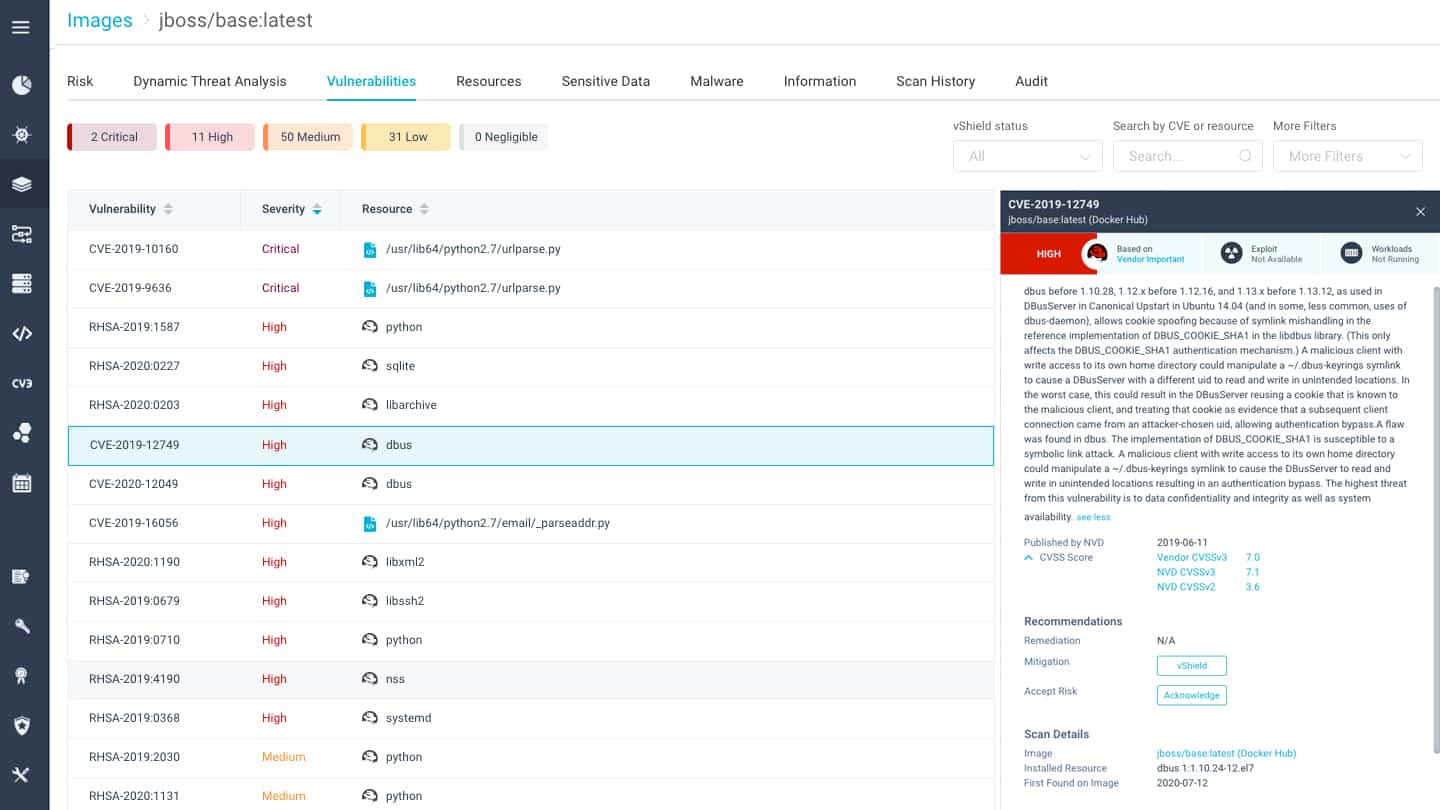
Containers offer a way of ensuring software solutions – enterprise or otherwise – run smoothly regardless of the environment they are running.
For example, thus, they have practical applications when these solutions need to be moved from a development environment into a production one or from a physical one into the cloud.
Furthermore, enforcing container security prevents these solutions from being compromised during these migration stages and during their time of residence on temporary hosts.
Here is our list of the best container security tools:
- Site24x7 EDITOR’S CHOICE This cloud-based platform ensures container security by monitoring critical metrics like CPU, memory, and disk usage. It identifies anomalies, bottlenecks, and vulnerabilities, providing real-time alerts for rapid issue resolution. Access a 30-day free trial.
- Datadog Cloud SIEM This security package operates as a vulnerability scanner as well as a SIEM and it provides fast solutions to security breaches. Track exploits and unusual activity for containers hosted on your site or in the cloud and get alerts channeled into your ticketing system.
- Anchore Versatile and open-source container security tool that integrates well; it is fast and efficient and offers CLI interfaces for optimal access. In addition, it performs deep inspections on the entire stack and combines with an array of platforms.
- Sophos Cloud Native Security A cloud workload security package that covers the major cloud platforms and their services, including containers. Use this cloud service to ensure protection, governance, and compliance.
- Bitdefender GravityZone AI-powered security tool for cloud Linux instances. And yet, it is platform agnostic making it a versatile tool capable of protecting hybrid environments. In addition, it offers forensic auditing for easier troubleshooting and quick issue resolution.
- Sysdig Secure A straight-to-the-point, and open source, security tool that performs scanning in real-time. Although it is already efficient straight out of the box, it is also highly customizable to meet unique requirements.
- RedHat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes A DevSecOps tool that will tracks the supporting services beneath your Kubernetes clusters as well as within the Kubernetes environment. Installs on Docker as part of the OpenShift environment.
- Aqua Security A highly scalable tool that keeps itself updated on the latest threats and vulnerabilities. It can be used to protect both Linux and Windows containers, regardless of their deployment platforms. In addition, it has many advanced threat prevention methods that help keep containers safe.
What are cloud containers?
Before we look at the container security tools, let’s look at what a container is.
Containers can be seen as a type of virtual operating system. They can be used to run everything from small microservices and software processes to larger enterprise-level applications. They are self-contained environments that hold all the necessary dependencies – including libraries, executables, binary codes, and any other necessary configuration files – required to run these applications properly.
“Containerization” helps create a self-sufficient and “contained” environment for the solutions to run in.
Some of the major cloud service providers offer containers as a service (CaaS), with the most popular of them being Amazon (AWS), IBM (Cloud Kubernetes Service), Microsoft (AKS), and, of course… Google (GKE).
The difference between containers and virtual machines (VMs)
A point that might need to be clarified here is the difference between containers and virtual machines (VMs).
Well, first, we can agree that both containers and VMs help improve application portability, empower DevOps, and enable IT services.
But, VMs solve infrastructure problems by leveraging servers, while containers solve application problems by leveraging software assets.
Also, VMs are created by including a guest operating system while the containers adopt their hosting server’s operating system and include only their applications’ required dependencies.
This means VMs are usually bulkier and resource-intensive, while containers are more streamlined and focused on catering to specific applications.
What is container security?
Container security is the process of implementing a security and compliance feature on all the stages of a container’s lifecycle – from creation to maintenance and its eventual destruction.
The process involves scanning container images in the continuous integration and delivery or deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and any existing registries. Once they are up and running, containers also need to be secured along with the host they sit on.
Other features included in container security involve incident responses, with forensic data that shows all activity within the containers, and compliance controls to ensure all necessary audit requirements are met.
What is a container security tool?
A container security tool allows for the management, protection, and security of containerized files, applications, systems, and the networks that connect them.
Administrators use these tools to set automated policies that prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited, unauthorized access, role or privilege abuse, and ensure regulatory compliance to various standards.
But, the bottom line is: container security tools are software solutions designed to protect containers and images.
What are the features of good container security tools?
Our methodology for selecting a good container security tool
Some features that helped in determining which container security tools belong on our list include:
- The ability to monitor access roles and permissions.
- A centralized policy management capability to enforce rules.
- Ability to scan whole container stacks as well as image vulnerability detection.
- Allowing for a testing environment to capture runtime malware and observe results of policies that are applied.
- Reporting, auditing, and container metadata storage for analysis and proof of compliance.
- Ability to detect runtime malware like unpatched vulnerabilities, insecure configurations, leaked sensitive data, weak credentials, and suspicious activity, including insider threats.
- Price – affordability and the return on investment (ROI) also help decide what solution is worth investing in.
The best container security tools
Here is our list of the best container security tools:
1. Site24x7 (FREE TRIAL)
Site24x7 is a cloud-hosted system monitoring platform. Its packages include full stack monitoring services from networks to servers and applications. This combination makes the package the ideal choice for watching over multi-technology systems, such as containers. The platform has specific plug-ins for tracking Docker and Kubernetes instances.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Performance Metrics: Monitors CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
- Automatic Discovery: Detects and starts monitoring new containers automatically.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies performance anomalies and bottlenecks.
- Customizable Dashboards: Offers personalized dashboards for monitoring container metrics.
- Resource Utilization: Ensures efficient utilization of container resources.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Site24x7 as a container monitoring system because it provides real-time visibility into container performance, resource usage, and health. Its integration with Docker and Kubernetes, customizable alerts, and detailed analytics enable proactive issue resolution, ensuring optimal containerized application performance and scalability. Simultaneous monitoring of networks, servers, and applications will catch all potential system problems.
The Site24x7 plugin library offers a wide range of integrations, including dedicated units for Docker and Kubernetes. These plugins enable seamless monitoring of containerized applications, providing real-time insights into performance, resource utilization, and health. With these integrations, users can efficiently manage and optimize their containerized environments.
By selecting an integration, the user expands the core dashboard of Site24x7, eventually customizing the system to track just the specific technologies that are in use. This framework means that buyers don’t have to deal with a console that is cluttered with screens that cover systems that they don’t have.
Each section of the Site24x7 comes with off-the-shelf performance expectation thresholds. As each statistic comes in, such as CPU utilization readings, the tool assesses the number, comparing it to the capacity threshold. If the threshold is exceeded, the system raises an alert. Performance thresholds are set at levels below 100 percent utilization so that technicians will have time to head off problems before resource shortages start to impact performance.
Site24x7 is also able to monitor cloud platforms and their service. This extends to storage accounts as well as compute and serverless hosting. This gives you the opportunity to keep an eye on the supporting resources for your containers, no matter where they are. As well as monitoring the performance of the containers in your system, you can simultaneously track the activity of the applications within them.
Site24x7 is a cloud-based system and it can monitor the activity of systems on any other platform – including your own servers or cloud platforms. The service will monitor many services, including those that aren’t related to your containers. The plans also include log management services, which provides a secondary opportunity for system performance and security monitoring. Logs can be forwarded to a SIEM tool for further container security monitoring.
Who is it recommended for?
Site24x7 is recommended for IT teams, DevOps professionals, and businesses of all sizes looking to monitor and optimize their infrastructure, applications, and cloud services. It is particularly valuable for organizations managing complex, hybrid, or multi-cloud environments, as well as those needing comprehensive performance monitoring and proactive issue resolution.
Pros:
- Quick Issue Resolution: Provides real-time alerts for proactive problem-solving.
- Health and Reliability: Maintains the health and reliability of containerized applications.
- Log Management: Collects, indexes, and analyzes logs from various sources to help with troubleshooting and compliance.
- Network Monitoring: Provides insights into the performance and health of network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls.
- Network Path Analysis: Offers hop-by-hop analysis of network paths to identify bottlenecks.
Cons:
- No on-premises version: Site24x7 is only available as a cloud-hosted SaaS package.
Site24x7 is delivered in packages – you can’t just sign up for container monitoring because the plans all include many other system monitoring and management services. The best way to assess the system is to ask for a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Site24x7 is our top pick for a container monitoring tool because it provides comprehensive, real-time visibility into the performance and health of containerized environments. With integration packages for Docker and Kubernetes, Site24x7 enables teams to efficiently monitor container metrics such as CPU, memory, and disk utilization, as well as network traffic, which are critical for maintaining optimal performance in a dynamic containerized environment. The platform’s customizable user-friendly interface makes it easy for both developers and operations teams to track container health, identify bottlenecks, and diagnose issues across multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments. Site24x7’s granular monitoring capabilities allow you to monitor containerized applications in real time, detect anomalies, and receive proactive alerts before issues impact end users or cause downtime. This feature is crucial for ensuring high availability and reliability in containerized applications. Site24x7 also provides detailed reporting and analytics, enabling teams to identify trends and make data-driven decisions to optimize container workloads and resource utilization. Additionally, it offers automatic scaling and management insights, helping teams optimize container orchestration and resource allocation across environments. What sets Site24x7 apart is its ability to monitor not only container performance but also the underlying infrastructure, providing end-to-end visibility across the entire stack. Whether you’re managing microservices in Kubernetes or Docker containers, Site24x7 helps ensure smooth, secure operations, making it a top choice for container monitoring and security.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.site24x7.com/signup
OS: Cloud based
2. Datadog Cloud SIEM
Datadog is a leading provider of SaaS-based data analytics services. The company makes some of the most popular servers and network monitoring and administration tools. They also make Container Security – a container tool for detecting and investigating threats in real-time.
Key Features:
- A SaaS Package: Priced by the number of events that get analyzed
- Combines Event Data Sources: Pools activity data from many sources, including containers
- Looks for Well-Known Attack Strategies: Benefits from a database of attack methods
- Alerts for Unusual Activity: Identifies sudden changes in patterns of activity
- Threat Hunting Automation: Scans large amounts of data that would be impossible to search through manually
Why do we recommend it?
Datadog Cloud SIEM is able to monitor live activity on cloud infrastructure and on sites through a series of plug-ins, called integrations, which channel logs to the tool from different technologies. This list of channels includes methods to send data from containers and Kubernetes. This tool is hosted in the cloud.
The Datadog service monitors the whole stack: applications, containers, hosts, and infrastructure. It will monitor systems no matter where they are hosted, so you can centralize the security protection for multiple sites, remote devices, and cloud services.
This isn’t just a live threat monitor because the package includes a vulnerability scanner that will spot misconfigurations in applications, networks, and infrastructure; it even detects threats from workload security events in seconds. Both vulnerability scanning and threat detection occur simultaneously and continuously.
The Container Security tool lets you set up playbooks, deciding on which warning levels should trigger automated responses, and which should just prompt the creation of a notification to staff. The service integrates with communication and collaboration platforms like Slack, Zendesk, Jira, and PagerDuty, making it easier to keep everyone in the loop via shared actionable alerts or collaborate while tackling identified threats.
This package collects log messages from all of the platforms that it monitors, making that data available for automated threat hunting and also manual activity analysis. The system is also useful for compliance auditing and reporting.
Datadog Cloud SIEM can identify threats to containers whether they are hosted on-premises or in the cloud. This system is tuned to many different container brands, including Docker, Azure Container Services, and Amazon ECS. You can use this system for development testing or operations monitoring because it provides vulnerability assessments as well as live threat detection. The service includes log consolidation, which provides source material for the SIEM.
Who is it recommended for?
The Datadog website stresses the suitability of the Cloud SIEM for monitoring cloud-based systems. However, it can easily monitor containers that are hosted on your own servers as well. If you want deeper protection for your cloud-hosted containers, you can add on the Cloud Security Posture Management unit.
Pros:
- Part of a Platform of System Monitoring Tools: Combine multiple modules
- Centralizes Threat Hunting: Unifies security for all assets
- Multi-Platform Security: Examine events on premises, on the cloud, and from physical and virtual systems
- DevOps Tool: Run tests on new packages before release and catch results in the SIEM
- Collect Data from Many Container Types: Includes cloud-based variants and Kubernetes
Cons:
- You Have to Know Where All of Your Containers are First: The package doesn’t include a discovery service
Datadog Cloud SIEM includes access to more than 500 vendor-backed integrations, over 350 pre-set detection rules, and other compliance rules to tackle threats misconfigurations, and run-time. Implement container security by assessing Datadog Cloud SIEM with a 14-day free trial.
3. Anchore
With the Anchore Engine, we get an open-source tool for monitoring the security of container images. Its Enterprise Edition is a complete container security workflow solution that would make any professional administration team happy.
And, as efficient as it is, there is no sacrifice to be made when it comes to speed as it is efficient and requires minimum resources to perform. All administrators need to do is submit a Docker image to Anchore; it will analyze and return details of existing vulnerabilities – if any – in an instant.
Key Features:
- Secures Applications: Assess the security of applications, including those delivered by containers
- Software Composition Analysis: Records all of the elements used in an application
- Root Cause Analysis: Uses composition data to track performance or security issues
- Compliance Reporting: Logs all events including successfully repelled attacks
Why do we recommend it?
Anchore is a software inventory composition tracker, which records the structure of your Web applications and cloud systems. This is called an SBOM or “software bill of materials.” The tool discovers and records software dependencies and then scans each unit for vulnerabilities. The tool is able to check on containers as part of this service.
The Anchore Engine evaluates Docker images using custom policies, which provide network security control and can be used with Zero Trust Access (ZTA). The system has a library of out-of-the-box security policies for you to apply but you can also create your own. Policies can be implemented in whitelist or blacklist formats.
Anchore gets inside the container with a scanning method that is similar to deep packet inspection. It looks at the container image, the OS within, and the software packaged inside the container. The hit list for the scan includes vulnerabilities, exposed configuration files, image secrets, and unprotected or open ports
The Anchore system integrates well with a wide selection of development tools and platforms – a few examples include Slack, Jira, Oracle, and Microsoft Teams. This enables the service to be used as a tester in a CI/CD pipeline through its availability as a plug-in for Jenkins.
Who is it recommended for?
Anchore can be used for DevOps environments because you can use it to check on components that will plug into your new application before they are integrated into the development and during coding. This includes the configurations of container image generation and how it interacts with the software that is to be delivered.
Pros:
- Compliance Management: Includes container security in the protection of sensitive data
- Activity Notifications: Sends alerts through Teams or Slack
- Security Tracking: Notes attack vectors
- Historical Analysis: Uses attack data to identify security weaknesses
Cons:
- Not Specifically a Container Security Tool: This package focuses on sensitive data protection
Anchore is a versatile tool with a handful of setup configurations: it can run as a standalone solution or on orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, Rancher (Kubernetes-as-a-Service), Amazon ECS, or Docker swarms. Get to know Anchore by accessing a demo.
4. Sophos Cloud Native Security
Sophos Cloud Native Security offers workload protection for systems that are hosted on cloud platforms, Windows and Linux. Container security tracking doesn’t cover Windows, but it does watch over Linux-based systems on-premises and in the Cloud. The system installs agents on the servers that support your containers and then centralizes reporting, including live feedback on container activity.
Key Features:
- A Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform: Also known as a CNAPP
- Includes Security Policies for Containers: Assesses the vulnerabilities of containers and Kubernetes plans
- Orchestrates Third-Party Tools: Communicates with SIEMs and other security packages
Why do we recommend it?
Sophos Cloud Native Security provides both preventative scanning and live security monitoring for cloud-based systems, including containers. It can also verify the security of containers that are hosted on your on-premises servers if they are running Linux. You need to install an agent on each platform that you want to monitor.
The Sophos tool spots attacker behavior, identifying initial entry through software or operating system features and subsequent system changes, lateral movement, data attacks, and defensive actions, such as persistence measures. These traces operate across platforms and include container activity.
The discoveries of the cloud detection system are sent into the Sophos XDR service. This correlates cloud platform and container data with information gathered by the XDR from applications and devices, such as switches, firewalls, and access rights managers.
Actions that the system can perform to block the suspicious activities that it spots include blocking the permissions of the container, such as its ability to write out to the operating system.
The Cloud Native Security Service assessment of each container provides an audit trail for security breaches and actions taken to remediate them. This provides an audit trail for compliance reporting.
Who is it recommended for?
The live security tracking function of this tool requires a threat detection module because the Cloud Native Security service just generates log messages to be streamed into a SIEM or XDR. So, the most likely buyers of this tool are the users of the Sohpos XDR package.
Pros:
- Controls Access to Applications: Fences applications with containers
- Integrated IAM: Identity and access management
- Color-Coded Risk Assessments: Orders weaknesses by severity
Cons:
- No Protection for On-Premises Systems: Won’t watch containers that are hosted on your own servers
The Sophos Cloud Native Security system is a cloud-based system that installs an agent on each of the platforms that you use, both on-premises and on the cloud. You can assess the Sophos system with a 30-day free trial.
5. Bitdefender GravityZone
Bitdefender GravityZone is a container security tool that also protects cloud workloads in the Linux environment. It is an AI-powered threat prevention and anti-exploitation solution that is aware of attributes like user, device, and location to provide optimal endpoint threat detection and response (ETDR).
Key Features:
- Focused on Containers Hosted on Linux: Looks for attacks
- Operates on Hybrid Environments: Scans containers that are hosted on the cloud or on your own servers
- Automated Responses: Shuts down attacks by disconnecting connections
Why do we recommend it?
Bitdefender GravityZone Security for Containers is a good choice for businesses that operate a hybrid environment across on-premises Linux servers and cloud platforms. It tracks containers as part of a general system defense strategy that includes data backup and antimalware scanning. Protection extends to host memory access scrutiny.
The Bitdefender system is a cross-platform tool and can protect containers running over any operating system or cloud platform. It merges container metrics with the information it gathers on operating system and application activity to spot the lateral movement and cross-infection of human and automated malicious activity.
As it simultaneously tracks supporting systems it can spot and block attempts to break out of containers. The system logs all intrusion events and the actions performed to root them out. This provides an audit trail for compliance reporting.
Who is it recommended for?
The Bitdefender package is similar to the Sophos system because it provides security monitoring for containers hosted on your own Linux servers as well as on cloud platforms. However, it won’t cover containers built on your Windows or macOS computers. This tool is suitable for tracking live container operations.
Pros:
- Alerts for Attacks: Notifies technicians of new attacks
- Scans the Linux Kernel: Blocks attacks from coming up through the operating system
- Uses Container Telemetry: Picks up activity reports emanated by containers
Cons:
- Doesn’t Operate on Windows: Won’t secure containers that are hosted on Windows
The core of Bitdefender GravityZone runs as a virtual appliance. The container security agent installs on Linux. You can try out the BitDefender GravityZone with a one-month free trial.
6. Sysdig Secure
Sysdig Secure is another security tool that performs at all stages of a container’s lifecycle. It offers security and compliance features that can stop known vulnerabilities at their earliest before they can cause substantial damage. Thanks to the tool’s capabilities of integrating scanning into the CI/CD pipelines and registries.
Key Features:
- A Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform: A CNAPP
- Secures Cloud-Based Containers: The containers can be hosted on any cloud platform
- Provides Container Monitoring: Also watches Kubernetes activity
Why do we recommend it?
Sysdig Secure provides container security monitoring as part of a CNAPP package. This platform will examine all of your cloud services, providing preventative scanning to identify misconfiguration as well as live attack monitoring. The tool can also be used for continuous testing in a CI/CD pipeline through repository and bug tracker integrations.
Sysdig Secure is a vulnerability scanner for cloud workloads that can operate through the lifecycle of your containers. The scanner has specific exploits that it looks for when approaching containers. The system will scan software and platforms as well. Issues that the tool looks at include configurations and software versions.
Vulnerabilities are flagged and raise alerts, which go to technicians as notifications for manual resolution. Data collection occurs as a live performance tracking function and also through log collection.
Administrators can create their own alert rules and even set up automated responses. Sysdig has a community forum that includes a package exchange where you can pick up alert and response automation rules developed and tested by others.
Sysdig Secure creates an audit trail for compliance reporting and detection rules can be tuned to data protection standards requirements.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is a good fit for use by development teams and also for operations. It scans container configurations and will also check the software that the container will deliver as it is being developed. The service will track Kubernetes controllers as well as individual containers and clusters.
Pros:
- Free Risk Assessor for Containers: This is called Falco
- Compliance Management: Auditing and reporting
- Tracks Application Access: Uses anomaly detection for threats
Cons:
- Cloud Only: Doesn’t monitor containers hosted on your servers
Sysdig Secure is a SaaS package. You can extend the system with Falco, which is an open-source container risk assessment package that installs on Linux. You can access Falco for free and Get Sysdig Secure on a 30-day free trial.
7. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes
RedHat Advanced Cluster Security (ACS) for Kubernetes is part of the RedHat OpenShift environment – you have to be running OpenShift to use ACS. This tool will monitor your Kubernetes clusters, no matter where they are – on premises or in the cloud.
Key Features:
- Cluster Protection: Operates in Kubernetes
- Cloud-Based Systems: Protects containers on AWS, Azure, GCP, and OpenShift
- Included with Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus: Built into the platform
Why do we recommend it?
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes focuses on the opportunities that hackers might have to interfere with the coordination of data and command exchanges between containers in a cluster. This is part of the Red Hat OpenShift platform but it can also scan containers hosted on Amazon AKS, Azure EKS, and GCP GKE.
As well as looking for a database of well-known Kubernetes-related hacker tricks, this tool deploys AI to baseline performance and spot anomalies. It can track the activities of resources that support Kubernetes clusters as well.
The system can be set to just detect weaknesses and generate notifications, which is probably what you want if you set it up for automated testing in a CI/CD pipeline. However, operations teams are more likely to opt for the automated remediation rules that can block the container activity from causing any more damage.
The security monitor scans all linked operations, applications, and services to spot when your containers, images, or Kubernetes clusters, within, above, and below, have been compromised or could be.
The dashboard for the system includes analysis facilities for manual activity assessments and there are pre-written threat-hunting rules and compliance reporting templates that fit in with the requirements of HIPAA, PCI, and NIST. You can also tweak more than 300 controls and assessments to create your own security policies.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a DevOps tool that is intended for use by teams that develop and support container-delivered apps and services. The tool can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines to provide configuration and compatibility assessments during development. It will also continue to monitor clusters when they are in operation.
Pros:
- Scans for Security Weaknesses: Operates as a vulnerability scanner
- Useful for Web Application Security Testing: Integrate it into your CI/CD pipeline
- Kubernetes Security Posture Management: Ongoing security monitoring
Cons:
- Only for Cloud-Based Container Clusters: Won’t secure the containers that you host on your servers
RedHat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes is an add-on for RedHat OpenShift. This system runs over Docker which can be on top of RHEL on your own server or on a cloud platform. You can get a 60-day free trial of OpenShift with ACS but you have to pledge not to use it for production during that time.
8. Aqua Security
Aqua Security is a platform of workload security monitoring services that includes a Container Security monitoring module. It will examine the activity of containers on Windows, Linux, cloud platforms, and virtual environments.
The tool updates its threat awareness using information from sources like the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) dictionary, vendor update advisories, and research entities – both public and private. This makes it a formidable tool against any current threats and reduces false positive detections.
Key Features:
- A CNAPP Solution: Container security is part of a Cloud-native Application Protection Platform
- Maintains a Threat database: Draws threat intelligence from multiple sources
- Development Security: Starts its work with testing during application development
Why do we recommend it?
Aqua Security provides Kubernetes Security Posture Management as part of a CNAPP package. This system can be integrated into your development management framework and provide continuous testing. It scans Kubernetes controls for container clusters and alerts to any configurations that would provide hackers with an exploit.
The Aqua system looks into APIs, frameworks, and open source code as well as within the software and operating system inside containers and the system services that support the containers.
The tool is able to identify security weaknesses in a continuous testing scenario for a CI/CD pipeline. If it is deployed for production, it will look out for automated attacks and misuses, such as malware, ransomware, crypto-mining activities, and RATs. It will identify intrusion, data theft, and system appropriation.
Assessments are performed with dynamic application testing within a locked-down sandbox environment. The system also offers static testing that combes through code. So, you get the best of both worlds with this tool and you don’t need to decide which strategy to adopt. Security clearance gets the image signed and unchangeable, gaining its approval for use and blocking tampering.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a DevOps tool for the providers of services. It forms a part of a cloud workload protection package that simultaneously implements CSPM for cloud systems, checking for vulnerabilities before they are discovered by outsiders. The system interacts with Kubernetes’ internal mechanisms to extract statistics.
Pros:
- Kubernetes Security Posture Management: Includes runtime protection
- Cluster Penetration Testing: Discovers security weaknesses before hackers do
- Anomaly Detection: Spots zero-day attacks by looking at usage activity
Cons:
- Only for Cloud: Won’t secure your on-premises containers
The Aqua Security system is a SaaS platform and you can get access to it with a 14-day free trial.
Why do we need container security tools?
Now that we have seen the seven best container security tools let’s close by visiting why an organization needs to install one.
It comes down to making sure all applications going through the development phase can leverage containers without being compromised – and keeping these containers secure is akin to keeping an organization’s mission-critical software secure.
Let us know if you think a container security tool should be included in this list. Leave us a comment below.
Container Security Tools FAQs
Which tools is used for container security?
Here is a list of the six best container security tools:
- Datadog Cloud SIEM
- Anchore
- Sophos Cloud Native Security
- Bitdefender GravityZone
- Sysdig Secure
- RedHat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes
- Aqua Container Security
What is a container in security?
Container security provides testing, monitoring, and remediation to identify weaknesses in container operations, including how those containers interact with other systems and supporting services. Operations teams need to implement security monitoring so that they can identify and shut down live attacks.
Why containers are not secure?
No IT system is completely secure and those that have never been attacked got lucky and just haven’t been attacked yet. It doesn’t pay to be complacent about container security because the financial rewards for hacking are large as are the potential losses for attacked organizations.