The best way to defeat malware is to understand it.
Security experts use a variety of tools and techniques to analyze malware to help develop malware detection systems. In this article, we’ll review some of the best malware analysis tools on the market and see exactly how they work.
Here’s a quick overview of our top picks for best malware analysis tools:
- ManageEngine Malware Protection Plus EDITOR’S CHOICE This next-gen antivirus uses AI to detect known and unknown malware threats, and adapts to the evolving threat landscape to keep your systems safe from malware attacks. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Cuckoo Sandbox This community project was developed by hackers who wanted to better understand the techniques of malware. The tool is completely free to use. It is a downloadable software package for Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android.
- IDA Pro A highly technical tool designed with forensic and cybersecurity pros in mind.
- CrowdStrike Falcon Insight This EDR analyzes malware on two levels and also identifies intruder activity.
- Hybrid Analysis Simple web-based tool, ideal for researchers looking to perform malware searches
- Limon Developed to detect Linux-based malware
- VirusTotal A massive repository of malware signatures available online for both end-users and researchers alike
- Wireshark Provides deep packet inspection to uncover malware communicating across a network
- PeStudio Designed to streamline the analysis process for malware researchers
- Fiddler Identifies malicious activity by monitoring HTTP/S traffic via proxy
- Process Monitor Uncovers the relationship between executables and procedures to help identify malware and its behavior
What to look for in malware analysis tools
Not all malware analysis tools are created equal. Some tools require a higher level of skill, while others can provide a high-level analysis automatically. However, here are a few key features to keep an eye out for.
Open Source Tools
Open-source tools allow anyone to view the source code, make changes, and build integrations or add-ons. This flexibility empowers creative researchers to make their features and ensures that tools aren’t indeed malware themselves.
Tools that follow an open-source framework usually have more dedicated communities, fostering more collaboration, information sharing, and a longer lifespan of the tools. Open-source projects also have a more comprehensive array of integrations, which can be vital if you incorporate a tool as a critical component of your malware analysis strategy. While not being open source isn’t a deal-breaker, it’s a “plus one” when comparing multiple tools.
Ease Of Use
Ease of use doesn’t just mean it has to be friendly to a non-technical audience. Malware analysis can get complicated quickly, so staying organized is critical even for security professionals. Some web-based scanning tools use an easy-to-use drag-and-drop feature to make it as simple as possible to analyze malware. The tradeoff is usually those tools offer fewerSo while manual tools for researchers.
On the other hand, manual analysis tools are geared towards cybersecurity professionals and often have a steep learning curve. Understanding what you’re looking for in a malware analysis tool ahead of time and help guide you through picking one. Often researchers use numerous tools to get the job done.
Large Malware Collection
The size of their threat library limits tools that use a signature-based approach for detention. This means the more popular a signature-based analysis tool is, the better it will be to detect malware within a file. Signature detection relies on fingerprinting each type of malware along with any variant that might be present. This requires a massive threat library to be effective and works best when paired with machine learning or behavioral analysis tools. Since undocumented virus variants haven’t been fingerprinted, they go undetected in systems that don’t also look at the behavior of the file.
Machine Learning & Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are some of the most powerful tools you can use in malware detection and analysis. Machine learning helps identify patterns and trends in malware, which is vital for detecting zero-days and undiscovered threats. Rather than fingerprinting each threat, machine learning looks at the behavior of a file and compares it to millions of known instances of other types of malware and non-infected files.
By understanding the differences between malicious behavior and expected behavior, machine learning can aid researchers in identifying malware more quickly and uncover complex behavior patterns that would take humans hours to determine.
What is a sandbox?
A sandbox is a secure virtual environment segmented from the network to test and analyze malware samples specifically. Sandboxes are a flexible and customizable way to see how malware reacts to different antivirus programs, operating systems, and countermeasures. Using a sandbox protects your entire network and operating system from infection while studying the impacts of malware. Many malware analysis tools come with a sandbox environment or support sandbox environments. A good sandbox environment is indistinguishable from a natural operating system, so intelligent malware won’t act differently when observed.
What is an Indicator Of Compromise (IOC)?
An IOC is the digital equivalent of a trail of breadcrumbs left behind by malware. IOCs help investigators identify a problem on the network or operating system and aid in tracking down malware or analysis and remediation. By proactively monitoring IOCs, organizations can detect attacks in progress and shut them down swiftly by malware detection tools.
Malware analysis tools look for IOCs while a suspicious file is being executed and after it has run. By measuring changes made during the file execution and examining the context of those changes, researchers can better understand how malware works and develop better prevention techniques.
Now that we know what to look for, let’s drive into our top picks for the best malware analysis tools.
The Best Malware Analysis Tools
Our methodology for selecting malware analysis tools
We reviewed the market for malware analysis systems and analyzed tools based on the following criteria:
- A system that is able to spot zero-day attacks
- The option to channel activity logs into a SIEM system
- A system that continues working if the device it protects is disconnected from the network
- A detection system that is kept up-to-date
- A malware scanner that doesn’t slow down the CPU of the protected device
- A free trial or a demo system for a no-obligation assessment opportunity or a free tool
- Value for money from an effective malware analyzer that is offered at a reasonable price or is free to use
With these selection criteria in mind, we selected a number of excellent malware analysis tools that offer constant protection without costing too much.
1. ManageEngine Malware Protection Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Malware Protection Plus is a Next-Gen AntiVirus (NGAV) that leverages AI to detect malware threats before they impact your system. With a combination of deep learning and dynamic behavior analysis, it identifies and blocks known and unknown malware threats. More importantly, it quarantines and disinfects the existing malware, without requiring any human intervention. As a result, your modified files and registries are automatically restored as part of the malware remediation process.
Key Features:
- Signature-based Detection: Combines traditional methods to identify known malware threats based on their patterns and signatures.
- Fileless Malware Detection: Identifies malware that operates without files. These malware kinds typically evade traditional antivirus software, but Malware Protection Plus detects them.
- Advanced Memory Scanning: Uses deep process inspection to detect in-memory threats.
- Real-time Detection: Analyzes patterns and behaviors using AI to detect and mitigate threats in real-time.
- Ransomware Defense and Recovery: Along with malware, it also detects and neutralizes ransomware attacks.
Why Do We Recommend It?
Malware Protection Plus offers strong protection against malware and ransomware. Going beyond traditional strategies, it uses deep inspection and behavioral analysis to detect threats in a threat landscape that’s becoming increasingly sophisticated and tech-driven. Its advanced approach that combines techniques like dynamic behavior analysis and memory scanning helps identify both known and unknown threats.
In particular, we like its self-remediation feature, where the tool automatically restores infected files and registries to their original state without any manual input. Also, what impressed us is its anti-exploitation techniques that prevent attacks from capitalizing on the existing vulnerabilities.
These advanced features come through a simple user interface that provides complete visibility and control to all users. Due to this combination of a simple user interface and advanced features, Malware Protection Plus runs on millions of endpoints today. The best part is that it has a greater than 99% accuracy rate in ransomware detection while using less than 1% of system bandwidth.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for Managed Service Providers (MSPs), IT administrators, and security teams managing multiple endpoints in medium to large organizations. It is particularly useful for organizations that want to upgrade from a traditional antivirus to an intelligent system that offers comprehensive protection. It is also a good choice for companies handling sensitive data and operating in regulated industries like healthcare and insurance.
Pros:
- Low system impact.
- Built-in tools for detection and remediation.
- Automated processes.
- Use of advanced technologies.
- Combined ransomware and malware protection.
Cons:
- No native support for non-Windows systems.
The annual subscription for a minimum of 50 workstations starts at $745, while the perpetual license starts at $1,863. It costs extra to add more technicians and for services, like adding a failover, secure gateway server, and multi-language pack. This tool offers extensive training as well. Get started with a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine Malware Protection Plus earns our Editor’s Choice for its all-in-one approach to endpoint security and malware defense. Its use of different advanced techniques ensures that known and zero-day malware and ransomware threats are stopped in real-time. Plus, its automated remediation process and root-cause analysis reduce the burden on employees to continuously protect systems from emerging malware threats.
Its ease of use, integration into the larger ManageEngine ecosystem, detailed audit logs, and hardening of endpoint vulnerabilities are other reasons to use this tool today.
Download: Start a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/malware-protection/
OS: Windows
2. Cuckoo Sandbox
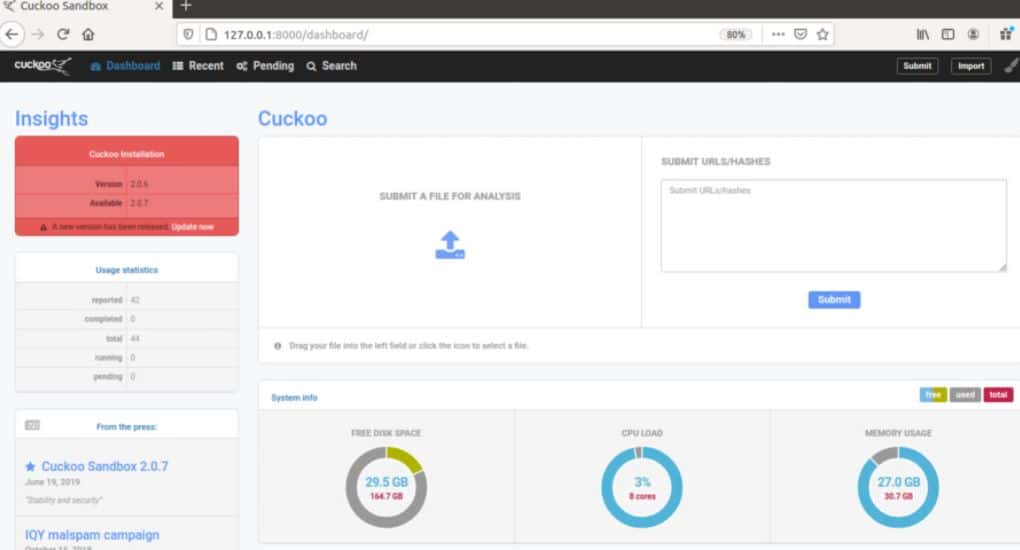
Cuckoo Sandbox is one of the most popular open-source malware analysis tools on the market. The tool is handy as it works automatically to study the behavior of malware. Simply input the suspected malware file into Cuckoo, and it will provide a highly detailed report of the file’s behavior.
Key Features:
- Behavior analysis: It conducts in-depth behavior analysis and executes the malicious files in an isolated environment to analyze their behavior and other records.
- Network analysis: The tool has multiple tabs for different network protocols, allowing users to filter the information on TCP, UDP, DNS, HTTP, and other protocols.
- Detailed reports: the tool actively analyzes the network and system and generates detailed reports on network activities, file modification, system calls, and other detected suspicious data.
- Open-source and modular: The best thing is that it is open-source, and it supports scripted analysis that allows testing on multiple machines.
- Malware analysis: Analyzes suspicious files and URLs in an isolated environment to observe their behavior.
Why do we recommend it?
Cuckoo Sandbox is a free tool, which makes it popular, and it can identify malicious software even if it is the first time it has infected a device. The package has many other functions, such as network traffic analysis and it can be automated to provide constant monitoring.
The platform opens the file in a controlled but realistic environment. This is key as some stealthy forms of malware have been known to evade detection by not executing if a sandbox environment is detected. In addition, unlike other malware analysis tools, Cuckoo Sandbox is easier to use, especially for new to cybersecurity.
Cuckoo allows users to customize their sandbox environment and test files in Windows, Linux, macOS, and Android virtual environments. Behind the scenes, API calls, DNS requests, registry changes, and network traffic are all recorded and automatically analyzed for reporting. The tool generates very detailed but not overwhelming reports, allowing non-technical users to understand the details without neglecting key data points.
Users can also use a host of manual tools to analyze malware and its impact on a system. For example, researchers can perform advanced memory analysis of the infected system through additional integrations into Volatility and YARA.
Who is it recommended for?
System administrators who have the skills and time to create automation scripts will love this tool. You run it on a suspicious file and get a report but you can put it into a script and create automated antivirus monitoring, which can also extend to network activity. The software runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android.
Pros:
- Active community support: if you face any difficulty during the usage or any feature understating, you can get help from its active community support.
- Trace API calls: It traces all API calls and minor information to understand the activity behavior and translate it into easily understandable language.
- Analyze encrypted data: It can also help analyze network traffic that is secured and encrypted by SSL/TLS.
- Easy integration: users can easily integrate the cuckoo sandbox with the existing framework and system without any hassle.
- Multi-platform support: Supports analysis on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Android environments.
Cons:
- Needs technical expertise: you might need to have technical knowledge to set up and configure this tool properly on the system.
Cuckoo secures a spot on our list for its flexible open-source approach to malware analysis and its ability to automatically create malware reports with little technical skills required. In addition, Cuckoo is entirely free to use.
However, there are a few points about the Cuckoo Sandbox that make us a little uncomfortable. For a start, the domain’s root page: cuckoosandbox.org is a page in Korean about Korean sports betting. Also, there seems to be a dual code tree for the website: there is both an about and an about.html page, which are different. The development team openly describes themselves as hackers.
3. IDA Pro
IDA Pro is one of the more advanced malware analysis tools geared towards cybersecurity professionals. The tool is an interactive disassembler and debugger that allows researchers to take apart potential malware files for manual analysis manually.
Key Features:
- Open-plugin architecture: it includes SDK for all IDA users, you can use programmable plugins to add extra functionality to your system.
- Lumina server: Lumina servers basically hold metadata about various functions to create disassembly listings via user search.
- FLIRT: the FLIRT feature monitors the standard library functions generated by the compiler to improve its use and readability.
- Programmable: Users can automate simple to complex tasks with the help of a macro language like IDC/IDA Python.
Why do we recommend it?
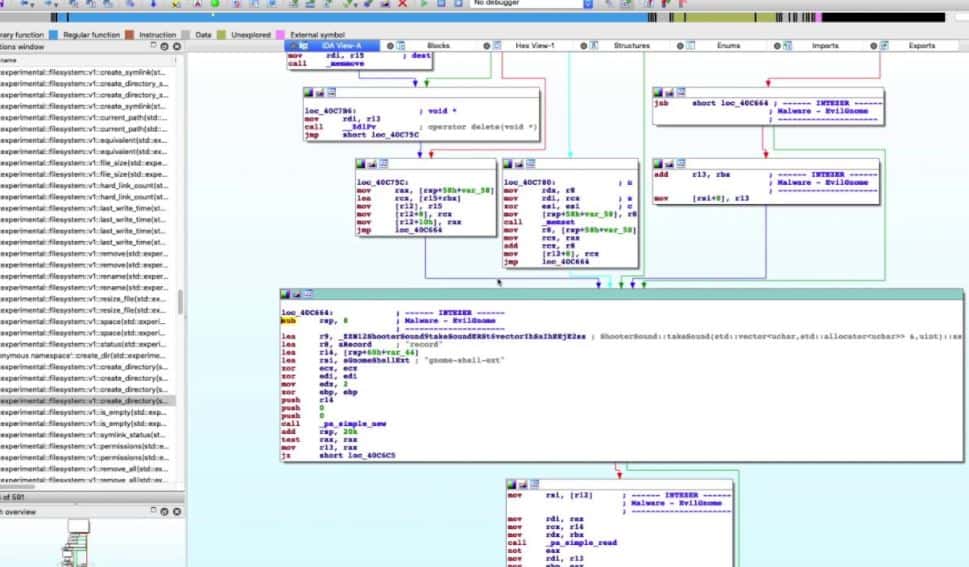
IDA Pro is a reverse engineering tool. It scans compiled programs and “decompiles” them. This process involves running the program and then looking at the actions performed by the chip, such as the movement of numbers in and out of registers. These actions can then be described by Assember instructions, which is the language into which programs are compiled.
IDA Pro is highly visual and cleanly displays the binary instructions executed by the processor in assembly language. The platform can also generate assembly language source code from machine code to make the malware analysis processor easier for humans to read and less complex.
IDA can debug multiple targets and supports remote applications that span across multiple platforms on the debugging side. The debugger is highly flexible and supports 64-bit systems as well as numerous integration possibilities. The platform runs on an open plugin architecture, meaning its functionality is easily extended via pre-built plugins or through the SDK for registered users.
Who is it recommended for?
IDA Pro is an important tool for use by cybersecurity consultants. Reverse engineering is a very specialized field and is a little different from penetration testing. You don’t have to buy IDA Pro because there is a free version: IDA Free. Both packages will run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Pros:
- Compatible with multiple OS: this tool can be easily used on Mac, Windows, and Linux for malware analysis and checking for suspicious things.
- Multiple debugging targets: It supports cross-platform debugging capabilities, which help handle remote applications and check for malware and threats.
- Comprehensive analysis: It comes with a disassembler and debugger, so it keeps complete checks on the system and tracks unusual activities.
Cons:
- Need more RAM and space: Users found it difficult to run Hex-Rays IDA on a virtual machine as it required more RAM for effective processing.
All in all, IDA Pro is incredibly versatile and robust and is best suited for cybersecurity researchers who want to perform their manual malware analysis. IDA Pro’s pricing varies depending on your target operating system, license type, and Edition, with prices starting from $365.00 USD.
4. CrowdStrike Falcon Insight
CrowdStrike Falcon Insight is an extended detection and response (EDR) solution that draws activity data from endpoints and analyzes those records for signs of malware and intruders. The CrowdStrike Insight system performs analysis at two levels: on the endpoint and on the cloud.
Key Features:
- Full-attack visibility: it gives full visibility of the attack by tracking third-party sources to make a wise decision based on the attack picture.
- Fast and lightweight: This tool has less operational complexity, which means you don’t need to perform any operations or reboot; it automatically gets deployed in a few minutes.
- Industry-leading threat intel: It provides detailed information about threats, including automatic submissions to sandboxes and comprehensive profiles of threat actors, so you can understand your dangers.
- AI-powered protection: Falcon Insight uses advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning to find and stop tricky threats. It doesn’t just detect them; it also prevents them from causing harm.
Why do we recommend it?
CrowdStrike Falcon Insight creates a private threat intelligence network and also contributes to a global malware database. The Falcon system relies on a local antivirus system that needs to be installed on each endpoint. This combats malware and also uploads activity data to a central threat analysis unit in the cloud.
Each protected endpoint needs a software package installed on it. This is also available as a standalone product, called Falcon Prevent and it is a next-generation anti-virus system. Falcon Prevent is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. The tool is an anomaly-based detection system. This means that it gathers activity data and derives a record of standard activity. This is a machine learning process that constantly adjusts the assessment of the activity baseline. Many cybersecurity tools now use this technique, which is called user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA). Behavioral outliers are flagged for investigation.
The Falcon Prevent unit ensures that protection continues even when the device is disconnected from the network and the AV can’t communicate with the Insight system in the cloud. Falcon Insight gathers activity data from all protected endpoints, giving it a global view of your system.
The Insight system performs threat hunting on a pool of endpoint activity data and also gets a feed of Indicators of Compromise (IoC) from the CrowdStrike research team. The cloud-based malware analyzer sends instructions to endpoints when it identifies an attack. This blocks the lateral movement of malware by creating a private threat intelligence feed.
Who is it recommended for?
The CrowsdStrike system is a little too pricey for small businesses. The tool is easily expanded just by installing Falcon Prevent on extra endpoints. The threat detection system works both locally and globally. It covers both intruder activity and malware behavior. CrowdStrike analysts contribute assessments.
Pros:
- Precision and automation: It provides Real-Time Response (RTR). Users can directly access systems that contain threats to execute commands and scripts according to severity.
- Experts at the ready: You can always get help from experts and benefit from proactive threat hunting and the top-rated Managed Detection and Response (MDR) service, which is available 24/7.
- Technical risk assessment: The tool conducts technical assessments to prepare responses. Hence, you can respond to widespread attacks and enhance your cybersecurity practices with comprehensive services tailored to your needs.
- Fully managed service: It comes with a fully managed solution where experts configure and operate the system for you. Additionally, users can access the remote remediation service without the need for on-site intervention.
Cons:
- Clarity in console menu: Uncertain menu structures or labeling within the console may make it challenging for users to navigate or locate specific features.
Protected endpoints in the scheme can be located anywhere – on multiple sites and also in the homes of telecommuting workers.
5. Hybrid Analysis
Hybrid Analysis is a web-based is a web-based malware analysis tool that combines ease of use with a customizable approach that allows users to generate reports quickly. For example, users can input a file in questions and receive feedback in just a few seconds through a drag-and-drop interface. Alternatively, files hosted on websites can be scanned by linking directly to them.
Key Features:
- Gives a holistic view of malware: hybrid analysis uses static and dynamic environments to showcase a comprehensive picture of malware.
- Run-time data analysis: All the source paths leading to malware are extracted using runtime and data memory dumps.
- File/URL sandboxing: This open-source tool easily sandboxes malicious software, results, and other executables using IOC and screenshots.
- Detailed analysis with reports: Users can quickly identify malware through YARA rules, string, and hex patterns to understand the malware threats in detail.
Why do we recommend it?
Hybrid Analysis is a web interface to a number of analyzers, including CrowdStrike Falcon Sandbox – CrowdStrike promotes it on the Falcon Sandbox web page as a free trial for its tool. The system also runs your file through Virus Total. It can examine zip files and Web pages as well as executable files.
The platform is powered by CrowdStrike Falcon, which uses a hybrid analytical approach to identity threats. This methodology looks at both threat signatures as well as general behavior to uncover malicious activity. In addition, machine learning algorithms tap into threat intelligence from multiple sources, including new uploads the system receives. Users can upload and share collections of files to get instant feedback, which is a great feature many online scanners seem to lack.
Hybrid Analysis also comes with a few advanced search options, allowing users to comb over 15 million indicators of compromise by IP, domain, or hash signature. Researchers can also search YARA as well as filter by string search that matches HEX and ASCII strings.
Who is it recommended for?
The tool doesn’t require you to install any software and you don’t need to sign up for an account in order to use it. However, you do need to enter your email address in order to run a scan. The tool publishes a report on its Web page with the results of your file’s analysis.
Pros:
- Dynamic analysis: it gives all basic details about network connection and malicious indicators regarding behavior and usage to allow users to make smart decisions.
- Detects third-party unknown threats: This tool has various other options for sandboxing files, such as YARA rules for string implementation.
- Automated reports: No manual headache, malware analysis is performed automatically, and reports are also generated.
- It supports intelligence sharing: users can upload and share groups of files that are checked in different ways. All the uploaded files become searchable by everyone, so more users can collaborate and work together for productivity.
Cons:
- Limitation in file uploading: Many users find that there is a limitation to file uploading, and file scanning is sometimes very time-consuming.
The platform offers a convenient portal for online malware analysis for both technical and non-technical users. Researchers will find the advanced search functionality convenient, while casual users will receive a straightforward answer if their file is infected.
6. Limon
Limon is a sandbox malware analysis tool designed to study malware found in Linux environments. The platform was developed in Python and automatically collects, analyzes, and reports indicators of Linux malware. For those who want to comb over the details manually, Limon allows users to inspect the operating system before, during, and after the malware execution in a sterile environment.
Key Features:
- Malware sandboxing: Allows users to examine Linux malware before, during, and after it runs. It uses open-source tools for static, dynamic, and memory analysis, allowing users to better understand how malware behaves and what it accomplishes.
- Runs on Linux: Limon was developed mainly for use in Linux operating systems. Therefore, it works with Linux-based systems and environments.
- Memory analysis: Limon allows you to analyze the memory of a malware-infected PC. This aids in the discovery and removal of malware by providing insight into how it acts within the computer’s memory.
- Determine Fuzzy Hash: Limon assists in analyzing malware samples to identify similarities using a technology known as “fuzzy hashing.” It analyzes the percentage similarity of files, making it simple to identify identical files.
Why do we recommend it?
Limon is a command line tool for Linux. This package is a sandbox, which runs a suspicious file in a safe environment and analyzes the program’s behavior. It scans the code of a program if it is available and it also extracts activity from memory during execution.
The platform monitors the behavior and child processes of the suspected malware to help determine the nature, purpose, and context of the attack. You can also configure Limon to perform memory analysis and review the data dump after the malware execution.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is most suitable for use by cybersecurity analysts. It is free to use and it performs both static and dynamic analysis. As a command line tool, it isn’t quite as user-friendly as the rival Cuckoo system. However, if you don’t have a GNOME environment, you will need this command line utility.
Pros:
- Determining the File Type: it helps to identify the file type of malware, which will help you better understand its target environment.
- Determining the Cryptographic Hash: Cryptographic hash values, such as MD5 and SHA1, uniquely identify files, making it easier to monitor malware versions even when they clone themselves or drop new malware.
- Strings Search: Limon searches for plain text characters in files, providing information about their functionality and accompanying commands. While not comprehensive, it can provide useful information such as URLs, IP addresses, and attack commands.
- File Obfuscation Detection: Limon detects tactics used by malware developers to disguise their code, such as packaging and encrypting files, which aids investigators with reverse engineering and comprehending the infection.
Cons:
- Limited Platform Support: Limon is only compatible with Linux systems hence restricts its usage to Linux-based environments and users with other OS cannot use it for analyzing malware.
The tool is very flexible and is similar to Cuckoo Sandbox in how it offers an automatic malware analysis option. Limon is ideal for anyone specifically studying malware in Linux environments but isn’t the best option for those studying viruses that infect other operating systems or can leap across the platform.
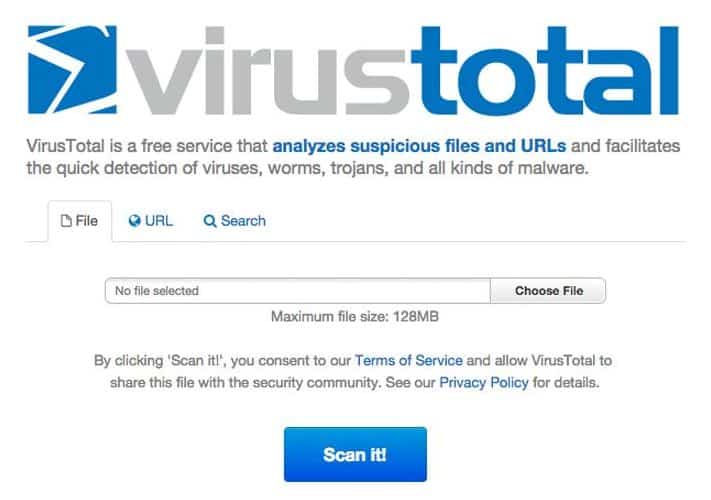
7. VirusTotal
VirusTotal has one of the largest repositories of malware samples of any online tool, making it essential for anyone analyzing malware. VirusTotal allows users to upload samples, scan suspicious URLs, and perform manual searches.
Key Features:
- Static Threat Indicators: It collects signals and identifies suspicious signals, such as OLE VBA code streams in Office document macros, irregular cross-reference tables in PDFs, and other properties, to track threats and malicious activity in your network.
- Behavior Activity and Network Communication: this tool helps you understand how malware behaves and communicates. Users can test files in controlled environments to trace their actions and interactions and generate detailed reports.
- Backend Information: VirusTotal runs backend activities such as sandboxing, inter-file relationship building, email attachment extraction, URL-to-file mapping, and honeypot file labeling.
- Powerful Search Tools: Users can search for similar files using various hashes/algorithms, including deep content similarity searches, imphash, icon visual similarity, and their own in-house structural feature hash.
Why do we recommend it?
Virus Total is one of the scans included in the Hybrid Analysis scan. This is an online service. You either drag a file over or use the file selector feature on the site to get a scan. You don’t need to enter any personal details to get a free scan.
The platform is one of the more user-friendly tools, making it more popular among casual users who want to scan their files for malware. This, in turn, makes VirusTotal even more powerful, as it records, catalogs, and categorizes every malware sample sent to its system. VirusTotal provides swift analysis paired with basic high-level details of the type of malware discovered for users looking to determine if a file is infected quickly.
Who is it recommended for?
There are three levels of service for Virus Total. Either access the scanner anonymously in the website, join up for the community to get more details and access to cybersecurity resources, or pay for a subscription to VT Enterprise. The free Virus Total system provides you with a presentable report.
Pros:
- Complete Scanning Information: with the help of comprehensive information, users can access all reports for a particular sample, understand how threat detections change over time, and discover how long malware remains active.
- Combine Modifiers: it also allows to combine different search parameters to identify files that match complex criteria. This way, you can filter out unnecessary information and focus on relevant threats for your investigations.
- Dynamic Information: Sandbox execution on major operating systems such as Windows, Android, macOS, and Linux provides users with insight into malware activity.
- Submission Metadata: you can access metadata that gives information about first-seen and last-seen dates, number of submissions, submission file names, submission countries, submission dates, and more to analyze the content effectively.
Cons:
- Slow File Scanning: Many users have noticed that scanning files takes a lot more time, which may result in delays when analyzing large volumes of data.
The search function is easy to use and allows researchers to search by URL, IP, domain, or file hash. While tools like Reverse.it provides additional HEX search parameters; VirusTotal may have more threat signatures recorded to compare against your file. Either way, if you’re looking for fast and straightforward malware analysis, VirusTotal isn’t a tool you’ll want to pass up.
8. Wireshark
Chances are you already know what Wireshark is about. If not, here’s a quick rundown. Wireshark is one of the most popular tools for capturing and analyzing network traffic. In addition, the tool allows for deep packet inspection, a result that is vital for advanced network troubleshooting and uncovering stealthy malware activity.
Key Features:
- Packet Capture and Analysis: Wireshark allows users to capture and analyze network traffic effectively. This capability is crucial for understanding how data moves across networks and identifying potential issues or threats.
- Deep Packet Inspection: The tool offers deep packet inspection, which allows users to delve into packet contents for detailed analysis. This feature is important for advanced troubleshooting and detecting stealthy malware activity within the network.
- Memory Analysis: This supports and allows users to examine network data stored in memory. This feature can be valuable for uncovering malicious activity that may not be easily visible through traditional packet analysis.
Why do we recommend it?
Wireshark uses the Pcap system (libpcap or WinPcap) to collect packets. The tool has its own search and filtering language so you can reduce the volume of captured packets for analysis and this same language can be used to analyze packets. This is a free tool.
Network traffic can be recorded, filtered, and sorted through to understand how malware impacts network traffic and interacts with firewalls. In addition, it can uncover multiple protocol layers supports numerous integration into other malware analysis tools.
Who is it recommended for?
Cybersecurity analysts use this tool extensively. It can also be of use to network managers. However, the packet capture process can produce a large amount of data and if you store it you could end up using a lot of disk space. This software runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Pros:
- Free Tool: Wireshark is free and available for multiple users, including cybersecurity analysts and network managers.
- Comprehensive Query Language: The tool includes its search and filtering language. It allows users to reduce the volume of captured packets for analysis.
- Flexible and Extensible: This tool is flexible for malware analysis. It supports integration with other malware analysis tools. You can also customize with the customization options according to your malware analysis needs.
Cons:
- Signature Knowledge Required: Users need to be familiar with signatures to effectively search for specific types of network activity or threats. This requirement may be challenging for less experienced users.
Wireshark’s flexibility and massive community make it a staple malware analysis tool everyone should have in their arsenal. In addition, Wireshark is entirely free to use.
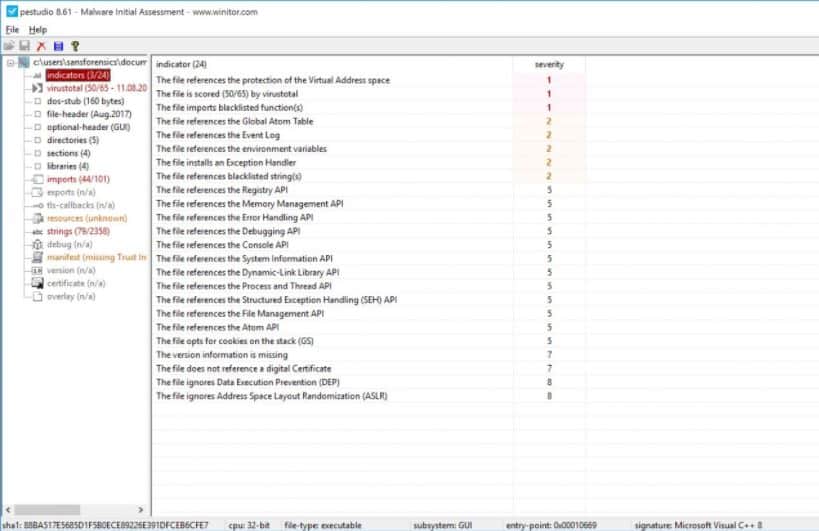
9. PeStudio
PeStudio is a simple yet powerful tool that allows researchers to analyze Windows-based malware and quickly identify suspicious behaviors, supply unique hashes, and uncover related processes to the malware.
Key Features:
- Signature Search: PeStudio offers a complete signature search capability. This allows users to identify known malware patterns easily. It improves efficiency in detecting malicious code.
- Suspicious Code List: This tool provides a pre-selected list of suspicious code patterns. This feature allows you to identify the process of malicious behaviors.
- Free Version: You will get the free version. It is easy for cybersecurity professionals and researchers without installing financial limitations. This accessibility secures wider adoption and usage within the cybersecurity community.
Why do we recommend it?
PeStudio is a digital forensic analysis tool that is widely used by cybersecurity analysts. One problem with the tool is that it can take a very long time to run and the output is extensive, which also takes a long time to explore. This is a free tool for Windows.
The platform is designed for professionals but adds plenty of quality-of-life features that streamline the malware analysis process. For example, as soon as a binary is loaded, PeStudio provides hashes and automatically runs them through VirusTotal.
If the malware is being obfuscated through code wrapping or packing, PeStudio can detect this through a form of entropy scanning. This essentially assigns a numerical value to how much entropy a file has. The higher the number, the more likely that code is being purposely hidden within the file.
Who is it recommended for?
Cybersecurity analysts regularly use this tool. The system isn’t really aimed at casual users, so those who encounter malware are more likely to pass that file to an analyst who would use Pe Studio rather than having a go with the tool themselves.
Pros:
- Automatic Scan: PeStudio automatically scans for well-known functions connected with malicious activities. This helps you quickly find potential dangers in analyzed files.
- Highlighting of External References: This helps users point out connections to outside sources, like command and control servers. It improves visibility into potential indicators of compromise and threat detection.
- Batch Processing (Paid version): The paid version of PeStudio offers batch processing capabilities. This version allows analysts to analyze multiple files at the same time, boosting productivity and efficiency in malware analysis.
Cons:
- Limited to Windows: PeStudio is only available on the Windows operating system. This limitation makes it harder for analysts who depend on macOS or Linux platforms to use it effectively.
The program highlights numerous indicators of compromise and even looks at what a program imports from Windows APIs to determine malicious activity. PeStudio is a great place to start for malware analysis, especially if you’re confident you have malware on your hands and want to study it further.
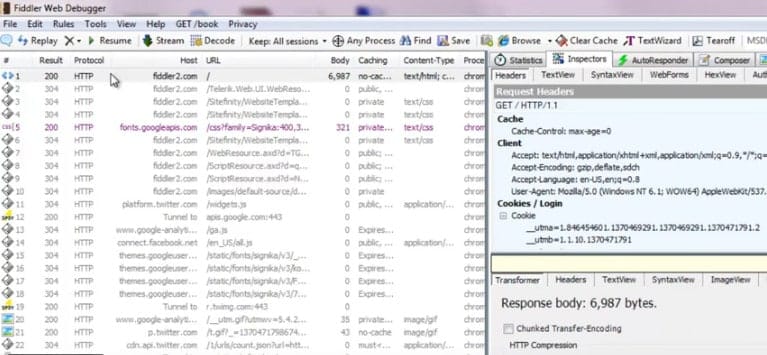
10. Fiddler
Fiddler is used to monitor active HTTP/HTTPS connections on the target machine, which can uncover hidden connections used by malware to contact their command and control (C2) servers. C2 servers are used by malware authors to exfiltrate data, send commands to installed malware, and open additional backdoors later use.
Key Features:
- Web Debugging Tool: This tool is designed for developers to debug web applications. It works as a proxy, focusing on web traffic. You can identify and analyze active HTTP/HTTPS connections.
- Identification of Communication: It easily spots all communication happening through web applications. Fiddler is very useful. It finds connections linked to malware’s command and control (C2) servers.
- C&C Contact Detection: Fiddler is good at finding connections and watching them command and control servers. These servers are important for malware creators to control and manage their harmful software.
Why do we recommend it?
Fiddler is a bug scanner for developers. It operates as a proxy and operates on Web traffic, so it focuses on We applications and you would need our coffee to be pretty much finalized before running the test. Therefore, it is an acceptance testing service that can be placed in a CI/CD pipeline.
Fiddler acts as a web proxy to capture and analyze traffic and is a simple tool to set up even for beginners. A good amount of analysis is already done for the user, where the tools highlight current connections and scan the document for any known malicious IP addresses or domains.
Since threat actors use multiple domains to host their malware, having a built-in way to detect all C2 servers is convenient when dealing with stubborn malware.
More advanced users can dive into the details of the traffic through the inspector tool. This helps paint a clear picture of which programs are communicating outbound and the context of that communication. Users even can modify requests, potentially highlighting flaws in how C2 servers communicate back with their infected hosts.
Who is it recommended for?
Fiddler is intended for use by Web app development teams. There are many versions of the system that range from the free Fiddler Classic, which runs on Windows up to the pricey Fiddler Core, which costs thousands of dollars. Fiddle EVerywhere and Fiddle Jam are affordable subscription services.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Fiddler is easy to set up and use, even for beginners. Its interface simplifies the process of capturing and analyzing web traffic. This gives users with valuable insights into the connections made by various programs.
- Built-in Analysis Features: highlight current connections and scan documents for known malicious IP addresses or domains, helping you find malware-related activities.
- Inspector Tool for Advanced Users: The Inspector tool allows advanced users to track traffic details. It helps users understand outbound communication and shows potential flaws in talking to C2 servers. This flexibility is beneficial for cybersecurity researchers.
Cons:
- Not suitable for virus scanning: Fiddler is great for web security testing. But it’s not a virus scanner. It is more focused on web traffic analysis and may not be suitable for detecting all types of malware.
Fiddler is a rock-solid tool that is great for both new and experienced cybersecurity researchers. Fiddler Classic is free for 30 days and then $10.00 per month.
11. Process Monitor
Process Monitor or ProcMon is a tool developed by Windows to allow additional insight into processes and the file system in real-time. You can think of this as a much more detailed version of Task Manager. However, since the interface is so familiar, the tool is excellent for those new to malware analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Insight: Process Monitor gives detailed, real-time insight into processes. It also covers the file system. It offers a deeper level of understanding than traditional task management.
- Source Identification: This tool effectively identifies the source of processes. It helps you trace any suspicious activity.
- Linked process Highlighting: Process Monitor highlights linked processes. So you can understand the relationships between different activities within the system.
Why do we recommend it?
Process Monitor is mercifully quick and it can be a lifesaver if you are waiting for some other long-running forensic analysis tool, such as PeStudio, to finish. This tool is a mainstay for digital forensics analysts and it is free to use, which makes it a much-loved tool by cybersecurity consultancy managers as well.
Process Monitor allows you to track down what created each process and comes with several filters that will enable you to see the child/parent relationship between an executable easily. When malicious files such as Word documents detonate, they often launch scripts or open ports stealthily in the background. ProcMon makes it easy to see this activity in real-time and through recorded analysis in CSV format.
Who is it recommended for?
ProcMon is a must-have tool for any cybersecurity analysis team. The package is free to use and it runs on Windows. There is also a version for Linux. This tool gives you a quick rundown of some important events, such as process spawning, giving pointers on areas of a file that require deeper analysis.
Pros:
- Free Tool: Process Monitor is a free tool. Cybersecurity analysts can use it without worrying about the budget.
- Fast and Easy Analysis: It offers easy analysis. This is beneficial when waiting for other lengthy forensic analysis tools to complete tasks. This speed enhances efficiency in cybersecurity analysis.
- Multiple filters: Users can filter monitoring by keys, processes, IDs, and values. These filter options allow you to focus on an analysis of system interactions and behavior.
- Advanced Logging: The logging structure can handle large volumes of captured events and log data, ensuring reliable tracking and analysis, even in complex IT environments.
Cons:
- Only for Windows: As a Windows tool, Process Monitor is limited to Windows environments. This limitation may leave out users who operate on different operating systems.
While Process Monitor won’t allow you to pick apart a binary, it will quickly highlight suspicious activity and enable you to investigate deeper into a situation. ProcMon is a Windows tool and is available for free.
Malware Analysis Tools FAQs
What is malware analysis tool?
Malware analysis tools search through the code of an executable file to look for specific actions that show typical activities in memory or contact with Command and Control servers and identify the system as malicious. If the executable is compiled, the malware analyzer will run the program in a controlled environment and extract its instructions from memory.
How do you analyze malware?
Although each piece of malware might be written to be completely unique, there is a pattern of undesirable behavior that can be sought out in code that would show the program to have malicious intent. Activities in memory and contact with external servers are typical activities to look out for. Specific commands that are well known for probing system vulnerabilities are known as Indicators of Compromise (IoC). While benign processes might call these functions, several together in a program would flag it as malware.
What are the three 3 steps of malware analysis?
There are three types of malware analysis and you should attempt all of them in order to perform a full assessment. These are:
- Code – also known as static analysis, searching for keywords and functions in the program if it is accessible.
- Behavioral – also known as dynamic analysis, this scanner runs an executable in a protected environment and looks at the interactions that it has with system resources.
- Memory Forensics – runs the executable and extracts its actions from system memory, enabling code scanning on compiled programs.