Java, as one of the most widely used programming languages for web applications and enterprise software, presents unique challenges when it comes to patch management. Due to its vast ecosystem and frequent security vulnerabilities, businesses need reliable patch management solutions to mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and maintain smooth operations.
Java patch management tools help automate the identification, deployment, and management of Java updates, saving time and reducing the chances of errors or missed patches.
Java patch management tools are essential for managing the complexities of keeping Java environments secure and up to date. These tools offer features such as automatic patch detection, centralized patch deployment, and real-time vulnerability assessments, ensuring that businesses can address Java security flaws promptly. Given Java’s widespread use in mission-critical applications and web servers, missing a patch could expose organizations to security breaches, data leaks, and compliance violations.
Here is our list of the best Java patch management tools:
- Atera Patch Management Software EDITOR’S CHOICE This cloud-based remote monitoring and management package includes a patch manager that can update Java and other applications as well as software and operating systems. The patch manager can also be used to launch system administration tasks and run custom scripts. Start a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL) Α Java patching tool from another major maker of administration and monitoring tools; it covers a wide range of devices, offers customizable patches for unique deployments, and allows for different versions of Java to be run simultaneously on the same network. Start the 30-day free trial.
- Syxsense Patch Management Α cloud-hosted enterprise IT and security management tool, that also comes with Java patching capabilities and would be an ideal solution for businesses that prefer cloud architecture and technology.
- Quest Patch Management Software Α software and hardware asset management tool with Java patching capabilities; features include scheduled scans, audit reports, and compliance level reporting for full control of a network.
- SolarWinds Patch Manager This is an enterprise solution from one of the best network and server administration application makers; a powerful tool on its own, it can be combined with other SolarWinds products for even more comprehensive security coverage of a network and its clients.
- Ivanti Desktop and Server Management Α Java patching tool that comes with pre-tested patches for easier, more accurate deployments; it is considerate of resources and works without disrupting or even slowing down the end-user’s working day.
Patch management solutions can streamline workflows by automating tedious tasks, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing human error. This review assesses the best Java patch management tools available, evaluating each based on features such as ease of use, automation capabilities, integration with existing IT environments, and security features.
We focus on solutions that provide comprehensive support for both desktop and server-side Java applications, enabling businesses to stay compliant with industry regulations, maintain secure environments, and ensure their applications continue to run smoothly. Our findings will cater to those who manage small applications or large enterprise environments. We will help you choose the right patch management tool for your Java infrastructure.
On average, Java releases six updates per year. These updates are critical in stopping vulnerabilities from being exploited. But sometimes, the patching process can cause network bottlenecks or mission-critical applications to crash. This could happen due to many reasons including improper updating procedures. And that is why you need Java patch management tools.
Java is a popular programming language and it is widely used. It is this popularity that makes it such a big target. Apart from websites, Java is used in hardware, Android devices, the cloud, IoT, and many more technologies. This means that there is a higher exposure of weaknesses and vulnerabilities for hackers to take advantage of.
One of the best ways of fighting these attacks is with the help of regular patching. This is where we need to know about the best Java patch management tools.
What is a Patch Management Tool?
A patch management tool is a software package created to make the patch management process easier as well as more accurate. It automates the process of detecting vulnerabilities, identifying the critical patches, and applying them without affecting the business process as a whole. It is a critical system security tool.
What makes for a great Java Patch Management Tool?
Features to look for when choosing a Java patch management tool include:
- It should offer a range of supporting tools and features to help streamline the patching process.
- It should be easy to install, easy to use, and easy to configure – usually done by a single administrator with a few clicks.
- It should integrate well into the current network infrastructure – with the right roles and privileges assigned – and monitor as many varieties and flavors of operating systems as possible, as well as patching all the software solutions running on them and not just Java.
- It should have a light digital footprint and not hog resources – it should have as little an impact as possible on the performance of the other software and hardware running alongside it. It should also appear seamless, in the background, when it comes to the users at the endpoints.
- It should expand existing Microsoft and third-party patch management capabilities to provide a more comprehensive view of potential system vulnerabilities.
- It should have patch compliance reporting because, as with any IT management process involving compliance, it may be necessary to retain a paper trail of management history by generating security reports.
- It should have Wake on LAN (WoL) capability to work with devices that are asleep or shut down; it needs to be able to reactivate LANs whenever a patch deployment is scheduled.
OK; getting into the details, let’s have a look at the best Java patch management tools:
The best Java Patch Management tools
1. Atera Patch Management Software (FREE TRIAL)

Atera Patch Management Software is part of its Remote Monitoring and Management solution that gives administrators full control over their patches from a centralized location. They can save time by automating patches for operating systems, applications, and hardware. They have a robust reporting tool to help them stay on top of every agent to ensure airtight security and control.
Of course, it can also install Java updates.
Key Features:
- Patch Status Summary: Provides a full overview of patch management jobs, including feedback on tasks that didn’t succeed.
- Automatic Reports: Generates three reports from patch management activities, which can be shared.
- Shared Script Library: Contains hundreds of quality-tested scripts for automation, customizable to meet unique patch management needs.
- Report Configuration: Allows exclusion of retired devices and filtering data to reflect only active devices.
- Customizable Parameters: Filters for time frames, customers, automation profiles, tasks, and script outputs.
- Task Planning: Can schedule tasks for servers and workstations, including installing Java and Adobe updates and handling driver updates.
- Integrated RMM and PSA: Combines RMM, PSA, remote access, billing, reporting, ticketing, and customer satisfaction surveying on one platform.
Why do we recommend it?
Atera is a cloud-hosted remote monitoring and management (RMM) system. The service is able to patch computers running macOS and Windows, including all fo the software resident on those devices. The patch manager interface is also a scheduler for maintenance task automation and you can also use it to launch scripts.
Who is it recommended for?
Atera is available in a version for IT support departments and another for managed service providers. Each version includes four plans. The MSP plans include accounting systems that are needed to run the business, which are not needed by IT departments. Pricing is per technician with no minimum team size and starts at $129 per technician.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Minimalistic design makes it easy to view important metrics.
- Flexible Pricing: Pricing model is per technician with no minimum team size, making it viable for small businesses.
- PSA Features: Includes multiple PSA features, ideal for helpdesk teams and growing MSPs.
- SLA Tracking: Tracks service-level agreements and includes time-tracking for maintenance tasks.
Cons:
- MSP Focused: Heavily geared towards MSP-related tools, which may not be fully utilized by other types of businesses.
Try Atera Patch Management Software on a free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Atera is our top pick for a Java patch management tool because it provides many other functions as well as its patching service. The patch manager itself includes task automation facilities, such as launching temporary file clean up or system reboots. The patch manager can update operating systems, software packages, and individual services and applications such as Java. The wider Atera package gives you automated asset management and system monitoring. The package is also available in a multi-tenanted architecture for use by managed service providers.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.atera.com/signup/
OS: Cloud based
2. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
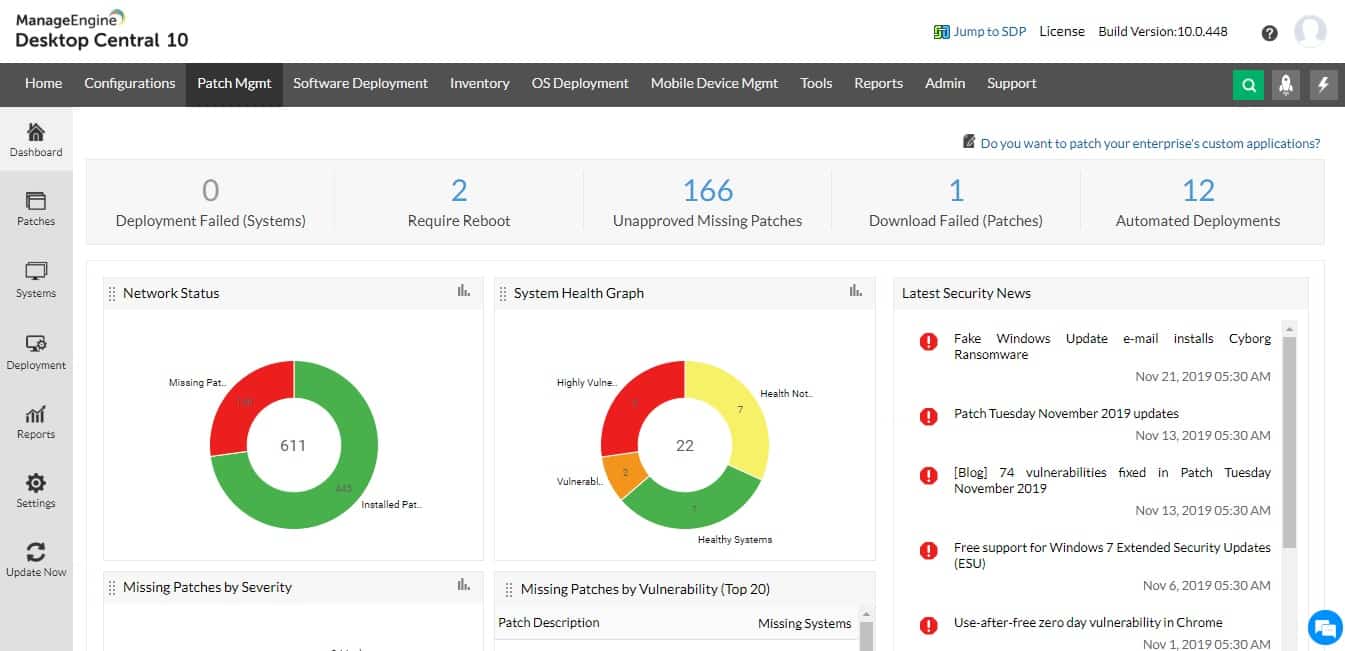
From ManageEngine we get Patch Manager Plus, an enterprise patching solution that works on Windows, macOS, and Linux endpoints. It offers patching support of over 650 third-party updates for over 350 third-party applications – including Java. This tool is available both as an on-premises or a cloud solution.
Key Features:
- Endpoint Scanning: Detects missing patches and selects and tests patches before deployment.
- Test Groups: Automatically creates test groups, tries patches on them, and approves them for production environments.
- Customizable Policies: Allows customization of patch deployment policies to meet unique business needs.
- Real-Time Audits: Provides insightful, flexible, real-time audits and reports for a clearer picture of patch compliance and status.
- Java Manager: Supports multiple versions of Java running simultaneously without conflicts.
- Patch Connect Plus: Allows for Java updates in Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM) for comprehensive endpoint coverage.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus patches Windows, macOS, and Linux and it also updates software packages running on devices. ManageEngine regularly gathers all new patches for 850 software packages, tests then and stores them on the cloud, so your Patch Manager Plus instance has one source from which to download.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is suitable for businesses of all sizes. There is a version to patch endpoints across multiple sites for very large businesses and small enterprises are catered for by a Free edition that patches 20 workstations and five servers. The system is available as a SaaS platform or for installation on Windows Server.
Pros:
- Flexible Deployment: Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux with both on-premises and cloud solutions.
- Broad Compatibility: Supports over 650 third-party updates for over 350 applications, including Java.
- In-Depth Reporting: Offers detailed reporting, ideal for enterprise management or MSPs.
- Extensive Integration: Integrated into more applications than most patch management solutions.
- Free Edition: Suitable for small enterprises, covering 20 workstations and five servers.
Cons:
- Steep Learning Curve: Feature-rich platform that requires time to fully explore and learn.
Try ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus on a 30-day free trial.
3. Syxsense Patch Management
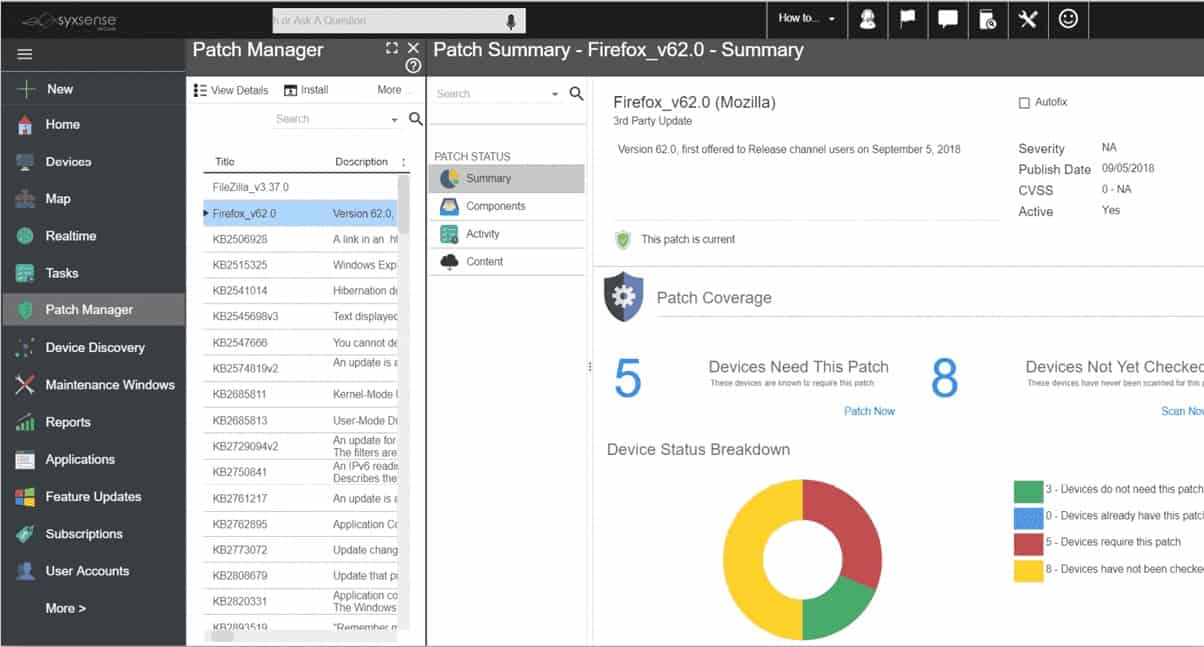
Syxsense is an enterprise tool for IT management and security monitoring, on top of patch management. It is cloud-hosted on Microsoft Azure making it remotely available from anywhere. What makes it even more versatile is the fact that it offers cross-platform support for all major operating systems – Windows, Mac, and Linux – be they connected or remote devices on the network.
Key Features:
- Automatic Deployment: Deploys OS and third-party patches and updates for all major operating systems.
- Cross-Platform Support: Supports Windows, macOS, and Linux, including remote devices.
- Vulnerability Management: Provides clear visibility of vulnerabilities, their severity, and required patches.
- Critical Risk Identification: Identifies devices posing critical risks that need immediate patching.
- Scheduled Patching: Allows patching processes to be planned around endpoint usage to minimize disruption.
- Insightful Reporting: Displays patching activities and statuses in customizable, filterable reports.
Why do we recommend it?
Azure-based Syxsense Patch Management reaches out to your site to manage operating systems and applications on your endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux. The applications that the tool will update include Java. The system scans your network and maintains a software inventory to detect patch statuses.
Who is it recommended for?
This service is suitable for businesses of all sizes. Unfortunately, Syxsense doesn’t publish its price list, so it is difficult to judge whether price-sensitive businesses would choose this option over the other patch managers on our list. The full Syxsense platform provides asset management and security services.
Pros:
- Intuitive Interface: Simple, user-friendly interface with effective use of color for displaying key metrics.
- Cloud-Based Flexibility: Hosted on Azure, making it accessible from anywhere, ideal for remote teams.
- Flexible Pricing: Suitable for networks of any size, with customizable pricing plans.
- Streamlined Onboarding: Offers configuration profiles to streamline the onboarding of new devices.
Cons:
- Short Trial Period: Could benefit from a longer trial period, such as 30 days, for thorough evaluation.
Try Syxsense FREE for 14 days.
4. Quest Patch Management Software
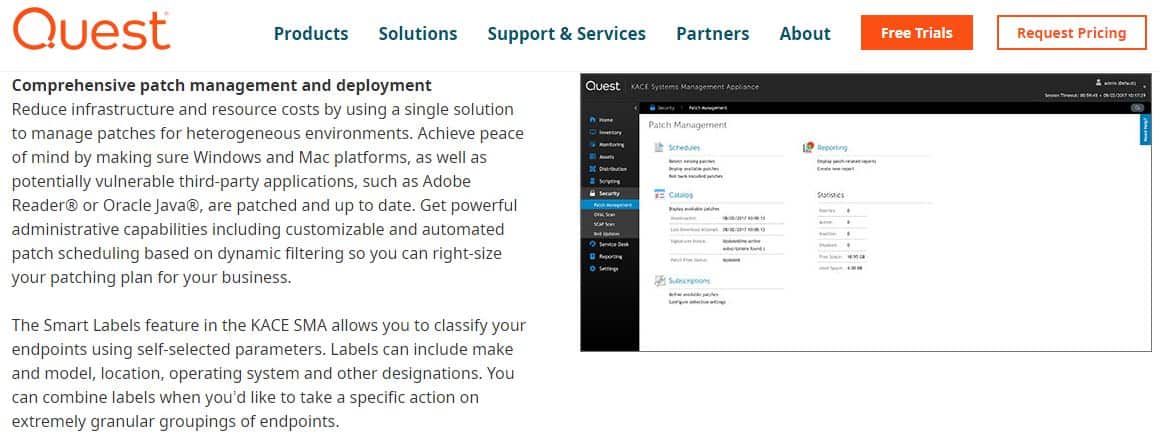
The Patch Management Software is a feature of the KACE Systems Management Appliance tool – Quest‘s comprehensive IT systems management for network-connected devices.
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform Patching: Supports patching and updating for Windows, macOS, and vulnerable third-party applications like Adobe Reader and Oracle Java.
- Real-Time Patch Assessments: Conducts periodic scans and real-time assessments to identify endpoints where automated patching may have failed.
- Security Audits: Helps identify vulnerabilities and discover non-compliant devices quickly.
- Custom Endpoint Classification: Classifies endpoints by parameters like make, model, location, or OS for customized actions.
- Script Deployment: Allows creation and deployment of pre-built or custom scripts for configuration and security policies.
- User-Defined Reboot Scheduling: Sets deadlines for patch installations while allowing users to choose reboot times to minimize disruptions.
Why do we recommend it?
The Quest Patch Management software is part of a package of system management tools. This package is called KACE and it available in a cloud platform or as a virtual appliance. It is even possible to buy both versions in a package. Patch Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
Who is it recommended for?
This system provides a range of option that gives it a wide audience. The KACE Systems Management Appliance version is even able to manage IoT devices. All of the versions will update applications, including Java, as well as operating systems.
This comprehensive solution automates endpoint-related administrative tasks, inventory of hardware and software assets, as well as serving as a patch management solution for mission-critical applications and operating systems.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Dashboard: Sleek and easy-to-navigate interface.
- Wide Third-Party Support: Supports a large range of third-party applications.
- Flexible Scanning Options: Includes both scheduled and manual scanning options.
- Compliance Reporting: Provides detailed compliance level reporting, ideal for regulated businesses.
Cons:
- Exploration Time: The comprehensive feature set may require time to fully explore and utilize.
Try Quest KACE Systems Management Appliance FREE for 30 days.
5. SolarWinds Patch Manager
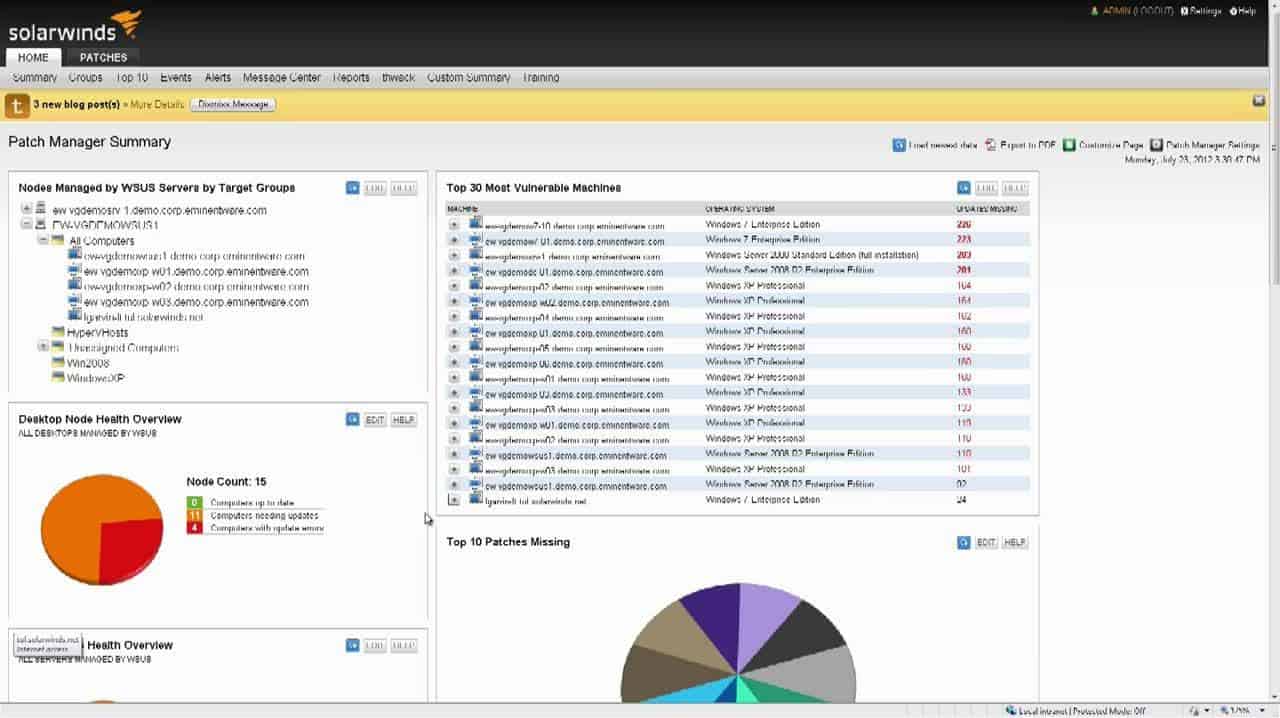
SolarWinds Patch Manager is an IT security product that is used to patch enterprise applications and also has a dedicated Java Patch Management feature. Of course, with it being a product from the leading maker of server and network management tools, this too is one of their powerful, multifaceted administration tools.
Key Features:
- Selective Patching: Allows administrators to choose specific patches to update.
- Virtual Machine Management: Organizes and inventories virtual machines across the architecture.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Provides powerful reporting options to show patch status and compliance.
- Extended Patch Management: Extends Microsoft patch management to include patches for third-party software like Adobe, Firefox, and Java.
- Integrated Dashboard: Displays important patch data alongside other SolarWinds products.
- Pre-Built Packages: Comes with pre-built and pre-tested packages to reduce errors and crashes.
- Internal Patch Store: Verifies, stores, and manages patch files for later use.
- Windows Update Agent Integration: Configures, repairs, and refreshes Group Policy on machines using the Windows Update Agent.
- Vulnerability Discovery: Identifies systems with vulnerable Java versions and directs administrators to correct patch files.
- Advanced Scheduling: Controls when and where updates are executed with advanced scheduling features.
Why do we recommend it?
The SolarWinds Patch Manager operates by updating the WSUS patching system so that it will install updates for software that was produced by businesses other than Microsoft – it still updates Microsoft products as well. This system scans all installed software and notices when new versions are available.
SolarWinds Patch Manager provides patching for operating systems and applications as well as Java code. The Java patch manager ensures that the package to be updated isn’t running before it launches the update. This is an important step because the patch won’t apply if the application is active. Other pre-installation checks and steps are also implemented before running the patch and the SolarWinds Patch Manager is able to order updates according to known patch dependencies. You set up a calendar in the console for the Patch Manager that indicates when patches can run and the system will queue up new updates and apply them at the next available maintenance window.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is suitable for large organizations. IT is able to operate without technician involvement, which is a great money saver. The package is particularly useful for companies that need to prove compliance with data security standards because the patcher’s products status reports for software inventories and patching activities.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Dashboard: Simple interface for tracking and visualizing patches and their progress.
- SCCM Integration: Direct integration with SCCM for smoother patch deployment.
- Wide Variety of Patching Options: Supports a wide variety of third-party software for patching.
Cons:
- Enterprise Focused: Designed for large organizations and may not be suitable for home labs or small networks.
You can check out the 30-day fully functional free trial of SolarWinds Patch Manager.
6. Ivanti Desktop and Server Management
Although the Ivanti Desktop and Server Management solution is just that – a device and server management solution – it can be coupled with its Patch for Endpoint Manager to monitor patch compliance and systems management. Administrators can patch vulnerabilities of apps like Acrobat Flash, Internet browsers, as well as Java from a single dashboard.
Key Features:
- Pre-Tested Patches: Comes with accurate, pre-tested patches vetted by in-house engineers.
- Comprehensive Device Coverage: Discovers, inventories, and patches online and offline devices, including virtual machines.
- Extended Patch Catalog: Addresses all devices and applications on a network, including remote, mobile, and asleep devices.
- Light Digital Footprint: Assesses and patches endpoints without slowing down the network.
- Multi-OS Support: Monitors vulnerabilities and deploys patches on Windows, macOS, Linux, and Chrome OS.
- Efficient Deployment: Allows testing, packaging, and pre-caching patches for quicker deployments with minimal user impact.
Why do we recommend it?
Ivanti Endpoint Manager is able to update operating systems and applications. It can patch Windows, macOS, Linux, and Chrome OS and it can even update IoT devices. Ivanti boasts that its patch manager can update software without any downtime for the endpoints. Cloud-based patching is available from two packages under the Ivanti Neutrons brand.
Who is it recommended for?
Ivanti systems are aimed at mid-sized companies, while larger organizations wouled probably be more interested the Ivanti Neurons system, which can consolidate the management of software on multiple sites. Ivanti doesn’t publish a price list and that might deter small businesses from enquiring.
Pros:
- Flexible Multi-Platform Support: Supports a variety of operating systems, including Linux, macOS, and Chrome OS.
- Patch Scheduling and Imaging: Offers patch scheduling in addition to imaging capabilities.
- User-Friendly Reporting: Provides simple graphical reporting that is easy to set up and interpret.
- No Downtime: Updates software without requiring downtime for endpoints.
Cons:
- No Cloud-Based Version: Lacks a cloud-based version, which may limit flexibility.
- Undisclosed Pricing: Requires contacting the company for exact pricing, which may deter small businesses.
Try Ivanti Desktop & Server Management for FREE.
Why is patching important?
Ok, now that we have seen the best Java patch management tools, let’s have a look at why it is important to keep Java updated:
To ensure security – patch management fixes vulnerabilities in software and applications that can be exploited.
To improve system uptime – patch management ensures software and applications are up-to-date and running smoothly to achieve higher system uptimes.
To achieve compliance – businesses and organizations need to meet compliances by regulatory bodies, and patch management is one way of doing so.
To improve software features – software makers include bug fixes as well as feature and functionality updates for a better product and user experience (UX).
Why is it a challenge to keep Java patched?
Now, let’s have a look at why it is a challenge to keep Java – and even other software – updated:
Reluctant users – many endpoint users find the task of updating it, or even clicking on the “OK” button of a Java Auto Update notification, to be an annoying or tedious task.
Being unaware – and even when users are willing to undergo the updating process, they might not be aware of the risks they find themselves and the urgency in the need to immediately patch their vulnerable applications.
Switching Java off – despite the important role it plays in a business computing environment, some users disable Java completely. When these un-patched versions come back online they can pose a critical threat.
Machines that don’t support patching – in some cases, some machines can’t handle patching due to inability to process scripts, low memory, weak processors, or incompatible and outdated operating systems.
And, so, that is why administrators need to use one of the Java patch management tools we have just seen.
If there are any other tools you feel belong on this list or have any thoughts about the ones we have chosen, let us know.





