Threat hunting tools are essential for organizations looking to proactively identify and mitigate security risks before they escalate into significant threats. In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, traditional defense mechanisms such as firewalls and antivirus software are often not enough to detect advanced threats. This is where threat hunting comes in by providing an active, research-driven approach to identifying hidden threats that might bypass automated security measures.
Here is our list of the best threat hunting tools:
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus EDITOR’S CHOICE Use this system to check your endpoints and network devices for weaknesses that represent security threats. Runs on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Log360 (FREE TRIAL) This on-premises package includes a SIEM for threat hunting with a threat intelligence feed and activity analysis to hone the accuracy of attack detection. Runs on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- VMWare Carbon Black Endpoint An EDR that is based in the cloud but includes data collectors installed on monitored devices.
- CrowdStrike Falcon Overwatch A full security operations center provided on a subscription basis that includes a SaaS EDR system, called Falcon Insight, plus technicians to run the software and security analysis for manual threat hunting.
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager One of the most competitive SIEM tools on the market with a wide range of log management features.
- Heimdal Threat Hunting and Action Center This cloud-based SaaS platform coordinates other Heimdal protection products to implement automated responses.
- Trend Micro Managed XDR A subscription service that offers both software-based and human threat hunting that will implement responses automatically to shut down attacks.
- Cynet 360 An innovative cloud-based cyber defense system that diverts intruders away from valuable assets through a Deception module that also exposes malicious activity to scrutiny and analysis.
- Exabeam Fusion Offered in SIEM and XDR formats, both options use the same threat-hunting routines. This is a cloud platform.
- Rapid7 InsightIDR A SIEM and XDR service that can be added to other services from the same cloud platform, such as a threat intelligence feed.
The best threat hunting tools empower security teams to actively search for signs of malicious activity, such as data breaches, malware, and insider threats, across networks and endpoints. These tools combine advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time monitoring to help uncover suspicious behaviors and anomalies that indicate potential security incidents. By continuously analyzing network traffic, user behavior, and system logs, threat hunting tools allow organizations to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, minimizing the risk of a successful attack.
What sets threat hunting tools apart from traditional security solutions is their ability to enable proactive defense. Instead of waiting for an alert to trigger, these tools allow security professionals to search through vast amounts of data to uncover hidden threats. This shift to a more active form of defense improves incident response times, reduces the damage caused by attacks, and enhances an organization’s overall security posture.
In this guide, we explore the best threat hunting tools available, highlighting their key features, benefits, and capabilities. Whether you’re looking for a tool that integrates with existing security platforms, offers advanced behavioral analysis, or provides deep network visibility, this comparison will help you choose the right solution to bolster your organization’s cybersecurity strategy. With the right tools in place, threat hunters can ensure that even the most sophisticated attacks are detected and neutralized before causing significant harm.
The threat hunter is the search tool that scours through activity data, looking for signs of unwanted behavior.
The types of systems that have threat hunting built into them are:
- Anti-virus (AV)
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
- Extended detection and response (XDR)
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
- Intrusion detection systems (IDSs)
- Intrusion prevention systems (IPSs)
- Cyber threat intelligence (CTI)
You will notice that firewalls are not included in the list. Although firewalls scan traffic, their activities are not generally classified as threat hunting. A firewall filters traffic.
Threat hunting strategies
Threat hunting systems look through system data for indicators of attack or unusual behavior. The source of that data is usually captured performance data and log messages. Threat hunting can be performed on a device but it is more effective if all activity data from all of the devices on a network are pooled in one central location. This enables the threat hunter to look for malicious activities that travel between devices so the cybersecurity system can spot and block a spreading attack.
Threats might be implemented in the form of software or manual activity by an individual. In almost all events, the malicious activity will be carried out within an authorized user account.
If an outsider is using a valid account, it will be due to an account takeover. This can occur because of weak security in the form of crackable passwords. Hackers can also get account credentials by tricking users into a disclosure.
If the malicious actor is a staff member, the user concerned might have been tricked or threatened into acting on behalf of an outsider. A disgruntled employee might want to damage the business by stealing or disclosing sensitive data or selling data for financial gain.
Although the software is usually involved in a malicious event, this is not always malware or unauthorized systems installed by a hacker. The authorized applications that you have installed for use by company workers can process and move data and they can serve malicious insiders and intruders as well.
Automated and manual threat hunting
Threat hunting processes are built into cybersecurity software. However, threat hunting can be a human activity as well. A data viewer with search and sorting facilities enables a cybersecurity specialist to analyze data and make inquiries into possible misuse of data.
Although a system manager might notice something odd about user account activity and want to investigate further, threat hunting is more usually an activity carried out by dedicated professionals. Not many businesses are large enough to be able to afford to keep a qualified cybersecurity specialist on staff, so these experts are more likely to be encountered working for consultancies and get involved in a client company’s data when called in to sort out an emergency.
Businesses can create an ongoing contract for consultancy services by signing up for a managed security package, which includes both the protection software and the services of cybersecurity experts to analyze data in the event of anomalies that the software cannot categorize.
The best threat hunting tools
The field of threat hunting offers a range of configurations and they encompass on-premises software packages, SaaS platforms, and managed services. When seeking out good examples of threat hunting systems to recommend, we need to be aware that different sizes and types of businesses will have different needs. Therefore, it is impossible to recommend a single package that can be easily identified as the best option available.
What should you look for in a threat hunting tool?
We examined the market for cybersecurity systems that incorporate threat-hunting processes and analyzed the available options based on the following criteria:
- A data collection service to feed event information into the threat hunter
- Data aggregation to standardize the format of event records
- Options for manual analysis
- Automated response settings
- Threat detection government by a security policy
- A free trial or a demo system to assess the system before paying
- Value for money, provided by comprehensive security protection at an appropriate price
With these criteria in mind, we identified reliable cybersecurity tools that include excellent threat hunting procedures. We made sure to include on-premises, SaaS, and managed service options.
1. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
Vulnerability Manager Plus provides a strategy to prevent threats from succeeding rather than waiting and looking for threats that are in progress. This is a system hardening package that scans endpoints and network devices, such as firewalls and gateways.
Key Features:
- Patch Manager: Triggered automatically by the vulnerability scanner
- Multiple OSs: Protects Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Identifies Weaknesses in System Settings: Configuration hardening
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is highly recommended for its proactive approach to cybersecurity. By focusing on system hardening and vulnerability management, it effectively prevents threats, making it an invaluable tool for maintaining robust network security.
This ManageEngine package scans endpoints and internet-facing devices. It spots configuration errors that provide opportunities for intruders and it identifies out-of-date operating systems and software packages. In some cases, those old software systems need to be completely replaced. However, where updates are available, the Vulnerability Manager Plus system will find those patches and schedule them for rollout.
The patch manager that forms part of the Vulnerability Manager Plus package will order patches according to known dependencies and it also gives you a chance to test the patches before they are applied.
Vulnerability Manager Plus addresses the system weakness that poorly planned elevated accounts and abandoned user accounts present. It identifies where credentials need to be tightened and where access rights management can be improved.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly suitable for IT administrators and cybersecurity professionals seeking a comprehensive solution for endpoint and network device security. Its capabilities in scanning, patch management, and configuration hardening make it ideal for organizations with complex IT environments, particularly those using Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.
Pros:
- Access Rights Assessments: Scans for abandoned accounts and weak password policies
- Web Server and Firewall Hardening: IIS and Apache Web Server
- Automated Scans and Software Updates: Does not require manual intervention
Cons:
- Not a SaaS Package: Only available for installation on Windows Server
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus installs on Windows Server. There is a Free edition that covers up to 25 endpoints. The two paid versions are the Professional edition to manage a LAN of more than 25 devices and the Enterprise edition, which is designed to protect endpoints on multiple sites. You can get either of the paid versions on a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is our top pick for a threat hunting tool because its abilities in vulnerability management, risk assessment, and patching are designed to bolster an organization’s security posture. It identifies security vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software, providing clear visibility into an organization’s attack surface. As a threat hunting tool, its key strength lies in its ability to proactively detect vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Vulnerability Manager Plus scans across endpoints, servers, and applications to pinpoint weak points, categorizing them based on severity and providing actionable insights. The software’s integrated threat intelligence helps SOC teams stay updated with the latest vulnerabilities and attack vectors, enabling more effective threat hunting. The tool’s real-time monitoring and automated patch management streamline remediation, ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed quickly, reducing the attack window. Its support for both on-premise and cloud environments makes it adaptable for hybrid infrastructures.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/vulnerability-management/download.html
OS: Windows Server
2. ManageEngine Log360 (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Log360 provides a SIEM system for threat hunting. This detection service is enhanced by a threat intelligence feed, which provides a list of known attacker addresses and methods. The system is also informed by a user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) service that cuts out false positive alerting by establishing a baseline of normal activity.
Key Features:
- Scans Through Logs: Looks for threats
- Log Server: Collects data from endpoints and cloud platforms
- Gathers Network Activity Data: Network activity feed
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Log360 is recommended for its comprehensive SIEM capabilities, enhanced by a robust threat intelligence feed and user and entity behavior analytics. Its ability to effectively reduce false positives and provide detailed insight into network activity makes it a standout choice for in-depth security monitoring and threat detection.
There are many other modules in this on-premises package that enable the system to automatically block malicious activity by malware, intruders, or insiders. These include cloud access security broker (CASB) to enforce security on cloud platforms, behavior analysis to spot insider threats and account takeovers, access logging and file integrity monitoring to block data theft, and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) to coordinate the automated responses to threats between all the tools in the package and third-party systems.
The SIEM requires log messages as its source data and so the Log360 system includes a log manager that collects, consolidates, and then stores messages. This service is also useful for compliance auditing and reporting. This system can be used to report for PCI DSS, GDPR, FISMA, HIPAA, SOX, and GLBA. This system also provides protection for Active Directory implementations, which is also a requirement of many data protection standards.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for organizations with complex IT infrastructures, including those heavily reliant on cloud platforms and diverse operating systems. It’s particularly beneficial for IT security teams that require advanced features like data loss prevention, compliance auditing, and automated threat response, making it suitable for large enterprises and organizations with stringent security and compliance requirements.
Pros:
- User Activity Tracking: Data loss prevention and activity logging
- Threat Intelligence Feed: IP address blacklist
- Automated Responses: Can include third-party tools
Cons:
- Very Large Package: Requires a team to manage it
ManageEngine Log360 is an on-premises package that runs on Windows Server. It is able to collect data from all your other operating systems, network devices, and cloud services. This system is available for a 30-day free trial.
3. VMWare Carbon Black Endpoint
VMware Carbon Black Endpoint protects multiple endpoints. Each enrolled endpoint has an agent installed on it and that unit communicates with the cloud-based Carbon Black data processor.
Key Features:
- Threat Intelligence Feed: Fast threat hunting
- Anomaly Detection: Looks for unusual activity
- SOAR: Security orchestration, automation, and response
Why do we recommend it?
VMware Carbon Black Endpoint is highly recommended for its advanced Predictive Cloud Security and SOAR capabilities, enabling fast and efficient threat hunting across multiple endpoints. Its mutual threat exchange and system hardening advice offer a dynamic approach to cybersecurity, essential in today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape.
A network agent also communicates with third-party security tools as part of a technique that is called security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR). The SOAR system gathers information from third-party security tools, such as firewalls, and adds this to the pool of information that is collected in the cloud.
The threat hunting module in the Carbon Black package is called Predictive Cloud Security, which is notable for its ability to search through large collections of data very quickly. The detection of a threat triggers response instructions that are sent to the device agents and also to the third-party tools that are enrolled in the SOAR system.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly suitable for organizations managing multiple endpoints across various sites, including those integrating third-party security tools. It’s ideal for IT teams seeking a comprehensive, cloud-based solution for endpoint protection, threat intelligence, and automated responses, making it a valuable asset for medium to large-sized enterprises with complex security needs.
Pros:
- Private Threat Intelligence Network: Mutual threat exchange between clients
- System Hardening Advice: Identifies configuration weaknesses
- Automated Responses: Shut down threats without manual intervention
Cons:
- Requires Support from Third-Party Systems: Doesn’t include a log manager
The SaaS package implements threat hunting per client and then pools all discovered data for a central search for all clients. This central threat hunting provides threat intelligence about hacker campaigns and warns clients ahead of the attack. You can request a demo of the VMWare Carbon Black Endpoint system.
4. CrowdStrike Falcon Overwatch
CrowdStrike Falcon is a cloud platform of security tools that include an EDR, called Insight, and an XDR. The EDR coordinates with CrowdStrike on-device systems and the XDR adds on SOAR.
Key Features:
- Anomaly-Based: Informed by threat intelligence
- Dual-Level Threat Hunting: Local on device and centralized on the cloud
- CrowdStrike Research: Improves threat intelligence
Why do we recommend it?
CrowdStrike Falcon Overwatch is recommended for its seamless integration of advanced EDR and XDR capabilities within a cloud platform, facilitating efficient and comprehensive threat hunting. The inclusion of Falcon Prevent and the added support of a full security operations center through Overwatch makes it an exceptionally robust cybersecurity solution.
The one product of CrowdStrike that runs on endpoints is a next-generation anti-virus package, called Falcon Prevent. This performs its own threat hunting and implements defense responses. If the buyer of Falcon Prevent has also subscribed to one of the cloud-based systems, the AV acts as an agent to it.
Both Falcon Insight and Falcon XDR perform threat hunting in the cloud on the pool of data uploaded from all endpoints enrolled in the plan. This threat hunting process can be enhanced with a threat intelligence feed, called Falcon Intelligence.
A business that doesn’t want to keep a security expert on staff would be missing out on the benefit of manual threat hunting and expert security analysis. CrowdStrike caters to this need with the Overwatch package. This is a full security operations center that provides system-wide threat detection and response management for subscribing clients. This is the Falcon XDR SaaS package with security analysts added on.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for businesses that seek extensive cybersecurity coverage but may not have the resources to maintain a dedicated security team. It’s particularly beneficial for organizations requiring a combination of automated cloud-based threat hunting and expert manual analysis, making it a top choice for medium to large enterprises focused on sophisticated, multi-layered cyber defense strategies.
Pros:
- SOC Available: Option for a managed service
- Threat Intelligence Feed: Gathered from all CrowdStrike clients
- SOAR: Gathers data and implements responses through third-party tools
Cons:
- The Platform has Many Units: Many options can take time to assess
The Overwatch plan includes an installation of Falcon Prevent on every endpoint. You can get a 15-day free trial of CrowdStrike Falcon Prevent.
5. SolarWinds Security Event Manager
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is the best option for those system managers that want to keep everything in-house. The package runs on your server and explores all other endpoints across the network. This system operates on live network performance data, drawn from sources, such as the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) as well as log messages.
Key Features:
- Log File Server: Consolidates and files log messages
- On-Premises: Runs on Windows Server
- Compliance Auditing: Stores logs for verification
- Signature-Based Threat Hunting: Out-of-the-box rules
- Data Viewer: Includes tools for manual analysis
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Security Event Manager stands out as an exceptional choice for in-house system management due to its comprehensive capabilities in log file collection, sensitive data management, and compliance auditing. Its strength lies in its ability to leverage live network data and log messages for proactive threat hunting, ensuring a robust security posture for businesses.
The package includes connectors that interface to applications and extract event data. The system also includes a file integrity monitor that records access to files and changes made to their contents. This is a sensitive data manager that supervises nominated files and folders.
The performance readouts and log messages then get converted into a common format, which is called “consolidation”. The tool presents these records to the threat hunting module for analysis.
The malicious activities that the threat hunter detects can be stopped immediately. This threat hunter is a signature-based service that looks for indicators of attack. The system includes a list of responses, which are called correlation rules. These specify an action to take if a threat is detected. Those actions can be blocking traffic from and to a specific IP address, suspending a user account, shutting down a process, and deleting a file.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is highly recommended for system managers and IT professionals who prioritize keeping their security management in-house. It’s especially beneficial for those who need a sophisticated approach to monitoring network performance, managing sensitive data, and ensuring compliance, making it ideal for medium to large-sized enterprises with complex network environments.
Pros:
- Acts as a SIEM: Mines log data
- Manages Log Files: Rotates log files daily
- Implements Automated Responses: Through third-party security tools
- Alerts for Suspicious Activity: Forwarded as notifications by email or SMS
- Uses Live Network Data as Well as Logs: Receives network activity feeds
Cons:
- No Cloud Version: Only available for Windows Server
SolarWinds Security Event Manager installs on Windows Server and it is available for a 30-day free trial.
6. Heimdal Threat Hunting and Action Center
Heimdal Threat Hunting and Action Center is a cloud-based service that links together other Heimdal products to create a unified threat management system. The package operates on the Next-Gen Anti-Virus service, which is an on-device system for Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. You will also need at least two other modules and then the Threat Hunting & Action Center adds extra threat detection to the bundle.
Key Features:
- Forms an EDR: Coordinates multiple Heimdal tools
- Cloud-Based: Communicates with on-premises Heimdal products
- Scans Computers and Mobile Devices: Performs local and consolidated threat hunting
- Automated Responses: Implemented through on-premises tools
Why do we recommend it?
Heimdal Threat Hunting and Action Center is recommended for its innovative integration of on-device and cloud-based cybersecurity tools. Its Extended Threat Protection (XTP) Engine is adept at identifying and mitigating complex threats, including credential access takeover and defense evasion, making it a robust solution for comprehensive cybersecurity.
Other Heimdal products that the EDR will work with include Network Security, Email Security, Patching & Asset Management, and Endpoint Security. While the NGAV with its integrated mobile device management (MDM) service scans all files against locally stored signature databases, the tool acts as an agent for the Action Center, uploading activity reports for threat detection.
The cloud service provides some great visualizations and activity data as well as seeking threats. The system links responses to different threats and will send instructions back to the Heimdal products on site to shut down the threats that the local scanners didn’t spot.
The Heimdal threat detection system is called the Extended Threat Protection (XTP) Engine. This looks for credential access takeover, defense evasion attempts, lateral movements, and data exfiltration. The XTP Engine also performs risk management by scanning for MITRE ATT&CK threats.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for organizations seeking a layered cybersecurity approach, combining on-premises and cloud-based solutions. It’s particularly suited for businesses that already utilize Heimdal’s other products, looking to enhance their cybersecurity infrastructure. The platform’s capability to protect both computers and mobile devices makes it a versatile choice for companies with diverse IT environments.
Pros:
- Dual Focus: On-device and cloud cybersecurity tools
- Risk Analysis: Delivered from the cloud
- Collects and Collates Activity Data: Provides a central pool of data for threat hunting
- Security for All Endpoint Types: Protects mobile devices as well as computers
Cons:
- Not a Standalone Product: Only available if other Heimdal products are on site
You can’t subscribe to the Heimdal Threat Hunting & Action Center service by itself. This is an add-on to other tools. The Heimdal threat-hunting strategy is very similar to the CrowdStrike Falcon system (see below), where the NGAV, called Prevent is the driving module. Heimdal consultants will give you a free demo of the Threat Hunting & Action Center.
7. Trend Micro Managed XDR
Trend Micro Managed XDR is a SOC-for-hire plan that adds the services of security specialists to the Trend Micro Vision One system security package. Vision One is a SaaS XDR with on-device agents and SOAR, reaching out to third-party security tools.
Key Features:
- Multi-Level Threat Hunting: On device and consolidated centrally
- Security Analysts: Available for consultation
- SOAR: Interacts with third-party tools
Why do we recommend it?
Trend Micro Managed XDR is recommended for its comprehensive blend of automated and expert-driven threat hunting capabilities. The integration of Zero Trust Risk Insight within the Vision One platform, combined with the expertise of security analysts, offers a robust, multi-faceted approach to cybersecurity.
The Vision One service is a cloud coordinator of on-device Trend Micro endpoint-resident AVs that perform their own threat hunting locally. These units upload activity data to the Trend Micro server for enterprise-wide threat hunting. The Trend Micro threat detection system is called Zero Trust Risk Insight. It looks for anomalous access to applications, identifying insider threats and intrusion.
The managed service includes automated systems and expert analysts. Manual threat hunting reduces the inconveniences of infrequent legitimate tasks being blocked by automated EDR processes. Analysis can also produce recommendations for system hardening.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly suitable for organizations seeking a SOC-for-hire model, offering both technological sophistication and human expertise. It’s ideal for businesses that need a balanced approach to threat detection, encompassing both on-device and cloud-based strategies. This makes it a valuable asset for enterprises looking for a dynamic, adaptive cybersecurity solution that can efficiently handle insider threats, intrusion, and system vulnerabilities.
Pros:
- Outsourcing: Suitable for businesses that have no security experts on the payroll
- Centralized Service: Can manage security for multiple sites
- Automated Responses: Implemented without the client’s involvement
Cons:
- Cost Saving: More expensive than self-managed options
You can get access to a demo system, which is called the Vision One Test Drive.
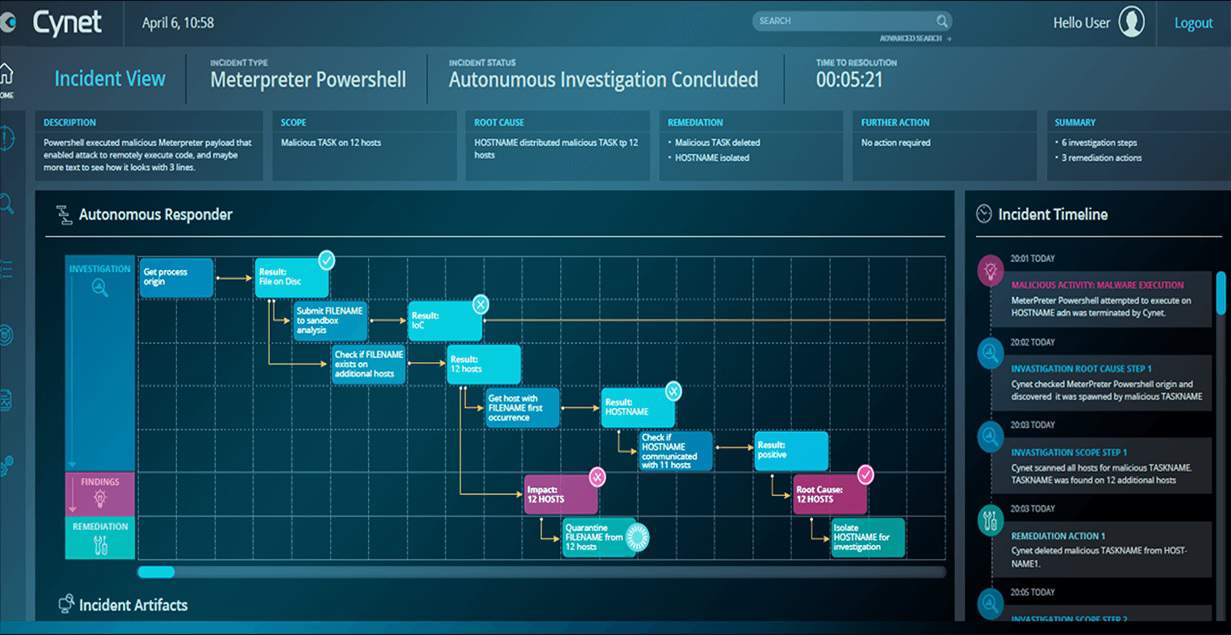
8. Cynet 360 AutoXDR Platform
Cynet 360 AutoXDR Platform includes a threat hunting layer that gathers information on malicious activity from third-party on-site tools. This platform is resident in the cloud and it provides several utilities to help the on-site automated systems detect threats.
Key Features:
- Cloud-Based: Managed detection and response
- Local Data Collectors: Contributes to a central intelligence pool
- Deception Techniques: Honeypots and false paths
Why do we recommend it?
Cynet 360 AutoXDR Platform is recommended for its innovative approach to threat detection, combining cloud-based analytics with local data collection and advanced deception techniques. Its use of sandboxing and honeypot systems, coupled with UEBA, makes it a powerful tool for identifying and mitigating cyber threats efficiently.
The threat identification services of Cynet 360 include sandboxing and a honeypot system that provides a fake teaser to hackers, drawing them to an analysis unit.
As well as its own research lab structure, the Autonomous Breach Protection system in Cynet 360 gathers local information through agents in a network called Sensor Fusion. The threat hunting process deploys user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to assess the intent of regular business traffic around the network and blocks malicious activity through SOAR.
Who is it recommended for?
This platform is particularly well-suited for organizations that require a sophisticated, multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. It’s ideal for businesses looking for a comprehensive solution that not only detects threats but also employs proactive measures to deceive and analyze potential attackers. This makes Cynet 360 an excellent choice for medium to large enterprises that prioritize advanced, autonomous breach protection and threat management.
Pros:
- Anomaly-Based Threat Hunting: Uses UEBA for baselining
- SOAR: Coordinates third-party security tools
- Memory Forensics: Looks for fileless malware and worms
Cons:
- No Log Manager: An additional purchase
Cynet offers a 14-day free trial of The AutoXDR platform.
9. Exabeam Fusion
Exabeam Fusion is a cloud platform with on-site agents that implements threat detection, investigation, and response (TDIR). The package can operate as an XDR or a SIEM. The tool draws in source data from its on-site agents to feed into the threat detection module that operates in the cloud.
Key Features:
- Anomaly-Based Threat Hunting: Looks for unusual activity
- UEBA: Identifies insider threats
- Compliance Reporting: For more than 45 standards
Why do we recommend it?
Exabeam Fusion is recommended for its advanced anomaly-based threat hunting capabilities, utilizing UEBA for effective activity baselining. Its ability to tailor services to specific data protection standards and generate compliance reporting makes it a highly versatile and efficient cybersecurity solution.
The Exabeam Fusion threat hunting service uses anomaly detection, which is built on UEBA for activity baselining. The service can be tailored to specific data protection standards requirements and then it will also automatically generate compliance reporting.
The system relies on log information for source data and it can interface directly with a list of software packages through a library of connectors. The service will also consolidate and store logs for manual threat hunting analysis and compliance auditing.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly suitable for organizations that require both XDR and SIEM capabilities in a unified platform. It’s ideal for businesses focusing on compliance and data protection, as well as those that value detailed analysis and investigation of security events. Exabeam Fusion’s flexibility and comprehensive log management make it a great choice for medium to large enterprises seeking a robust, adaptable approach to cybersecurity.
Pros:
- Gathers Activity Data from Applications: Through integrations
- SIEM Operations: Examines log files from operating systems
- Log Management: collects, consolidates, and files log messages
Cons:
- Internet Connection is Essential: Endpoints are not protected if disconnected from the network
You can assess Exabeam Fusion with a demo.
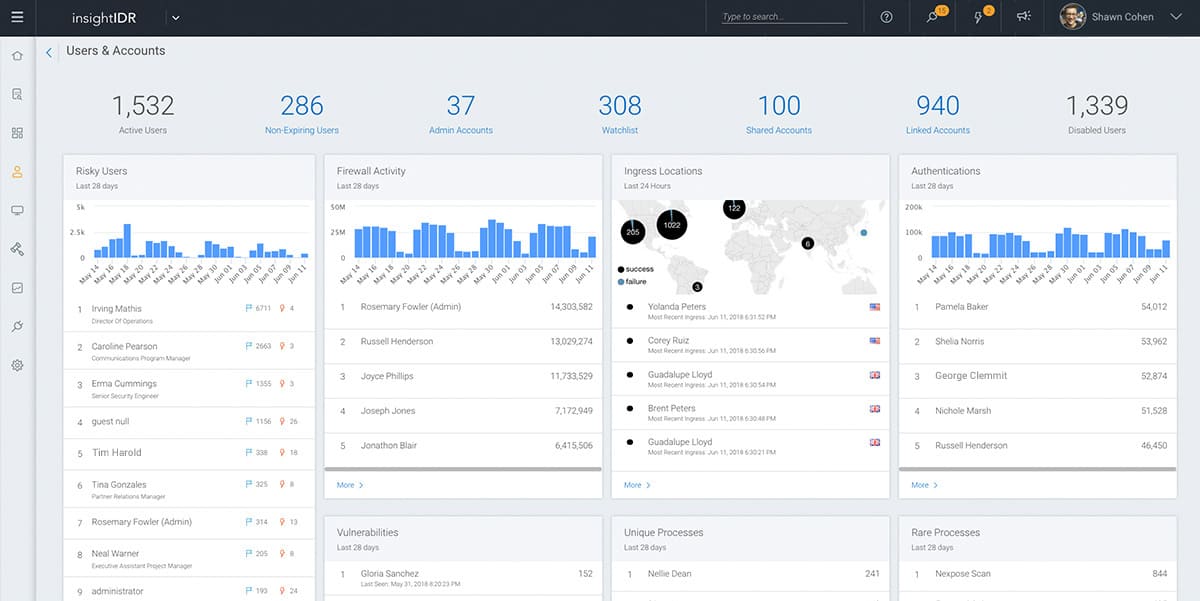
10. Rapid7 InsightIDR
Rapid7 is a cloud platform of cybersecurity modules. You select which services you want from the menu of options and those packages slot together. The cloud system is called Rapid7 Insight and the XDR package on that platform is called InsightIDR – IDR stands for “incident detection and response” and it can also be used as a next-gen SIEM.
Key Features:
- A SIEM: Scans log messages
- Attack Behavior Analytics: Threat intelligence
- Multiple Strategies: Both anomaly and signature-based
Why do we recommend it?
Rapid7 InsightIDR is recommended for its effective combination of SIEM capabilities and advanced threat intelligence. The platform’s anomaly and signature-based detection integration, complemented by its Attack Behavior Analytics module, offers a comprehensive and dynamic approach to incident detection and response.
The InsightIDR service requires agents to be installed on protected endpoints. The uploaded logs that are gathered by those agents provide the source material for SIEM searching and they will also be stored in log files for manual threat hunting and compliance auditing.
Rapid7 provides a threat intelligence feed into the threat hunting service, which is called the Attack Behavior Analytics (ABA) module. That ABA system is signature-based but it interacts with anomaly-based UEBA searches to provide a blended threat hunting strategy.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for organizations seeking a flexible cloud-based cybersecurity solution with robust SIEM and XDR functionalities. It’s particularly well-suited for businesses that require detailed log analysis, compliance auditing, and a blended threat hunting strategy. Rapid7 InsightIDR’s adaptability makes it a valuable asset for a wide range of enterprises, from small businesses to large corporations, particularly those prioritizing a multi-faceted approach to cybersecurity.
Pros:
- Fast Threat Hunting: Fueled by triage informed by threat intelligence
- Uses UEBA: Looks for insider threats
- Automated Responses: Does not require human intervention
Cons:
- Multiple Purchases: SOAR costs extra
Another package available on the Insight platform is Insight Connect, which extends the capabilities of InsightIDR by adding SOAR connectors.
You can assess Rapid7 InsightIDR with a 30-day free trial.