Keeping software up to date is one of the most critical aspects of maintaining a secure, efficient, and functional IT environment. Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities, bug fixes, performance improvements, and compatibility enhancements.
Here is our list of the best software update tools:
- Atera RMM Patch Management EDITOR’S CHOICE A complete support solution for IT departments and MSPs, the RMM bundle included with Atera includes a patch management system. Start a free trial.
- NinjaOne (FREE TRIAL) This package of tools for MSP technicians helps managed service providers automate patching and cut costs. This is a cloud platform. Access a 14-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL) An automated patching system for Windows, macOS, and Linux that automatically detects out-of-date software. Runs on Windows Server or can be accessed as a SaaS package. Download a 30-day free trial.
- SuperOps (FREE TRIAL) This cloud-based package includes Asset Management, Policy Management, Patch Management, and Alert Management. The system is also partnered by a PSA module.
- N-able N-sight Patch Management A remote monitoring and management tool that includes a patch management utility.
- Syncro This all-in-one package for managed service provides and it includes a patch manager. This is a cloud-based system.
- SolarWinds Patch Manager A top pick for software updates. Patch management software for Windows that supports WSUS and SCCM with automated patching, a dashboard, patch compliance reports, and more.
- Kaseya VSA Remote monitoring and management (RMM) and patch management software with automated software updates, network discovery, reports, and more.
- Connectwise Automate RMM and patch management software with automated software updates, device discovery, notifications, and more.
- ITarian Patch management software for Windows that can automatically discover devices and deploy updates, with reports, change management, and more.
- GFI LanGuard Patch management software with autodiscovery and automated software updates, reporting, and more.
By neglecting updates, organizations expose themselves to unnecessary risks, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and system malfunctions. For example, hackers frequently exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access to networks or compromise sensitive information.
In addition to security, keeping software current ensures that systems run smoothly, with the latest features and improvements at your disposal. This can lead to enhanced performance, better user experience, and a more stable IT environment. Without regular updates, users may experience issues like slow system performance, software crashes, and incompatibility with other applications, which can disrupt operations and reduce productivity.
Manually managing software updates for an entire organization can be time-consuming, especially in large or complex IT environments. This is where automated patch management tools become invaluable. Automated patch managers streamline the process of keeping software up to date by scanning systems for missing patches and automatically deploying them across the network. This ensures that security patches and updates are applied quickly, reducing the window of vulnerability.
The convenience of automated patch management lies in its efficiency and reduced workload for IT teams. It minimizes the risk of human error and ensures updates are consistently applied, even across large networks or remote environments. Automated tools can also be configured to test updates before deployment, preventing disruptions and ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
The Best Software Update Tools
Our comparison includes a range of tools including patch management tools with automated patching, software updaters, and more. We’ve kept a lookout for those with highly-configurable GUI’s, custom dashboards, notifications, alerts, and automation capabilities.
Our methodology for selecting software updater tools
We reviewed the market for patch management solutions for software updates and analyzed tools based on the following criteria:
- Centralized software updater
- Polling for update availability
- Combined operating system and software updates
- Patch application automation
- Management for a fleet of devices
- A free trial or a demo package for a no obligation assessment opportunity
- Value for money from an automated system that is offered at a reasonable price
With these selection criteria in mind, we looked for systems that will centralize update management for a long list of software installed on a fleet of devices.
1. Atera RMM Patch Management (FREE TRIAL)
Atera RMM is a cloud-based service that provides all of the software that IT departments and MSPs need. The bundle of utilities in the Atera system includes both PSA and RMM functions. The RMM part of the Atera service has a patch management utility built into it.
Key features:
- Patch Automation: Streamlines the process of applying updates across systems.
- Reboot Management: Offers options for post-patch application reboots.
- Multi-Tenant Support: Ideal for managing multiple client environments simultaneously.
- Reporting Insights: Provides comprehensive status reports on patch management activities.
Why do we recommend it?
Atera RMM Patch Management is part of a full remote monitoring and management package that is delivered from the cloud. The Atera system is packaged into plans that all include the patch manager. The interface for the patch manager also enables administrators to command standard maintenance functions, such as clearing out temporary files.
Atera’s patch management function is an automated process. An agent on each client site logs all of the firmware, operating systems, services, and software installed on each host. This enables the central Atera system to check regularly for updates for each. When patches arrive, the Atera patch manager knows which devices they need to be applied to.
Those patches will be applied automatically to each client host. However, the patch manager interface allows individual patches to be put on hold either entirely or for specific endpoints on the client’s system. It is also possible to specify a reboot after the implementation of a patch.
Who is it recommended for?
The Atera system is produced in a version for IT departments and another for managed service providers. Each version includes four plans but the services included in each are different depending on the target market. Plans are priced per technician, which makes the package suitable for all sizes of businesses.
Pros:
- Intuitive Dashboard: Simplifies monitoring with a user-friendly interface.
- Flexible Pricing: Adapts to business size with per-technician pricing, making it accessible for small to large enterprises.
- Comprehensive PSA Tools: Includes a suite of PSA features beneficial for helpdesk and MSP growth.
- Efficient Tracking: Offers SLA and maintenance task time tracking for improved service delivery.
Cons:
- IT Focus: Primarily designed for IT departments and MSPs, which may limit its utility for non-IT focused businesses.
Each installation generates a log record and the patch run also results in a status report. Atera is charged for by subscription with a rate calculated per technician per month. This pricing model is great for startups and growing businesses because there are no upfront costs to start using the system to support customers. Licenses can be added or reduced as the MSP’s technician pool changes in size. Pricing starts at $129 per technician. Atera is available for a free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Atera is our first choice. The feedback system in the Atera dashboard also lists each patch, the devices it was applied to, and the success or failure of the update. Troublesome patch runs can be reapplied either automatically, or individually according to the reason for the installation failure.
Download: Get a Free Trial
Official Site: atera.com
OS: Cloud-based
2. NinjaOne (FREE TRIAL)
NinjaOne is a cloud platform that provides all of the tools that managed service providers need to support the IT systems of their clients. The console for the service is resident in the cloud and can be accessed through any standard Web browser. That means you don’t need to install any software on your site or maintain your own servers. The bundle of tools that are accessed through that dashboard includes an automated patch manager. When considering market validations, NinjaOne’s 11-time acknowledgment by G2 speaks volumes about its capabilities.
Key Features:
- Windows Patching: Ensures up-to-date security and performance for Windows systems.
- Third-Party Updates: Keeps non-Microsoft software current, enhancing overall security.
- Flexible Patching: Offers both scheduled updates and on-demand patching for flexibility.
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne is a rival to Atera. This is an RMM package and it includes a patch manager. The NinjaOne system discovers all assets and creates an inventory. Searches of each endpoint generate a system-wide software inventory. This is the basis for the automated patch manager, which identifies patch statuses for software version numbers.
The patch management system can maintain endpoints running Windows and macOS. The system scans the network of a client site and records all of the connected devices that it encounters. It then scans each device, noting all of the software installed on it. This software inventory includes a record of the version number for each installation of an operating system or application. These version numbers indicate the patch status of each piece of software.
Knowing what software is being managed, the NinjaOne system automatically checks with providers for the availability of patches. When one becomes available, the system copies over the installer and notifies the MSP.
As well as looking out for patches to operating systems, the NinjaOne service will poll for the availability of updates to more than 135 software packages. Patches aren’t installed instantly. The MSP needs to set up allowed maintenance windows for each client site. The NinjaOne patch manager will queue up all incoming patches until the next available maintenance slot. Those patches are then applied unattended.
The console allows for individual patches to be held up for analysis and it is also possible to adjust the expected rollout date and time. Normally, patches are applied out of office hours because it is common for the installation to require a system reboot in order to complete. The NinjaOne logs the actions of the patch manager and patch events with their termination statuses are shown in the console.
Failed patches can be examined and then rerun manually or re-queued for the next maintenance period. The logs generated by the patch manager are also available for SLA confirmation.
Who is it recommended for?
Unfortunately, NinjaONe doesn’t publish a price list, so it is difficult to judge whether this package will be more appealing than Arera for price-conscious small businesses. The NinjaOne system is suitable for use by managed service providers. However, IT departments could also use it.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Toolkit: Integrates a full suite of MSP tools, from remote access to patch management, in one package.
- Automated Processes: Streamlines tasks like inventory management and patch application for efficiency.
- Seamless Integration: Enables smooth data flow between different system components for better management.
- Productivity Tracking: Monitors task completion and staff productivity to optimize operations.
Cons:
- Limited OS Support: Does not support patching for macOS or Linux, restricting service scope for MSPs.
NinjaOne is a subscription service with a rate per monitored device. They provide a full interactive demo where you can experience all the features for yourself. You can assess the platform on a 14-day free trial.
3. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus includes an endpoint scanner to discover which operating systems and software packages are out of date. It then collects the required patches, schedules them for rollout, and applies them at an appropriate time.
Key features:
- Multi-OS Support: Patches for Windows, macOS, and Linux are seamlessly integrated.
- Broad Software Coverage: Automatically updates over 850 software packages.
- Patch Testing: Enables pre-deployment testing of patches for stability.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus provides patching for devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux. It will update the operating systems and any software that is installed on those computers. ManageEngine maintains a repository of verified patches for well-known software packages. The system can also be used to implement routines for updating software that isn’t on the ManageEngine list.
Much of the patch management service is automated. The tool scans all endpoints and notes operating systems and software version numbers. This indicates patch statuses and then the system checks providers for the latest version of each system and gathers patches where appropriate.
You need to set up the system with a calendar of office hours that provides the patch manager with maintenance windows. When patches are available for installation, the patcher will sequence them according to dependencies and then apply them at the next available maintenance window.
While patches are in the queue to be applied, you can query individual patches and test them to see their effects on your system and then optionally put them on pause. Patches are applied out of office hours and you don’t need to sit and watch it run. The service provides completion statuses so you can discover later which patches failed. All actions are logged for compliance reporting.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is particularly interesting for businesses that have computers that run macOS and Linux because there are many update systems for Windows, but not many for those other two operating systems. The software runs on Windows Server or can be accessed as a SaaS, cloud-based platform.
Pros:
- Automated Patching: Streamlines the patch management process with extensive automation.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Offers detailed reports on patch completion and compliance for audits.
- Dependency Management: Skillfully sequences patches to respect software dependencies.
Cons:
- Limited Scope: Does not function as a vulnerability management tool.
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a software package that runs on Windows Server and it is also available as a cloud-based hosted SaaS package. There are three editions of the package and the first of these is free. The Free plan is suitable for businesses with up to 20 workstations and five servers. The Professional edition is good for a LAN and the Enterprise edition will monitor multiple sites. You can get either of the paid versions, on the cloud or on-premises on a 30-day free trial.
4. SuperOps Patch Management (FREE TRIAL)
SuperOps.ai is a package of services for MSPs. This bundle includes PSA and RMM functions. The RMM part of this deal includes Asset Management, Policy Management, Patch Management, and Alert Management. These packages are intended for use by the technicians that implement the management of client systems.
Key Features:
- Automated Processes: Streamlines operations, minimizing manual tasks.
- Windows Endpoint Management: Specializes in managing Windows-based devices.
- Asset Discovery: Automatically identifies and catalogs network devices.
- Activity Logging: Maintains detailed records of technician interventions.
Why do we recommend it?
The SuperOps Patch Management tool is part of a SaaS package of remote monitoring and management tools. This system is delivered from the cloud, so it is able to operate on multiple sites. It will patch software as well as the operating system, but only on devices running Windows.
The Patch Management module is able to maintain the operating systems and software inventories of desktops and laptops running Windows. The service looks through a software inventory that is compiled by an associated asset manager. It then constantly checks with software suppliers for patch and update availability. When one becomes available, the system copies down the installer and queues it up for installation, listing the patch in the system dashboard.
The system is adaptable and presents the subscriber with options over how the patch manager should run. You need to set up a calendar of acceptable maintenance times in the dashboard. The patch manager can be set up to automatically apply those patches or to hold them for improvement.
Patch rollout can occur overnight and technicians can check on the completion status of each patch in the dashboard. All actions are logged for auditing.
Who is it recommended for?
The SuperOps platform is designed for use by managed service providers. It has a number of packages and the RMM-only plan, which includes the patch management service, could be used by IT departments. MSPs benefit from the tool’s multi-tenant architecture to keep the data of clients separate.
Pros:
- Efficient Discovery: Automates the detection of devices, easing asset management.
- Inventory Management: Generates and updates software inventories automatically.
- Proactive Patching: Actively checks and prepares software updates for deployment.
- Flexible Scheduling: Offers customizable patch installation schedules.
- Approval Mechanism: Provides options for patch approval or direct implementation.
Cons:
- Windows Only: Exclusively supports Windows endpoints, limiting versatility.
SuperOps, with its Patch Management module and its associated PSA service is offered in four editions These are Standard (PSA Only) – $79 , Standard (RMM Only) – $99, Pro Unified Basic – $129, and Pro Unified Advanced – $159. These are subscription packages that are priced per technician per month for up to 150 endpoints. All editions are available for a 14-day free trial.
5. N-able N-sight Patch Management
N-able N-sight is a cloud-based system that enables IT departments to manage several sites centrally. This is remote monitoring and management software, so the functions within the package include all of the tools needed by an IT department to successfully run IT services — and that includes patch management.
Key Features:
- Streamlined Automation: Simplifies patch management with automated processes.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Offers detailed status reports on patch management activities.
- Flexible Deployment: Allows on-demand patch rollout for targeted management.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Utilizes a cloud-based system for enhanced accessibility and scalability.
Why do we recommend it?
N-able N-sight Patch Management is a SaaS tool that is part of a remote monitoring and management platform. The N-sight bundle also operates automated monitoring of endpoints and networks and it will trigger the patch manager to queue updates when its routine sweeps spot path availability.
The Patch Manager in N-able N-sight includes a great deal of automation. The service checks on all of the software, services, firmware, and operating systems installed on each site and then makes regular sweeps for available patches.
The network manager can set a daily window when patch rollouts are appropriate. Within this timeframe. The Patch Manager can then be set to automatically apply patches whenever they are available. Patches can also be applied manually through the system and individual patches can be put on hold or canceled.
Overnight patch rollouts occur unattended with statuses of each update shown in the Patch Manager interface. Failed runs can then be investigated and reset for automatic application or applied on demand.
Who is it recommended for?
N-able produces two RMM packages and N-sight is designed for large, well-established managed service providers. Its other product, which is called N-central is designed for use by smaller MSPs and IT departments. Although N-sight can manage endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux, the patching is only for computers running Windows.
Pros:
- Advanced Dashboard: Provides an exceptional monitoring experience, suitable for both large MSPs and NOC teams.
- Scalable Solution: Cloud-based deployment adapts easily to varying business sizes.
- Remote Monitoring: Enables patch management and monitoring from any location via a web browser.
- Effortless Asset Discovery: Automates the discovery of network assets, simplifying inventory management.
- Diverse Administration Tools: A wide range of automated remote administration options supports effective help desk operations.
Cons:
- Complex Interface: Navigating the platform and utilizing all its features can require a significant time investment.
N-able N-sight includes all of the processing power and storage space needed to run the RMM software. IT professionals access the cloud-resident system dashboard through any standard browser and there is also a N-able N-sight mobile app for access when out of the office. The service is changed for by subscription and there is a 30-day free trial available.
6. Syncro

Syncro is a platform of systems for managed service providers. In fact, it includes every tool that an MSP needs in order to operate. This involves Professional Services Automation (PSA) systems, which the managers of the MSP use to run the business, and a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) unit that provides all of the tools that technicians need to support the clients’ systems. That RMM package includes a patch manager.
Key features:
- Automated Patching: Facilitates the seamless application of updates to both software and operating systems.
- Cloud-Based Management: Accessible via any web browser, eliminating the need for on-premise software installation.
- Broad Software Support: Capable of patching Windows, macOS, and over 135 third-party software packages.
Why do we recommend it?
Syncro is a big bundle of every tool that a managed service provider needs, so this isn’t just about its patch management capabilities. The benefit of getting all technician and management software in one package is that interoperability is guaranteed. Activity tracking data from the ticketing system automatically flows into timesheets and billing.
The monitoring system compiles a software inventory, which is kept up to date by repeated endpoint scanning. This process also helps security because it reveals unauthorized software installations. The software inventory also provides automated license management.
The patch manager will automatically line up updates for the software on a client’s site. However, technicians have the option to intervene and choose to reject or apply a patch manually instead of letting the automated process roll on. However, most patches will be applied automatically because that provides the greatest efficiency and value for money from the Syncro subscription.
Who is it recommended for?
Like most RMM and PSA packages, Syncro charges per technician and that payment gets access to all tools, such as the PSA system, the RMM tools, and a remote access package. There isn’t any need to buy any other software, except, perhaps, an accounting package. The package even integrates payment processing via third-party services.
Pros:
- Silent Operations: Capable of silently installing and uninstalling applications and patches, minimizing work disruptions.
- Automated Scheduling: Allows for the easy scheduling of patch management and other maintenance tasks to optimize operations.
- Versatile Platform: The web-based, platform-agnostic management interface ensures flexibility across different operating systems.
Cons:
- Extended Trial Desired: A longer trial period would allow for a more thorough evaluation before commitment.
The Syncro package includes contract management, payment processing, and integration with accounting packages. The one problem with the system is that it can’t manage endpoints running macOS or Linux, which would limit the business opportunities for the MSP that subscribe to the Syncro system. The full Syncro platform can be experienced with 14-day free trial.
7. SolarWinds Patch Manager
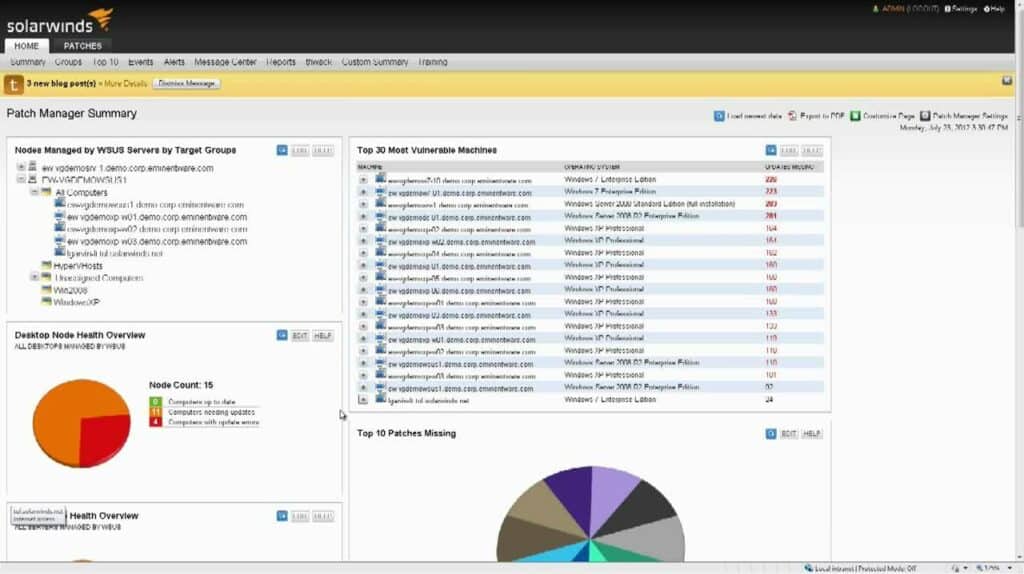
SolarWinds Patch Manager is a patch management tool for Windows that can monitor and install software updates. SolarWinds Patch Manager uses automated patching to automatically update patches on devices. The platform is great for Windows environments as it can diagnose performance issues with Windows Update Agent. There is also integration with SCCM so you can manage endpoints with SCCM installed.
Key features:
- Automated Updates: Streamlines the patching process by automatically applying updates.
- Patch Compliance: Offers detailed reports on patch status for compliance tracking.
- SCCM Integration: Seamlessly works with SCCM for enhanced endpoint management.
- Customization: Allows the creation of custom packages for specific needs.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Patch Manager provides a library of software updates, which are each up to date and verified. Therefore, the patch manager has one source that it needs to visit to access the latest patches for a list of software. It also provides patching for operating systems.
Monitoring the status of patches with SolarWinds Patch Manager is easy. Through the patch status dashboard, you can view available patches and see an overview of patches that are missing. Visualizations like pie charts provide you with more details. You can view a pie chart of the Top 10 patches missing to see where your network is vulnerable.
There are also patch compliance reports. Reports allow you to monitor patch status and find devices that need to be patched. The reporting feature is very useful for demonstrating regulatory compliance and showing that devices are updated if you are audited by a third party.
Who is it recommended for?
This is an on-premises software package that runs on Windows Server. It patches computers running Windows. So, if your site has only Windows for its endpoints, this tool is suitable for you. The package is most suitable for large organizations. Businesses that already use SolarWinds tools will be especially interested in this system.
Pros:
- Intuitive Dashboard: Simplifies monitoring and managing patches with a user-friendly interface.
- SCCM Compatibility: Enhances patch deployment capabilities within SCCM environments.
- Compliance Reporting: Facilitates regulatory compliance with comprehensive patch reporting.
- Extensive Support: Provides broad coverage for third-party software patching.
Cons:
- Enterprise Focus: Primarily designed for large organizations, potentially overlooking smaller networks or home users.
Prices start at $6,440 (£5,191), and it is available for Windows. You can start the 30-day free trial.
8. Kaseya VSA
Kaseya VSA is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) tool that can be used to automatically scan and deploy software updates for Windows, Mac, and third-party software. Kaseya VSA enables you to use policy-based patch management to create policy profiles to control when patches are deployed.
Key Features:
- Automated Updates: Streamlines software updates across systems.
- Policy Management: Enables granular control over patch deployment with policy profiles.
- Asset Discovery: Effortlessly identifies and catalogs network devices.
- Customizable Reporting: Offers tailored reports for insightful analysis.
- Remote Management: Facilitates control over devices from anywhere.
Why do we recommend it?
Kaseya VSA is an RMM package that includes a patch management module. The entire VSA platform is strong on process automation and the patching service is fully automated from software inventory management to patch availability detection, patch queuing, and patch rollout. All the actions of the patching system are documented for billing and compliance reporting.
For example, you can block specific patches for a machine or set of machines so that your devices aren’t updated without your permission. Software updates can be scheduled and approved to continually update your infrastructure. You can also use blackout windows to stop scheduling for a defined period of time.
Configuring the software is also quite simple, as you have the support of network discovery. You can discover devices and view them in a table. From there you can monitor extensive information on your asset inventory including Name, OS type, CPU, RAM, license, version, manufacturer, and more.
Who is it recommended for?
Kaseya markets the VSA system for use by managed service providers. The patch manager in the package is able to patch computers running Windows and macOS but not Linux. So, if your MSP has clients that have Linux computers, this tool is not for you.
Pros:
- Seamless Integration: Automates new device deployments, enhancing network expansion.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Offers robust device health and resource usage insights.
- Flexible Grouping: Simplifies the creation and management of asset groups with custom policies.
- User-Friendly Interface: Provides a customizable and intuitive dashboard for easy navigation.
Cons:
- Trial Limitations: A more extended trial period is desired for thorough evaluation.
- Feature Complexity: Some patch management functionalities, like patch blocking, can be challenging to navigate.
Kaseya VSA is a high-quality solution that’s ideal for enterprises looking for an all-in-one RMM and patch management tool. To view the pricing information for Kaseya VSA you must contact the company directly. It is available for Windows and macOS. You can start the 14-day free trial from this link here.
9. ConnectWise Automate
ConnectWise Automate is an RMM solution that can automatically apply updates to third-party applications. ConnectWise Automate supports a range of applications including Adobe Flash, Adobe Reader IX and DC, Apple iTunes, Google Chrome, Mozilla Thunderbird, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Skype for Business, PDF Creator, VLC Media Player, and more.
Key Features:
- Patch Management: Streamlines the update process for multiple applications.
- Device Discovery: Automates the identification of network devices.
- Remote Control: Facilitates management of devices from any location.
- Alerts: Keeps you informed with timely notifications.
Why do we recommend it?
ConnectWise Automate is a cloud-based RMM package that includes a patch manager. As the name suggests, ConnectWise Automate is a highly automated package. It discovers all devices on a network, scans each to create a software inventory, polls for patch availability, downloads installers, schedules installation, and then applies patches.
Automated asset discovery seamlessly discovers devices with network scans so you can monitor the software status of your devices. In effect, you can automatically discover a device and then deploy an agent. Managing your infrastructure in this way is incredibly efficient and allows you to stay on top of updates with ease. Automated notifications let you know when there are performance issues that need to be addressed.
Who is it recommended for?
ConnectWise markets the Automate package for use by managed service providers. The company also offers a PSA package to help MSPs run their businesses and that package includes a ticketing system. The patch manager updates third-party applications; it doesn’t patch operating systems. The service is aimed at mid-sized MSPs.
Pros:
- Unified Dashboard: Centralizes remote management, inventory, and reporting features for ease of use.
- Customizable Interface: Allows for personalized templates for individuals or teams.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: Supports non-disruptive remote troubleshooting with automation features.
- Ready-to-Use Commands: Offers over 100 pre-configured commands and templates for immediate deployment.
Cons:
- Trial Period: A more extended trial period would be beneficial for a comprehensive evaluation.
- Complex Interface: The interface, particularly in reporting and management, can be challenging to navigate.
- Policy Issues: Patch deployment policies may sometimes not execute as expected, requiring complex troubleshooting.
- Learning Curve: Presents a more significant learning curve compared to other patch management solutions.
ConnectwWise Automate is one of the top software update checkers on account of its blend of autodiscovery and patch management. The vendor provides customized quotes for customers, so you need to request a quote from the company directly for pricing information. You can download the free trial from this link here.
10. ITarian
ITarian is a patch management tool for Windows that can discover updates for Microsoft, Microsoft Security Bulletin, and third-party applications. ITarian automatically discovers connected devices and identifies those that are missing patches. Discovering unpatched divides allows you to take action to eliminate the vulnerability.
Key Features:
- Patch Management: Efficiently manages updates for Microsoft and third-party applications.
- Auto Discovery: Automatically identifies devices needing patches.
- Change Tracking: Monitors and records patch management activities.
- Detailed Reporting: Provides comprehensive reports on patch status and system health.
Why do we recommend it?
ITarian is a cloud platform of system management tools. The systems on the platform include an RMM package, called ITarian Device and this provides patch management. The patching system creates a software inventory and then periodically polls suppliers for patch availability. It then schedules and applies those patches.
Patches can be scheduled so that you can automatically deploy critical updates to run each day. You also have the option to prioritize patches based on severity, type, or vendor to make sure that your most important assets are patched before anything else.
You can also use the program’s change management capabilities to monitor patch policies. Here you can see patches that have been applied, those that are missing, and even failed deployments. You can also generate status and health reports to view more information on your infrastructure and prepare for compliance.
Who is it recommended for?
If you run an MSP you can add on a PSA package, called ITarian Basic, which is free. This is a great offer that managed service providers should pay attention to. The only problem with this tool is that it updates computers running Windows but not those running macOS or Linux.
Pros:
- Freemium Model: Offers a free version for up to 50 devices, ideal for small-scale MSPs.
- Effective Remote Control: Enables swift remote access and agent deployment.
- Machine Learning: Enhances threat detection capabilities for technicians.
- Extensive Reporting: Includes a broad array of technical and service level agreement (SLA) metrics.
Cons:
- Pricing Model: Costs escalate with the addition of more endpoints.
- User Interface: Could benefit from a redesign for improved intuitiveness.
ITarian is one of the best software update checkers for enterprise users. The platform supports up to 50 endpoints for free. The price depends on the number of endpoints you need to manage. 100 Endpoints costs $75 (£60) per month. You can sign up for the program from this link here.
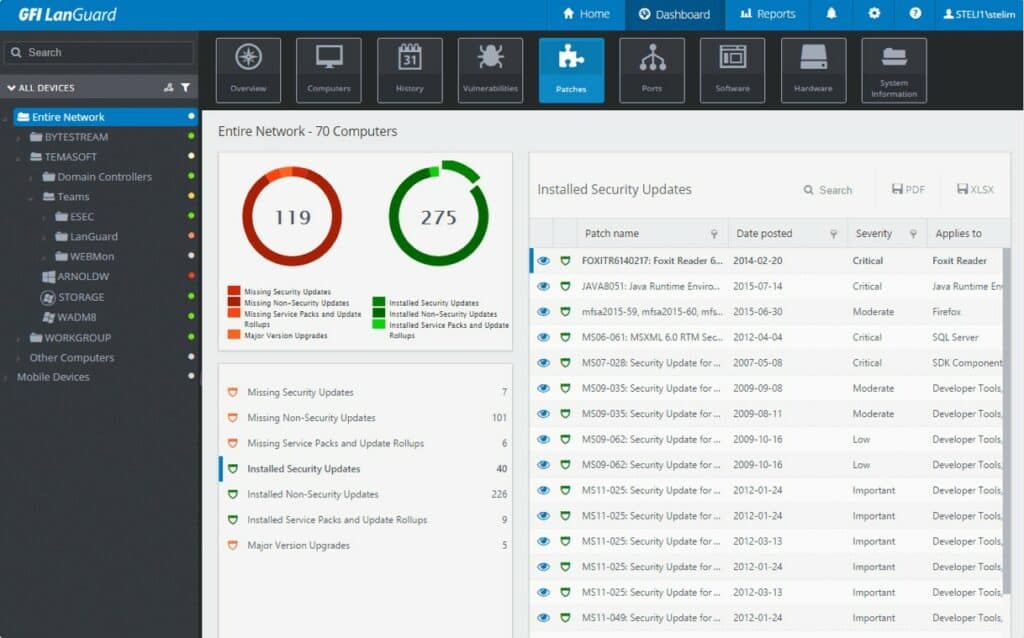
11. GFI LanGuard
GFI LanGuard is a patch management tool that automatically discovers devices connected to your network. With GFI LanGuard you can discover updates for Windows, macOS, and Linux devices. You can automatically deploy updates to devices. If a patch disrupts your operations then you can use the roll-back feature to revert to an earlier version.
Key Features:
- Auto Discovery: Identifies connected devices for comprehensive network management.
- Vulnerability Database: Catalogs over 60,000 known issues for thorough risk assessment.
- Patch Rollback: Offers the ability to undo updates if they negatively impact operations.
- Reporting Capabilities: Generates detailed compliance and status reports.
Why do we recommend it?
GFI LanGuard is a vulnerability manager that includes patch management to resolve discovered software and operating system vulnerabilities. The tool also identifies misconfigurations, so it gives you a complete risk assessment of your endpoints and network devices. The system provides device discovery, hardware and software inventory creation, and patch availability polling.
The platform maintains a list of over 60,000 known issues and vulnerabilities to test your network. There is also extensive support for third-party software with updates available from over 60 providers including Adobe Acrobat, Adobe, Mozilla Firefox, Java Runtime, Apple QuickTime, and more.
When it comes to managing regulatory compliance, you can create and schedule reports through a web-based console to highlight the patch status of your devices. Reports are compliant with a range of regulations including PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOX, GLBA, PSN, and CoCo. Export reports in PDF, HTML, XLS, XLSX, RTF, and CSV.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is suitable for businesses of all sizes. It is able to communicate with other security systems, such as your SIEM and it will also provide reporting for data protection standards compliance. This system will patch devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux and also check configurations for endpoints and network devices.
Pros:
- Cross-Platform Support: Manages updates for Windows, macOS, and Linux, along with key third-party applications.
- Comprehensive Interface: Combines ease of use with powerful functionality.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Integrates patch data into security evaluations to aid in vulnerability management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Supports creation of reports for standards such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and more.
Cons:
- Scheduling Flexibility: The system could benefit from enhanced patch scheduling options.
- Application Coverage: Needs broader support for the latest third-party software versions.
GFI LanGuard is a great patch management solution that’s fully equipped to centrally manage a network full of devices. Pricing starts at $26 (£20) for 10-49 nodes. You can start the 30-day free trial from this link here.
Choosing a Software Updater Tool
If your devices are going to stay in tip-top shape, then they need to be regularly updated. As the world found out during the 2017 Wannacry crisis, outdated OS’s with unpatched vulnerabilities are a liability. Software update checkers are essential tools for making sure that all devices stay updated with the latest protections.
Our top picks for the best software update checkers are Atera RMM Patch Management and NinjaOne for cross-platform patch management capabilities, and SolarWinds Patch Manager for Windows patch management.
Software Updater FAQ
What will upgrading firmware do?
Device providers regularly provide firmware updates to add new features and close of security vulnerabilities. Firmware upgrades also get issued when the provider discovers bugs in its coding for the operating system. As a general rule, you should always install any firmware update immediately.
How do I update my network adapter software?
The network adapter’s controlling software can be accessed through the network management utility of your device’s operating system. For example, in Windows, this is in the Device Manager, which can be located in the system settings. Under the Network adapters node, right-click on the adapter in question and select Update driver from the context menu.
What is patch management policy?
A patch management policy is a working practice that your company has decided upon and it sets rules on when and how to apply firmware and operating system patches. This might be settled by the use of an automated patch manager or it might be a manual workflow.
What are the common errors in patch management?
The biggest patch management problem is overlooking devices that need to be patched. The patching process is usually initiated when the producer of a device creates an update for a driver, firmware, or operating system. If that system has been deprecated, there will no longer be any patches for it. Not all patches are delivered automatically but need to be checked for.