Patch management tools that deploy updates to devices throughout your network remotely are one of the greatest time-saving solutions you have at your disposal. Nobody likes to spend the day hopping on and off computers to install patches, and a good patch management solution can turn a long-winded chore into a simple process
Effective patch management is a cornerstone of maintaining secure and efficient Linux systems, especially in environments where vulnerabilities can have serious consequences. Whether you’re managing a few servers or a large-scale infrastructure, patching ensures that your systems remain protected against known exploits, bugs, and performance issues. However, patching in Linux environments can be challenging due to the diversity of distributions, software configurations, and the critical need for uptime.
Linux patch management tools are designed to simplify and automate this process. They help IT administrators monitor for available updates, test patches in controlled environments, and deploy them systematically across devices. Many of these tools also offer additional features like rollback options, detailed reporting, and compliance checks to ensure that updates do not disrupt critical business operations.
Choosing the right tool involves considering factors such as ease of use, compatibility with various Linux distributions, and the level of automation. For businesses managing multiple client environments, multi-tenant support and detailed SLA reporting are crucial. By leveraging advanced patch management solutions, organizations can reduce the risk of security breaches, improve system reliability, and maintain compliance with industry standards.
This guide offers an in-depth look at the best Linux patch management tools available today, helping IT professionals select the right solution to meet their needs.
Here is our list of the Linux Patch Management tools:
- NinjaOne Patch Management EDITOR’S CHOICE This cloud platform offers multi-tenanted accounts that are ideal for use by MSPs to manage client systems, including watching over endpoints running Linux, macOS, or Windows. Access a 14-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL) Patch management solution for managing Linux, Windows, and Mac devices. The user can set deployment policies, schedule future patches, test patches, and generate reports. Download the 30-day free trial.
- Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence Web-based patch management tool for Linux, Unix, and Mac. It comes with automatic patch deployment, scheduling, and testing. It also includes a customizable reports system.
- GFI LanGuard Patch management software for Linux, Microsoft, and macOS devices. On Linux, the tool supports RedHat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, SUSE Linux Enterprise, openSUSE, and Fedora 19.
- Automox Cloud-based patch manager for Linux, Windows, and macOS. Configure policies and automatically patch devices throughout your network or create custom scripts with Automox Worklets.
- Kace Systems Management Appliance Systems management solution with software deployment and patch management for Linux, Windows, and macOS. It also supports custom package installations.
- SanerNow Patch Management Cloud-based patch management tool that supports Linux, Windows, and macOS. Includes automated patch discovery, task scheduling, and reports.
- HCL Software BigFix Patch management tool compatible with Linux, UNIX, Windows, and macOS. Automatically discovers and distributes software to connected devices.
- Red Hat Satellite A software and system management package that automatically introduces patches for registered software.
- SysWard Patch management tool compatible with CentOS, Ubuntu, RedHat, Debian, OpenSUSE, SUSE, Fedora, Oracle Linux, and more. It includes a dashboard and an alerts system.
See also: Best Patch Management Tools
The Best Patch Management Tools for Linux
Our methodology for selecting a Linux patch management tool
We reviewed the market for Linux patch managers and analyzed tools based on the following criteria:
- A software asset inventory
- Automated scans for updates
- Processes to queue available patches for installation
- A maintenance calendar that allows patches to be applied at unobtrusive times
- Completion reports and the option to rerun patches manually
- A free trial or a demo account for a cost-free assessment
- Value for money from a tool that will save technician time, sold at a fair price
With these selection criteria in mind, we investigated Linux patch management systems for Linux that provide automation to improve efficiency.
1. NinjaOne Patch Management (FREE TRIAL)
Tested on: Cloud/SaaS
NinjaOne is a cloud platform that provides system monitoring and management tools. Those tools include a patch management module and this system can manage endpoints running Linux, Windows, and macOS. The patching console is able to handle update processes for different operating systems within the same queue.
Key Features
- Automated Patching: Streamlines update processes, saving time and resources.
- Patch activity documentation: Needed for compliance reporting
- Multi-OS Compatibility: Able to manage patches for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- Remote Management: Facilitates patching of endpoints across different locations.
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne Patch Management is part of a cloud platform of remote monitoring and management services. This service is able to connect to any LAN and manage the patch statuses of devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux. You also get other tools in the NinjaOne package, which include system monitoring for networks, servers, and applications, and remote access utilities for troubleshooting and problem resolution.
NinjaOne is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) package and it provides automated system monitoring services for endpoints and networks. The system offers technician tools for troubleshooting and support, such as remote access. Endpoint management modules in the platform offer patch management and the Linux service is implemented so that patch queuing is automated.
You set up a schedule in the NinjaOne console for each sub-account. This lets you define maintenance windows that permit the NinjaOne system to kick off automatically and apply patches to Linux computers outside of office hours without the need for technicians to intervene manually.
NinjaOne documents all of its actions and technicians can see in the patching queue the completion status of each patch run. This enables failed patches to be investigated and rerun. There is an option to launch a patch run on demand.
Who is it recommended for?
NinjaOne is designed for managed service providers (MSPs) and it provides a multi-tenant architecture that enables the MSP to set up a separate sub-account for each client. This keeps all of the data and settings for each client completely separate. The package can also be used without the sub-account feature by IT departments for IT asset management.
Pros:
- Efficient Automation: Reduces manual intervention, enhancing productivity.
- Versatile Endpoint Management: Ideal for businesses managing multiple OS types.
- Sub-Account Feature: Offers client data segregation for MSPs, ensuring data privacy.
Cons:
- No Transparent Pricing: Absence of a public price list may hinder decision-making.
On the topic of reliability, it’s worth noting that G2 has consistently ranked NinjaOne as the #1 choice in its category. NinjaOne is a cloud platform so you start your usage of the service by setting up an account on the cloud servers for the package. The NinjaOne RMM with its patching service is available for a 14-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
NinjaOne Patch Management is our top pick for a Linux patch manager because it is able to assess all software and operating systems to detect those packages that need to be updated. The NinjaOne server continuously updates its patch availability report, so any local scan needs only compare to one list to find out what the latest versions should be. This system isn’t only for Linux because it can also patch Windows and macOS and all of the software running on top of those operating systems. The service needs to be set up with a calendar and then it will automatically download patches and apply them at the next available maintenance window. This system’s automation enables support technicians to get on with more complex tasks that require human ingenuity.
Download: Access a 14-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.ninjaone.com/freetrialform/
OS: Cloud-based
2. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
Tested on: Linux, Mac & Windows, On-premises or Cloud
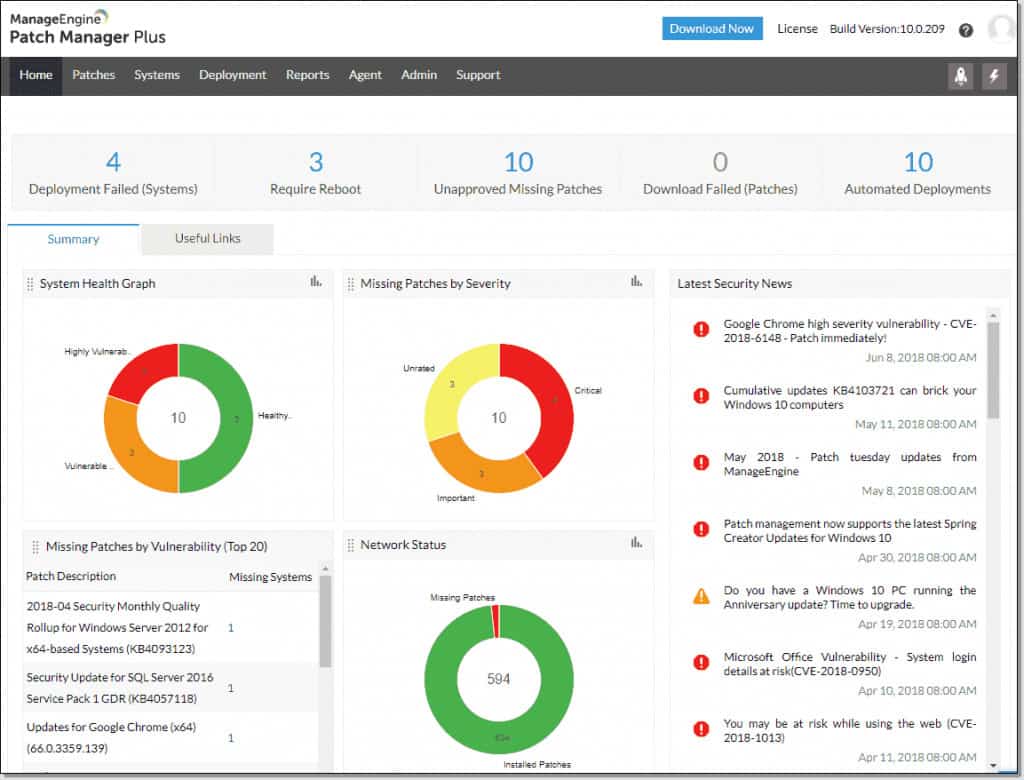
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a patch management solution that can manage Linux, Windows, and Mac devices. The platform offers an agent for the following OS’s; Red Hat, SUSE Linux, Ubuntu, Debian, and CentOS. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus scans online for missing patches and tests them before deploying them to your computer. The user can schedule patch scans to continually find new scans.
Key Features
- Cross-Platform Support: Manages patches for Linux, Windows, and macOS, ideal for mixed OS environments.
- Automated Patch Prioritization: Automatically prioritizes patches, ensuring critical updates are deployed first.
- Health Reports: Offers insightful reports post-patch deployment to assess system performance and security.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a self-hosted system with deployment options. You don’t have to host it on a Linux machine because it can reach across the network to your Linux computers. It can also patch Windows and macOS. So, if you have a mixed inventory of operating systems, you can still manage all of your systems with this one tool.
To ensure that you stay protected, ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus allows you to set deployment policies and prioritize searching for patches with the highest priority. For example, the software will install critical patches before focusing on low or moderate severity level updates.
With System Health Reports you can check how your computers are performing after the patch has been installed. Here you can view the patch status and verify that the vulnerability is secured.
Who is it recommended for?
Patch Manager Plus is available in three editions, which makes it a relevant option for businesses of all sizes. There is a Free edition for small businesses that will manage patching on up to 20 workstations and five servers. There is also a version for LANs and another for multi-site operations. The software runs on Windows Server but if you don’t have that operating system, you can opt for the SaaS version of the patch manager.
Pros:
- Versatile Patching: Its ability to patch multiple OS types makes it suitable for diverse IT environments.
- Intuitive Health Reports: Simplifies monitoring post-patch status, enhancing system maintenance and security.
- Flexible Licensing Options: Offers various editions, catering to different business sizes and needs.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: The platform’s comprehensive features may require some time to master.
- Multiple Editions: While offering flexibility, the different versions can be confusing to choose from.
There are three On-Premises versions of ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus available: Free Edition, Professional, and Enterprise. The Free Edition supports up to 20 computers and five servers free of charge.
The Professional annual subscription costs $245 (£205) with third-party patch management and report scheduling. The Enterprise version costs $345 (£290) with automatic testing and approval. You can start the 30-day free trial.
3. Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence
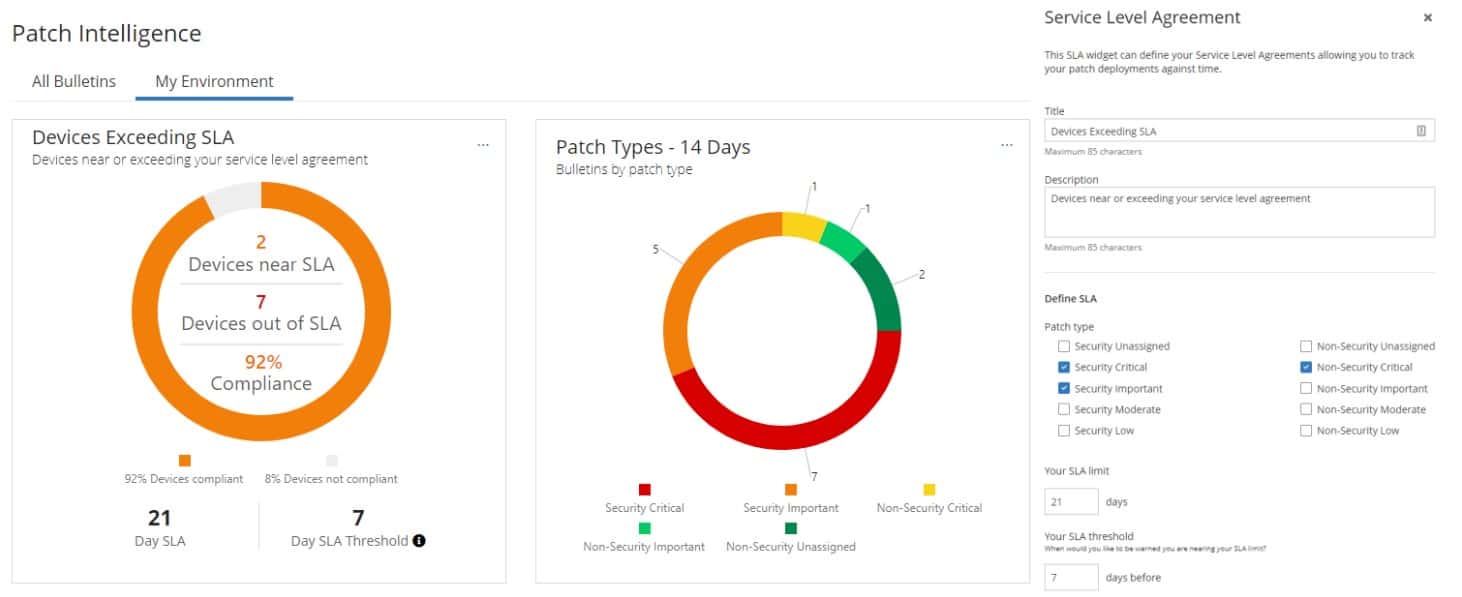
Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence is part of a cloud platform of system protection and compliance tools. The package includes a vulnerability scanner and a patch manager that acts on the results of the scans.
Key Features
- AI-Driven Patching: Leverages artificial intelligence for effective patch management.
- Compliance Reporting: Simplifies meeting regulatory requirements with detailed reports.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Identifies and addresses system vulnerabilities efficiently.
Why do we recommend it?
Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence is a SaaS platform that provides a vulnerability scanner that will trigger a patching routine if a vulnerability that it discovers is resolved by a new update from the software producer. This is a great solution because it also provides misconfiguration advice, enabling you to keep your entire system secure.
The vulnerability scanner is tailored and constantly adapted to recent threat vectors that are listed in a threat intelligence feed. The vulnerability manager then uses AI processes to work out which services and applications will be vulnerable. As well as launching the patch manager, the package will implement configuration changes to close off weaknesses.
The software also has a reporting function, which shows how many devices haven’t been patched, with graphs and pie charts for greater visibility. Reports are customizable so you can choose how the patch data is displayed on the screen. These reports are very useful for regulatory compliance because they help to verify that your infrastructure is up to date.
Ivanti is a solution suitable for companies seeking to deploy patches in cross-platform environments. It’s easy to use and gives the user complete control over device security.
Who is it recommended for?
One problem with Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence is that it will only operate on devices running Linux, macOS, and Unix – not Windows. Ivanti produces another patch manager for Windows and Microsoft products that operates through SCCM. So, if you don’t have any Windows endpoints or servers, you will benefit from the combined vulnerability scanning and patching services of Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence. However, businesses that have Windows on site, as well as Linux, would need to subscribe to two products from Ivanti, which is less appealing than many of the other tools on the list, such as ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus.
Pros:
- AI-Enhanced Scanning: Offers sophisticated, proactive patch management.
- Detailed Reporting: Facilitates compliance and security assessments.
- Cross-Platform Support: Manages patches for Linux, Mac, and Unix systems.
Cons:
- Windows Exclusion: Lack of support for Windows systems may limit its applicability.
- Direct Contact Pricing: Requires contacting the company for pricing details.
To find out the pricing information for Ivanti, you will have to contact the company directly. You can get a 45-day free trial of the entire Ivanti Neurons platform.
4. GFI LanGuard
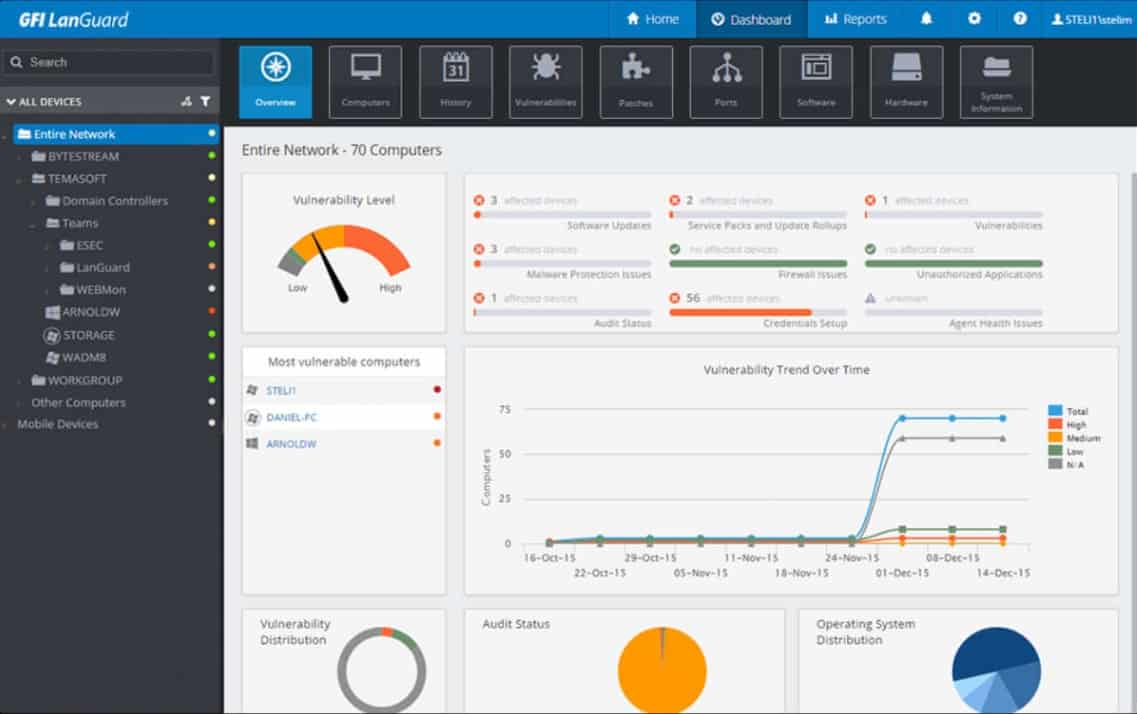
GFI LanGuard is a piece of patch management software that can patch Linux, Microsoft, macOS, and other third-party applications including Apple QuickTime, Mozilla Firefox, Adobe Acrobat, Adobe Flash Player, Shockwave Player, Mozilla Thunderbird, Java Runtime, and more. For Linux, users, GFI LanGuard supports a range of distributions including RedHat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, SUSE Linux Enterprise, openSUSE, and Fedora 19.
Key Features
- Extensive Linux Support: Patches a wide range of Linux distributions including RHEL, SUSE, CentOS, and more.
- Vulnerability Manager: Identifies and resolves security weaknesses alongside patch management.
- Automated Patching: Streamlines the update process across various platforms.
Why do we recommend it?
GFI LanGuard is an especially good choice for patching Linux because it explicitly lists the distros that it can patch. These are RHEL, CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, SUSE Linux Enterprise, openSUSE, and Fedora 19. Very few businesses only have Linux on their sites, so it is good to see that GFI LanGuard can also patch Windows and macOS from a single console. A great feature of this package is that it also includes a vulnerability manager, which will discover security weaknesses that can be patched. It will then automatically launch the patch manager to fix detected problems. The patch manager can also be run manually.
The tool comes with a quality GUI where you can manage patches across all of your connected devices. Scan your network manually or automatically to download new patches. Automatic patch downloading is great for reducing the manual administration you have to do to update devices.
There is also a vulnerability assessment feature, which can detect over 60,000 vulnerabilities. Vulnerability scans use a combination of OVALand SANS Top 20 to scan for vulnerabilities within your devices. If there is a problem then the software provides you with additional information about the status so you can resolve it.
Who is it recommended for?
The extensive competence of GFI LanGuard in patching Linux makes this a very attractive package. It is also great that this service can patch macOS and Windows, which makes it a better prospect for most businesses than the Ivanti package. Businesses that aren’t intensively Linux-based should also consider ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus. However, the linked vulnerability scanner in GFI LanGuard gives this tool the edge.
Pros:
- Diverse OS Patching: Its capability to patch various operating systems makes it versatile.
- Integrated Vulnerability Scanning: Enhances security by identifying and patching vulnerabilities.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies patch management with an intuitive GUI.
Cons:
- Scheduling Flexibility: Could benefit from more advanced scheduling options.
- Third-Party Application Support: Needs updates for newer third-party applications.
GFI LanGuard is offered in three plans: Small, Medium, and Large. The Small plan covers 10 to 49 nodes and costs $26 (£21.80) per node per year. You can download the 30-day free trial.
5. Automox
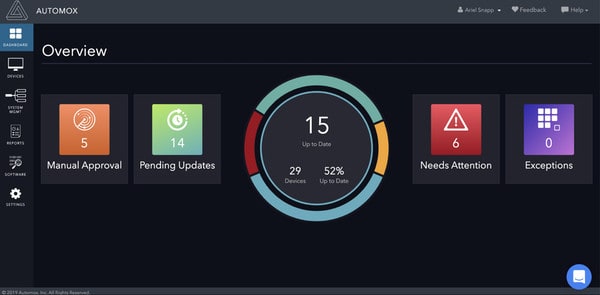
Automox is a cloud-based patch management platform for Linux, Windows, and macOS. Automox can automatically patch vulnerable devices. The tool is easy to use and deploy with a lightweight agent that has a minimal impact on your system resources.
Key Features
- Cross-Platform Patching: Efficiently manages updates for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- Group-Based Patching: Allows organizing devices into groups for streamlined management.
- Custom Scripting: Enables tailored automation with scripting capabilities.
Why do we recommend it?
Automox is another patch manager to consider if you have Windows and macOS computers on your network as well as Linux machines. This system has its own scripting module that enables you to create automated workflows for device management and it is able to orchestrate with your other on-site security systems to exchange data and protect resources. This system also provides configuration management and troubleshooting tools.
Through the GUI the user can create policies and assign them to devices or groups. Grouping devices together makes it much easier to manage a high number of devices. For example, if a user creates a group of devices then they can edit policies and affect the entire group.
Grouped devices can also be supported by department, OS, or region, enabling simple navigation. If you need more control then you can use Automox Worklets to script custom tasks.
Automox is one of the most low maintenance patch management tools on this list with excellent configuration options.
Who is it recommended for?
Automox is a very compelling package because of its ability to link to third-party security systems. Probably the most important links that you will set up will be between a vulnerability scanner and Automox. This system runs on the cloud, so you don’t need to host it or make sure the software is up to date – that’s all taken care of.
Pros:
- Cloud-Based Convenience: Eliminates the need for on-premise server installation.
- Intuitive Interface: Facilitates easy navigation and management with a visually appealing GUI.
- Effective Grouping System: Simplifies managing large numbers of devices.
Cons:
- Compliance Reporting: Could improve features for compliance reporting like HIPAA, PCI, etc.
- Limited Third-Party Patching: Could enhance support for patching third-party applications.
There are two versions of Automox available to purchase: Patch, and Patch & Manage. Prices start at $3 (£2.50) per device per month. You can start the 15-day free trial.
6. KACE Systems Management Appliance
KACE Systems Management Appliance is a systems management solution with a patch management feature. On Linux, the software agent is compatible with Linux Red Hat Linux AS and ES, Ubuntu, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, and Raspbian Linux.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Linux Support: Patches a variety of Linux systems including RHEL, SUSE, and Ubuntu.
- Asset Management Integration: Combines patch management with IT asset management.
- Automated Patch Deployment: Facilitates the automated updating of systems.
Why do we recommend it?
KACE Systems Management Appliance is an interesting product but its main appeal lies in the reliability of the Quest brand – the company that provides the KACE line of products. The patch manager is just a part of the KACE Systems Management Appliance – albeit a very important element. This is a full IT asset management package with a strong emphasis on software management.
The software deploys automated updates to Linux, Mac and Windows computers or servers. The software also supports custom package installations, in .rpm, .zip., .bin, .tgz.m and tar.gz on Linux.
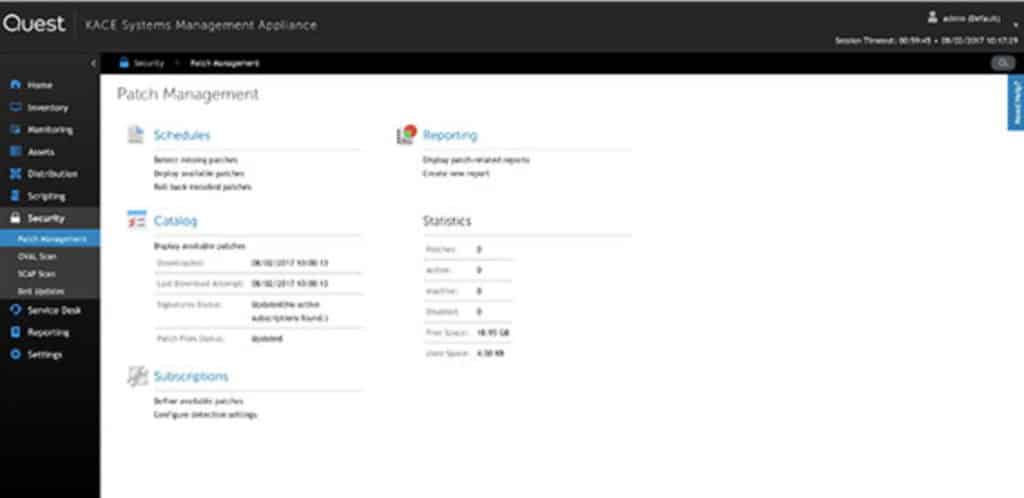
The GUI allows the user to monitor their entire asset inventory through the dashboard. On the dashboard, you can view devices and monitor performance. If you click through to the Patch Management screen you can view statistics and complete actions such as detecting missing patches, deploying available patches, and rolling back installed patches.
KACE Systems Management Appliance is one of the most complete patch management tools on the market. The tool is available as a virtual or hosted appliance.
Who is it recommended for?
KACE Systems Management Appliance is not a physical appliance – that makes the tool more affordable. It operates as a virtual appliance over Hyper-V, VMware, or Nutanix. An alternative deployment option is available from a SaaS version. This is a very comprehensive Service Desk tool, so it wouldn’t be suitable for small businesses that don’t have many assets to manage. However, mid-sized and large businesses will benefit from this system because it is able to manage and patch devices running Windows and macOS as well as Linux.
Pros:
- Versatile OS Support: Capable of patching multiple Linux distributions effectively.
- Dual Deployment Options: Can be used as both a virtual or hosted appliance.
- Holistic IT Management: Combines patch management with broader IT asset management.
Cons:
- Pricing Transparency: Requires direct contact for pricing information.
- Dashboard Usability: Could benefit from enhanced filtering options in reporting dashboards.
To receive a quote you will need to contact the company directly. You can download the 30-day free trial.
7. SanerNow Patch Management
SanerNow Patch Management is a cloud-based patch management solution that automates patches to Linux, Windows, and macOS. SanerNow Patch Management can automatically discover new patches and apply them without manual intervention. If a patch causes problems then the software can roll them back.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Application Coverage: Patches operating systems and over 300 applications.
- Vulnerability Association: Tightly integrated with a vulnerability scanner for enhanced security.
- Automated Patch Discovery: Streamlines the process of finding and applying new patches.
Why do we recommend it?
SecPod SanerNow Patch Management provides automated patching for operating systems and more than 400 third-party software packages. This is a SaaS package so you don’t need to worry about patching the SanerNow software because SecPod takes care of that for you. This system runs automatically on a schedule and it will operate overnight when the office is closed and all of your devices are unoccupied. It will patch RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, Oracle Linux, Amazon Linux, Ubuntu, and Debian Linux. IT will also patch Windows and macOS and the software that runs on top of them.
To use the tool, the user configures patch rules and then schedules tasks for the tool to complete. For example, you can configure a rule to automatically patch devices. You can also prioritize patches according to the level of severity.
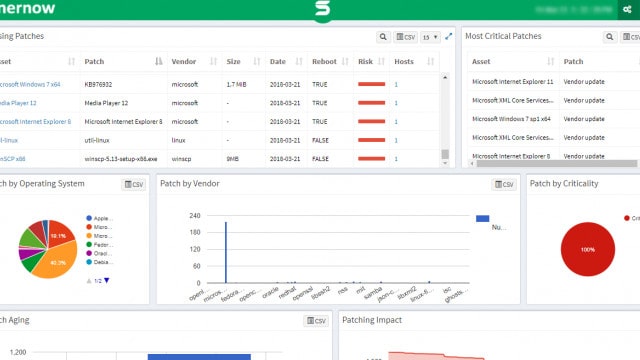
To help you keep an eye on what devices have been patched, SanerNow Patch Management comes with a reporting feature. Reports show you which patches have been rolled out and what risks they’ve protected you against. Elements like patching impact analysis and historical tracking help to show what changes have been made to your network.
SanerNow Patch Management is one of the top patch management tools for those enterprises that want a basic asset management experience. The software supports Redhat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, Fedora, Oracle Linux, Amazon Linux, Ubuntu, and Debian on Linux.
Who is it recommended for?
SecPod’s patch manager is a close competitor of ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus. The SanerNow system doesn’t have an on-premises version, but its console is accessible from anywhere through any standard browser, so it will seem as though you are using it on your own workstation. The tool is suitable for all sizes of businesses.
Pros:
- Cloud-Based Efficiency: Simplifies patch management without the need for server setup.
- User-Friendly Patch Rules: Aids in the easy scheduling and prioritization of updates.
- Effective Deployment Tracking: Offers detailed tracking and impact analysis of patch deployments.
Cons:
- User Interface Complexity: Could be streamlined, especially for managing a large number of devices.
- Direct Sales Pricing: Pricing information requires contacting the sales team.
For pricing information you will have to contact the sales team directly. You can try the free trial.
8. HCL Software BigFix
HCL Software BigFix is endpoint management and patch management software for Linux, UNIX, Windows, and macOS. HCL Software BigFix combines automated asset discovery with automatic software distribution to update devices efficiently with minimal user intervention. The tool is scalable and can monitor up to 250,000 different endpoints.
Key Features
- Endpoint Management: Offers comprehensive management for various endpoint types.
- Scalable Patching: Efficiently manages a large number of endpoints, up to 250,000.
- Compliance Reporting: Provides detailed reports for compliance purposes.
Why do we recommend it?
HCL Software BigFix is an endpoint management tool that includes patching. This service can operate on endpoints running Linux, Windows, and macOS and it will also update software running over those operating systems. The system can identify physical, virtual, mobile, and cloud-based assets and it will scan each discovered device to compile a software inventory. This is the basis of the BigFix automated patching and also its compliance reporting services.
You can use the tool to monitor endpoint states in real-time. Real-time monitoring enables you to see patch levels and confirms whether a patch has been deployed successfully before updating the management server.
Confirming installations is useful for providing evidence of patching in a regulatory compliance scenario. There is also a reporting system that allows you to highlight entities that need updates.
HCL Software BigFix is worth investigating if you need to manage devices divided up between different operating systems. It also has the bandwidth to support everyone from SME’s to large companies.
Who is it recommended for?
Although HCL Software states that its BigFix package is suitable for all businesses, the upper end of size definition is worth noting because one installation of this package can manage up to 250,000 endpoints. That is a remarkable scale and recommends the BigFix service for very large organizations. The system is an on-premises software package that will install on RHEL or Windows Server.
Pros:
- Lightweight Management Tools: Combines patch management with asset management features.
- Broad System Support: Effectively supports Linux, Windows, and Unix systems.
- High Scalability: Suitable for large organizations with extensive endpoint networks.
Cons:
- Pricing Inquiry: Requires contact with sales for pricing details.
- Demo Only: Does not offer a free trial, only a product demonstration.
To view the pricing information you will have to contact the company directly. You can schedule a demo.
9. Red Hat Satellite
RHEL owners can maintain their operating system, RHEL utility components, and any other software installed on the system with the RHEL Satellite service. This is a complete system management tool that will monitor all versions of software installed on your RHEL machine and the operating system, too.
Key Features
- RHEL Specialization: Tailored specifically for managing Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems.
- Comprehensive Suite: Includes a range of tools for lifecycle management and support.
- Integrated Patching and Management: Offers centralized control for OS and application updates.
Why do we recommend it?
Red Hat Satellite is intended as a software manager for Red Hat systems. So, RHEL is top of the list in that group of products and Satellite is a complicated package of tools and Katello is the important component that implements patch management. The main drawback of this system is that it doesn’t extend to other operating systems or even other distros of Linux.
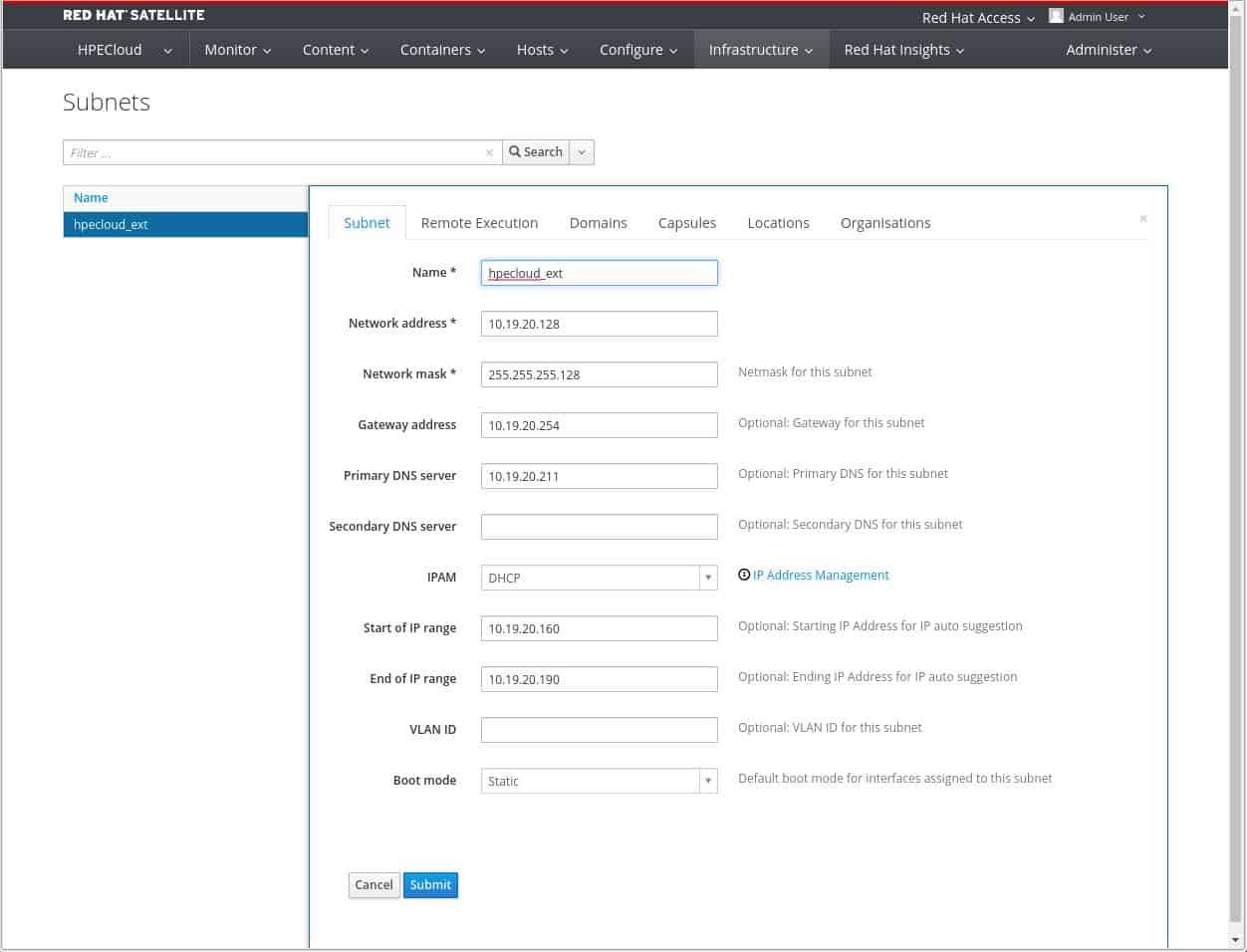
The Satellite software is a suite of tools. This is a substantial package and it takes 90 minutes to install. The nine components are:
- The Foreman: A provision and lifecycle management tool for both physical and virtual systems.
- Katello: Subscription and repository management.
- Candlepin: The subscription management part of Katello.
- Pulp: The content and repository management part of Katello.
- Hammer: A command-line interface for all Satellite functions.
- REST API: A RESTful API to enable the creation of integration modules.
- Apache Tomcat: The embedded server for the front end of the Satellite system.
- Puppet: A Puppet Master server.
- Hiera: a key-value database needed for Puppet.
The key element in all of this is Katello, which is where all the patch management functions lie.
Who is it recommended for?
The customer pool for Red Hat Satellite is composed of users of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. This is the most important Red Hat tool that anyone could use. Red Hat Virtualization is probably the second most prominent product of the company that needs to be kept up to date. Businesses that run a mix of endpoint operating systems will have to supplement this free tool with other patch managers.
Pros:
- Dedicated RHEL Focus: Ideal for environments heavily reliant on Red Hat Linux.
- Complete Lifecycle Management: Provides extensive tools for managing RHEL systems.
- Expert-Level Toolset: Designed for professionals well-versed in Linux.
Cons:
- Complexity for New Users: Can be overwhelming for those new to RHEL management.
- Lengthy Installation: Requires a significant amount of time for full setup.
- Single OS Limitation: Focuses only on Red Hat systems, limiting cross-platform utility.
The Satellite system is able to manage the operating system and software of several hosts owned by an organization and it can also include remote and cloud servers. The system is free to use and is available from the Red Hat website.
10. SysWard
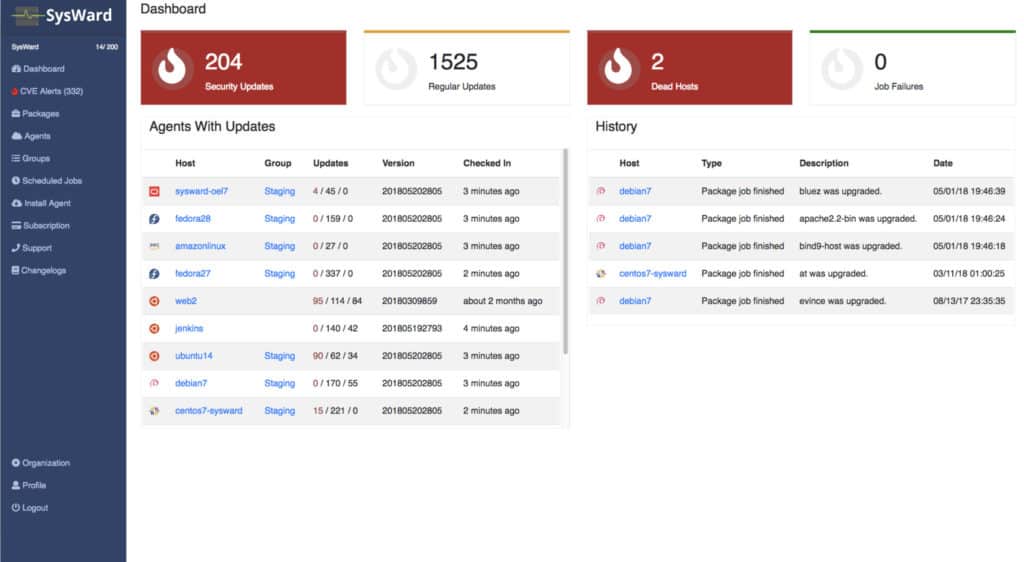
SysWard is a patch management solution that supports a range of operating systems for Linux including CentOS, Ubuntu, RedHat, Debian, OpenSUSE, SUSE, Fedora, Oracle Linux, and more. Through the dashboard, you can view a view of updates broken down into Security Updates, Regular Updates, Dead Hosts, Job Failures, and more.
Key Features
- Wide Linux Distribution Support: Patches a variety of Linux systems including RHEL, SUSE, Ubuntu, and others.
- Asset Inventory Creation: Offers detailed insights into software installations and updates.
- Vulnerability Management: Identifies and addresses software vulnerabilities effectively.
Why do we recommend it?
SysWard is a Linux-only security system that is centered on a patch manager. The tool is able to operate with just about all distros of Linux. This system will scan your Linux endpoints and assess which need patching and then go and get the installers for those update. It will apply patches at the next available maintenance window.
You can also view a list of Agents within your network. The Agents view shows you information including the OS, Hostname, Group, Updates, Memory, Version, and Last Checkin. The Agents view is good for managing your asset inventory and monitoring update statuses. If you need to, you can export this data in CSV format.
The platform also comes with an alerts system that produces a notification whenever a new patch is available for a package. Alerts are assigned a level of severity based on how important they are to your network. The alerts feature is useful because it keeps you updated on changes to your infrastructure.
Who is it recommended for?
SysWard is a good choice for businesses that only have Linux on their endpoints. If you also run macOS or Windows, you would probably be better off with another tool, such as ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus. Very small businesses that only have two Linux servers to manage can use this package for free.
Pros:
- Multiple Linux Distros: Supports a broad range of Linux distributions, enhancing versatility.
- Resource Utilization Tracking: Monitors hardware resource usage alongside patch management.
- Effective Alerting System: Keeps users informed about new patches and their importance.
Cons:
- Reporting Enhancements: Could benefit from more comprehensive reporting features.
- Additional Export Formats: Expansion of export formats would increase usability.
SysWard is a good choice for enterprises that want a simple patch management tool with a low price tag. The software is available for free for up to two agents. If you need more, you can purchase a paid plan starting at $2.50 (£2.10) per agent per month. You can download the program for free.
Choosing a patch management tool for Linux: Reporting is a Must!
Going from device to device searching for updates and installing them isn’t the most efficient way to patch dozens of devices. Linux Patch management tools take care of the tedious task of finding and installing patches so that you can focus on more pressing issues.
The less time you spend installing updates manually the more time you can spend on more important tasks. We’ve listed a variety of tools on this list to suit enterprises of all kinds. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a great place to start if you’re looking for a basic and accessible solution.
When searching for a patch management solution it is a good idea to purchase one with reports. A good reporting feature will allow you to check up on what vulnerabilities have been patched and verify that your network is secure. They can also be extremely useful if you’re ever audited by a third party!
Linux Patch Management FAQs
How often should patch management be performed?
Perform a patch run at least once a week. That’s a good compromise cycle length but each business has different constraints. The typical non-committal advice given all over the internet is “that depends” because network managers are also constrained by service level agreements that sometimes require constant availability. Ensure that contract managers insert a once-a-week window in system availability agreements for patches that require the system to be bounced.
Why is patch management important for network security?
Patches are issued to close off security vulnerabilities that have been revealed by hacker attacks after the current version of the software was finalized and released. In most cases, new versions of software and operating systems have been extensively tested and analyzed for bugs before they are released. So, patches are not usually issued because the developers got something wrong in their original software versions. Patch management is an essential part of system security procedures and should be regarded as a priority task.
What is a kernel patch?
A kernel patch is an update to the operating system in Unix and Unix-like systems. This group of operating systems includes Mac OS, Linux, BSD, Android, Amazon Fire OS, and Raspberry Pi.

















Spacewalk project has been discontinued on May 31 2020.
Thanks for letting us know Gahan!
Hi Spacewalk is not viable solution, as it is no being actively developed or used
Your omitted RedHat Satellite Server and its base open-source derivatives Foreman and Katello as top products for Linux patching and configuration management. They should be included as they beat Spacewalk and many of your other products hands down for features and usage
There are also good native cloud tools like AWS Patch Manager, that deserve a mention
Thanks for the feedback Otto! We agree with your suggestion, Red Hat Satellite and its open-source derivatives are worthy candidates for this list.