo to assess the Zscaler strategy.
3. Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a cloud-based version of the Windows Defender system that can be found on any PC as part of the Windows operating system. The cloud system is a service on the Azure platform. This package combines cloud security posture management and cloud workload security to prevent security weaknesses and then watch software-based or manual threats.
Key Features:
- Hosted on Azure: Protects systems hosted on Azure, AWS, and GCP
- Vulnerability Assessments: Preventative measures
- Live Protection: Cloud workload security
Why do we recommend it?
Microsoft Defender for Cloud providers both preventative and live protection for cloud workloads. This system scans your cloud-based system and looks for vulnerabilities. It will recommend how you can tighten the configurations of your cloud systems. You then target ongoing activity scanning that looks for malicious behavior.
Although Microsoft Defender for Cloud is hosted on Azure, it doesn’t just protect assets on that platform. It can also provide security for workloads running on AWS and Google Cloud Platform. The service even covers on-site systems as well, so this is a complete security package for hybrid and multi-site networks. It will protect virtual systems and containers, plus applications, such as databases, mail systems, and web servers.
Who is it recommended for?
This system will appeal to companies that already use services on the Azure platform. When there is a selection to make for any product, buyers will always lean towards the brands with which they are familiar. The package is able to apply data privacy standards, although, at present, it is only able to implement PCI DSS, CIS, and ISO 27001.
Pros:
- Security Monitoring: Watches processes on AWS, GCP, and Azure
- Infrastructure-as-Code Scanning: Also container protection
- Compliance Management: PCI DSS, CIS, and ISO 27001
Cons:
- Limited List of Data Protection Standards: Doesn’t implement GDPR or HIPAA
Microsoft offers a free tier for this and 25 other services on its Azure platform. This gives you a service value of $200 for the first month. Usage above that level is charged at a pay-as-you-go rate.
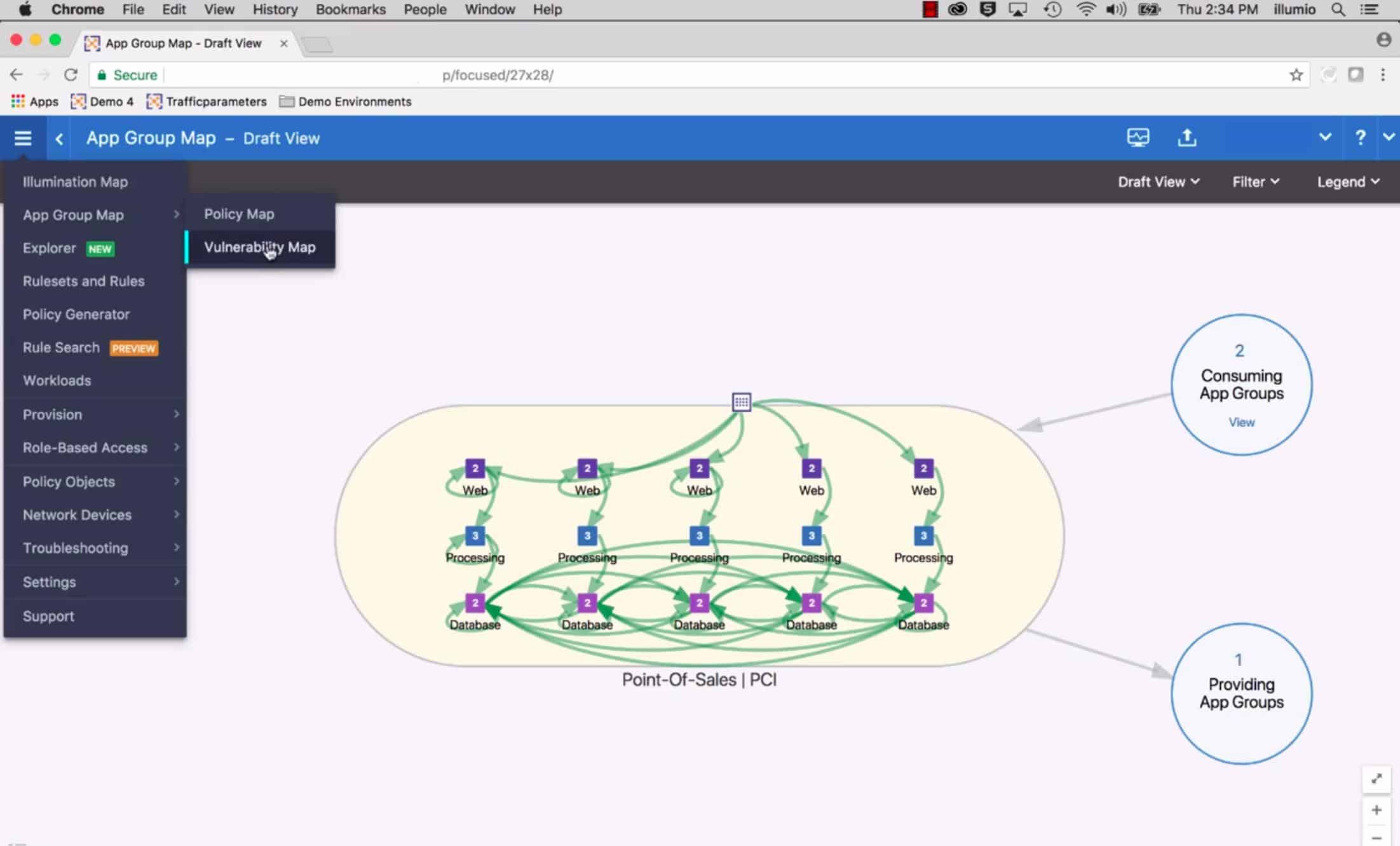
4. Illumio Core
Illumio Core uses a micro-segmentation strategy and is application-focused. These are buzzwords that boil down to a wrapper around a bundle of services that contribute to a single user-facing application. This is the same strategy that Zscaler uses.
Key Features:
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Implements microsegmentation
- Performance Monitoring: Examines traffic flows
- Application Protection: Creates a wrapper around a collection of contributing functions
Why do we recommend it?
Illumio Core is a similar system to the Zscaler Workload Communications service. The tool blocks access to applications unless it is made through the system’s VPNs. The VPNs connect authorized users to applications and also connect applications to each other. The result of this strategy is that all traffic flows through the Illumio server, where it can be inspected and optionally blocked.
Like Zscaler, Illumio grants access to applications rather than to platforms or equipment, such as servers. This is a difficult concept to understand but it is a meaningful solution to the complexity of dealing with components that run on different servers. The containerization of several services into a virtual application blocks malware attempts to get into a running system – if a program isn’t on the list of participating modules, it isn’t getting in. Similarly, the outer shell encrypts data exchanges between units, so intruders and snoopers are confounded.
The Illumio method cloaks internal components to the outside world but not to its monitoring service. As part of its micro-segmentation work, the Illumio Core system researches all contributing services and creates an application dependency map. Thus, while creating a wrapper to protect the group, it still tracks the activity of each unit individually.
Who is it recommended for?
This package goes a little further down in scale than the Zscaler system because it looks at microservices. That is, it will protect each individual function that contributes to the operations of an application. The service has a discovery phase that identifies all connections between application elements and draws up an application dependency map.
Pros:
- Protects Microservices that Contribute to a Single Application: Protects communications between them
- Application Dependency Map: Identifies the links between applications, functions, and services
- Monitoring of Components and Groups of Services: Also controls access
Cons:
- Could Slow Performance: A fragmented application would require many secure connections and access rights checks
If you are the type of person that needs to understand all of the technology you use, you might be put off using this service because it requires a complete shift in comprehension to the way you are used to thinking about how your network runs and how it should be protected. You can get a look at the Illumio Core system by attending a Virtual Lab session.
5. Broadcom Carbon Black Workload
Broadcom Carbon Black Workload is a cloud workload protection platform that you can run on your AWS or Azure account as a service from the marketplace. The package includes a sensor that you can deploy on other cloud platforms to monitor and protect the workloads that you run on them. The system will perform a discovery service once those sensors are in place. The core of the monitoring system is a workload inventory, which is the result of the discovery service.
Key Features:
- Workload Discovery: Scans cloud platforms
- CIS Benchmarking: Assesses discovered workloads for security vulnerabilities
- Next-Generation Antivirus: Applied to cloud workloads
Why do we recommend it?
Broadcom Carbon Black Workload is an extension of the Carbon Black brand, which VMware acquired in 2019, then Broadcom in 2022. There is also a container security module in the Carbon Black platform.
After discovering and documenting all workloads, the system will commence scanning for threats. The package also includes a benchmarking service, which is, effectively, a cloud security posture management (CSPM). This feature doesn’t run automatically – you launch the assessment manually. The benchmarking also acts as a system audit and provides the necessary inputs for compliance reporting.
Carrying over the Carbon Black Endpoint processes, this service will implement automated responses to the detected threats. These responses are not automatic but they are recommended because they will continue to operate around the clock, even when your technicians are out of the office.
Who is it recommended for?
Broadcom is a very trusted system producer and many businesses already use their virtualization products. The Carbon Black brand also has a long history, protecting endpoints for a decade. The application of the Carbon Black system for cloud workloads is a new development, but it is founded on years of experience in blocking malware. So, this service is recommended for any type of business.
Pros:
- Reliable Brand: From a respected provider
- Cloud-Based system: Install it on your own AWS or Azure account
- Compliance Reporting: Only available for HIPAA
Cons:
- Container Security is a Separate Module: Would be nice to see the two units merged
6. Trend Micro Deep Security
Trend Micro Deep Security is a combined vulnerability manager, anti-malware, and intrusion detection system for on-site, cloud, and virtual resources. This system includes an autodiscovery mechanism that will identify any new software installed on a monitored platform and then search through to discover all of its supporting services and create an application dependency map.
Key Features:
- Protects Hybrid Systems: Physical, virtual, and cloud platforms
- Identifies System Vulnerabilities: Preventative security scanning
- Blocks Malware: Includes a next-generation antivirus
Why do we recommend it?
Trend Micro Deep Security is a comprehensive package of cybersecurity systems. These include security evaluations and live monitoring. The system is able to protect applications running anywhere – that includes cloud workloads. It will also protect on-premises systems. Other features include a discovery service for all processes and a threat intelligence feed.
This service will interface with the native reporting tools provided by AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Azure, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Hyper-V, Citrix XEN, VMWare, Docker, and Kubernetes to track activity and then establish a baseline of normal behavior. It then looks for deviations from that pattern that would indicate the presence of malware, an insider threat, or an intruder.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a very comprehensive package because it provides a vulnerability scanner and an antivirus service for on-premises assets plus cloud security posture management (CSPM) and a cloud workload protection platform (CWPP) for cloud-based systems. The service provides compliance management for GDPR, PCI DSS, NIST 800-53, FedRamp, and HIPAA.
Pros:
- Includes Application Dependency Mapping: Can cross platforms
- Uses Anomaly Detection: Also includes a threat intelligence feed
- Self-Hosted Option: Run it as a virtual appliance
Cons:
- Doesn’t Include Code Profiling: Doesn’t provide distributed tracing
Trend Micro Deep Security is a SaaS platform. However, you can also request the software to run as a virtual appliance on-site or on your private cloud. The service can also be used for application security testing on systems under development. You can assess this system with a 30-day free trial.