Windows Server Update Services, better known as WSUS, is a software update facility bundled into Windows Server. The utility will automatically check for Microsoft software updates, hotfixes, and patches and then distribute them to all the computers on the network.
Although the WSUS server is a free automatic update service, it is a little rudimentary as a patch management solution. The system produces logs, but these can be difficult to comb through manually.
Fortunately, several small utilities can organize the data produced by WSUS and help you keep track of the software versions operating on your network.
Here is our list of the best WSUS server tools & software alternatives:
- NinjaOne Patch Manager EDITOR’S CHOICE This remote patch manager provides automation to improve technician productivity from its cloud-based dashboard. Patches devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux. Start a 14-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL) Patch management with automated rollouts, update testing system, and version status audit reports for software resident on Windows, Mac OS, Linux, and the Cloud. Download the 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus (FREE TRIAL) An SCCM-based patch manager that is able to manage updates to Microsoft and third-party software. Installs on Windows Server.
- Atera RMM (FREE TRIAL) Manages operating system and firmware patching as part of a suite of remote monitoring and management tools.
- AJ Tek WSUS Automated Maintenance A package of useful tools for managing and improving WSUS. Installs on Windows.
- AFDesign’s WSUS Tool for Spiceworks User-community-provided front end to the standard WSUS process.
- WSUS Offline Tool Registers the need to update internal software on offline devices.
- BatchPatch Windows-based interface to WSUS procedures.
The best WSUS server tools and software alternatives
Our methodology for selecting a WSUS server tool
We reviewed the software patch manager market and analyzed tools based on the following criteria:
- The ability to integrate with WSUS to enhance functionality
- Samples of WSUS replacement options
- Patch gathering and storage
- Automated patch rollout
- Full action logging for compliance reporting
- The option for manual patch application
- The offer of a free trial for assessment
- Valuable tools that are worth the money
1. NinjaOne Patch Manager (FREE TRIAL)
The NinjaOne Patch Manager – formerly NinjaRMM – is part of a bundle of tools that help technicians working for a managed service provider (MSP) to support the networks of client companies. This package would also be useful for IT professionals working in the central IT department of a large, multi-site enterprise.
Key Features:
- Patch Management Best Practices: You can ensure that your software and systems are up-to-date with the top patch management best practices. This ensures that your technology is secure and running smoothly.
- Centralized management: allows you to monitor and control all your IT assets, operations, and helpdesk tasks from one convenient dashboard.
- Complete visibility: users can get insight into your helpdesk activities, endpoint health, and network performance. This visibility allows you to manage your resources and proactively address any issues efficiently.
- Remote Management: NinjaOne is fully cloud-based, which means you can manage devices anywhere, even for remote or hybrid workers, without hassle.
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne Patch Manager is part of a remote monitoring and management package that is delivered as a SaaS platform. This service is able to patch Windows, Linux, and macOS. It will also patch 135 software packages. The platform provides automated patching, which maximizes the productivity of technicians.
This patch manager focuses on updating endpoints and servers that run Windows, Linux and macOS. It also updates more than 135 third-party applications. The success of the patch manager relies on the autodiscovery functions embedded in NinjaOne. Whenever the system is set up to monitor a new network, it scans that site, logging all endpoints and then scouring each device for all installed software.
The software inventory of NinjaOne notes the version numbers of each operating system and package that it encounters. This version number indicates the patch level applied in each instance. The first sweep of a system triggers a key patch management phase. In many instances, businesses don’t coordinate the patching of all of their devices, so the software scanner will likely find that many instances of the same software, such as the operating system, are at different patch levels.
Bringing all instances up to date isn’t as simple as just installing the latest patch. In many cases, patch systems are incremental improvements and rely on all previous patches being present before the latest patch can be applied. Therefore, onboarding a new company can result in many rounds of updates. NinjaOne’s system manages those tasks autonomously.
The technician sets up a calendar of maintenance windows for the client’s system. Most of these periods will be standard for all clients, such as evenings and weekends. When the RMM system detects the availability of a patch, it copies over the installer to its own cloud server and then waits for the next maintenance window before applying those new patches. The technician can elect to hold up a patch by finding it in the list of pending patches in the NinjaOne dashboard.
The NinjaOne patch manager is designed for unattended execution. It is assumed that all rollouts will occur out of office hours. The patch manager produces execution logs and shows end statuses in the dashboard. Technicians can then look through the results of the rollout, investigate failed actions, and optionally re-apply a patch manually.
Who is it recommended for?
The NinjaOne platform is a SaaS system that has a multi-tenant structure that is designed for use by managed service providers. IT departments also use the system for in-house technical support. The entire NinjaOne package implements remote monitoring and management which is ideal for use by multi-site businesses.
Pros:
- Single Panel IT Management: Manage all your IT tasks and operations from one easy-to-use dashboard. This saves time and simplifies your workflow.
- No Infrastructure Required: NinjaOne is cloud-based, so you don’t need to set up any additional infrastructure. It’s hassle-free and saves resources.
- Easy and Reliable Patching: With NinjaOne, patching software becomes simple and reliable. You can keep your systems up-to-date without much effort, ensuring security and performance.
- Insightful Scheduling: With NinjaOne, you get insights into the best times for patching scans and updates. This helps you stay secure while minimizing disruptions and tailoring patching to different needs.
Cons:
- Reinstallation Hassle: Reinstalling NinjaOne on a PC that previously had it can be troublesome. It may require extra effort and time, which can be inconvenient for users.
NinjaOne is a cloud-based system with a subscription rate per monitored device. It is available for a 14-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
NinjaOne Patch Manager is our top alternative to WSUS server tools because it is a cloud-based service that is able to patch any system anywhere in the world. This system is suitable for IT departments and managed service providers and it can be used in conjunction with a remote monitoring and management package. The service will patch the operating system and software on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Its automation enhances the productivity of system management technicians. In line with industry recognition, G2 has consistently hailed NinjaOne as a top solution in its domain.
Download: Get 14-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.ninjaone.com/freetrialform/
OS: Cloud-based
2. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine offers a software monitoring service that allows you to keep all of your utilities up to date automatically. Patch Manager Plus is part of the stable of IT infrastructure management tools offered by the company, and it can also be integrated as a plug-in into Spiceworks.
Key Features:
- Automate patch management: users can make the entire process systematic with proper resource usage and save time because it will scan entire systems to check for missing patches, test various patches, and deploy them accordingly.
- Third-party app patching: the tool supports up to 850 plus third-party integrations, which helps you to detect dangerous vulnerabilities across the network.
- Flexible deployment policies: The user can flexibly decide the day and time and specify the start and end times to deploy patches across the network without affecting important work and application processes.
- Insightful reports: The tool provides insightful reports that provide all the details about patches and the system affected, initial statuses, critical updates, failed updates, vulnerabilities, and more.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is able to patch Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems and update the software that runs over it. The system scans all endpoints and creates a software inventory. It then checks for patch availability. This tool benefits from a central repository of software updates.
The software for Patch Manager Plus runs on Windows and Windows Server environments. However, there are agents available that enable the system to monitor software statuses on Mac OS and Linux systems as well. Patch Manager Plus agents can run on Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL, and SuSE Enterprise Linux.
The tool scans all contactable endpoints, making an inventory of their software. A check on the latest versions of each of these products reveals which modules are out of date. Patch Manager Plus then communicates with the servers of the relevant software producers and downloads all of the necessary patches. These patches can then be installed automatically without human intervention. However, you can specify that all candidate patches should be listed in the centralized dashboard first for human approval.
The approval process might demand a test of the new update. The Patch Manager Plus interface includes a test system that will try out the new update on a small number of devices first so that you can assess the impact of software changes before they roll out to your entire network.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine caters to a very wide market because its Patch Manager Plus is available for installation on Windows Server or it can be accessed on the cloud as a SaaS package. The system is suitable for small businesses because it has a Free edition that will patch 20 endpoints and five endpoints.
Pros:
- Cross-platform support: You can automate the patch process for various OSs, such as Windows, Linux, and Mac; hence, it acts as a single interface to keep your OS secure and error-free.
- Test and approve patches: Testing and approving patches helps protect your network from risks and vulnerabilities. It also ensures that only tested and secure patches are deployed on the network to run the software application smoothly.
- Decline patches or apps: You have the authority to decline patches from specific groups of computers and uncertain applications that are found critical during the testing process.
- Patch compliance: Every organization wants 100% compliant patch status. This tool comes with a patch policy, which is also known as a system health policy. It represents the health status of the managed systems.
Cons:
- Learning curve: Users may find it difficult to learn other advanced configurations if they are not aware of some technical terms, which might waste time.
All of the facilities of Patch Manager Plus are available for software running on a cloud server. However, those servers will need to be running Windows. The utility is available for installation on-premises or as a cloud-based service. ManageEngine offers a free edition of Patch Manager Plus, but that will only monitor up to 25 devices. If you have a larger network, you can decide between the Professional edition, which covers LANs or the Enterprise edition, which is suitable for managing deployed software across multi-site WANs. You can get a 30-day free trial of either of these paid options.
3. ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus is an SCCM-dependent software update manager that is able to monitor the versions of more than 330 software packages. The screens for this ManageEngine tool create an adaptation of the SCCM system so its own functions can be accessed through the SCCM console. Although SCCM is a Microsoft product, Patch Connection Plus doesn’t limit its capabilities to just Microsoft software updates – it manages the products of other software houses as well.
Key Features:
- Native plugin in for SCCM: The tool includes a plugin list for third-party updates, and users can patch the application without filtering entire third-party apps.
- Application management: It supports various applications, so users can create custom applications using SCCM and Microsoft Endpoint Manager. It also allows customization while deploying with predefined templates and scripts.
- Auto-detect and publishing of patches: it auto-detects and gives notifications for newly added patches and newly installed applications across the network.
- Third-party software catalog: It has a huge software catalog; you can use up to 600 third-party apps.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus is an adaptation of the Windows SCCM and Intune systems. This alteration enables SCCM to install third-party software on Windows endpoints and the Azure platform. This is a very similar system to the SolarWinds Patch Manager. The tool is highly automated and can identify new updates and install them without manual intervention.
The Patch Connect Plus scans a system for all installed software and then searches the information feeds of the suppliers of those packages for any available updates. This process is instant and creates a list of candidate patches. The user can read through that list and suspend some available updates if required. The way patches are rolled out depends on the settings chosen by the System Administrator. The behavior of patch installation is governed by the chosen Deployment Template.
Patch Connect Plus doesn’t just create a software inventory when it starts operations and then sticks to that list, it detects new software and updates the inventory automatically throughout its service life. The service also profiles each enrolled machine, giving a status report on software versions and available patches for each. All update actions are logged and failed patches are highlighted for investigation or a re-run.
ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus is implemented as on-premises software for installation on Windows Server. There are three editions of the system: Standard, Professional, and Enterprise. The Standard edition is free to use and its sole task is to load a list of third-party software updates into SCCM.
Who is it recommended for?
This ManageEngine system is specifically aimed at businesses that only have endpoints running Windows or Windows Server. This system is also useful for businesses that have installed software on the Azure cloud platform. This software is only available for Windows Server.
Pros:
- Deployment Reports: Users can easily access detailed deployment reports for Intune and SCCM. These reports allow users to track patch installation status across client machines, identify missing patches, and address failed installations efficiently.
- SCCM Right Click Tools: Perform essential functions directly from the SCCM console, such as client troubleshooting and system management actions, streamlining operations, and improving efficiency.
- Import CVE IDs: Mitigate network vulnerabilities by importing CVE IDs and deploying corresponding patches, ensuring your systems stay protected against the latest security threats.
- Automated Third-Party Patching: Use SCCM to automate the deployment of third-party patches, simplifying the patch management process and ensuring that all software vulnerabilities are addressed promptly.
Cons:
- Dependency on SCCM: Since many features rely on integration with SCCM, organizations without SCCM may not be able to fully utilize all functionalities; hence, this will limit its usage for many companies.
The Professional version has a lot more features, including the option to implement third-party patches with WSUS. This service integrates into SCCM, adding a whole section to it. The Professional edition makes constant scans to form a software inventory – a feature not included in the Standard edition. The Enterprise edition includes more tools, such as an Applications Management system. You can try the Professional and Enterprise editions on a 30-day free trial, which is restricted to monitoring 10 apps.
4. Atera RMM (FREE TRIAL)
Atera is a remote monitoring and management tool (RMM) that includes patch management functions for Microsoft Windows devices.
Key Features:
- Remote Monitoring and Management: Users can monitor all devices from anywhere, anytime, without worrying about extra costs. Monitor and manage unlimited devices at a fixed price, making it easy to stay on top of your IT infrastructure.
- Atera AI: Supercharge your IT operations with Atera’s AI capabilities, which help boost your team’s efficiency by up to 10 times. Revolutionize your IT environment with advanced automation and intelligent insights.
- Network Discovery: Ensure the security of your network with real-time scans provided by Network Discovery. You can identify potential vulnerabilities and take action to protect your network from threats.
- Remote Access: Instantly access devices and troubleshoot issues remotely using popular remote access tools like AnyDesk, Splashtop, TeamViewer, or ScreenConnect. Start sessions quickly and easily, ensuring timely resolution of IT issues.
Why do we recommend it?
Atera RMM is a remote monitoring and management package that is provided as a SaaS platform. The service is offered in four plans and all of them include the Patch Management module. The system is able to patch the Windows and macOS operating systems and the software that runs on top of them.
Available patches are recognized by the patch manager and listed in the management console. The operator has an opportunity to nominate any of them to be excluded from the update. Patches can be rolled out to all devices on the client’s network, to a group of devices, or they can be sent to individual devices.
Each Windows patch arrives with metadata that indicates its importance: Critical, Important, Security, or Service Pack. The Atera environment is able to read these categorizations and gives you the option of installing one, some, or all of the patches in these status types. The patch rollout service can be used to update Microsoft Office software, Java, and Adobe services.
The patch manager can be set to run weekly or monthly. When the update run is scheduled, the patch manager will apply all patches that are available in its working directory as long as none of them have been specifically blocked by the operator.
Who is it recommended for?
Atera is available in two versions – one for managed service providers and the other for use by IT departments. Both versions are offered in four plans and both are delivered from the cloud. The subscription rate for Atera is calculated per technician. That pricing model makes this a good option for all sizes and types of businesses.
Pros:
- Helpdesk and Ticketing: Quickly address issues using AI-powered helpdesk and ticketing features, ensuring efficient resolution and customer satisfaction.
- Patch Management: Automate software patching across Windows, Mac, and Linux devices, keeping them up-to-date and secure without manual intervention.
- Monitor Unlimited Devices: Monitor unlimited devices at a fixed price, with a quick onboarding process, ensuring comprehensive coverage and cost-effectiveness.
- Minimalist Interface: Enjoy a clean and easy-to-navigate interface that focuses on essential metrics, making it simple to track performance and manage IT operations effectively.
Cons:
- Limited Scripting Capabilities: Users may find Atera RMM’s scripting capabilities somewhat lacking, limiting customization and automation options for advanced users or specific use cases.
Atera is a cloud-based service, so you don’t need to install any software on your premises. The remote system that is being monitored will need agent programs installed, however. The pricing model for Atera levies charges per technician per month, with an annual tariff also available that starts at $129 a month. Atera is available on a 30-day free trial.
5. AJ Tek WSUS Automated Maintenance
AJ Tek produces a range of WSUS maintenance tools that cover standalone and distributed WSUS servers. All are very reasonably priced for the useful utilities that these bundles contain.
Key Features:
- Simple Configuration Experience: this tool has a hassle-free setup process with the installer handling the configuration. You can opt for a standard installation with default settings selected for convenience.
- Backup the WSUS Database: you can backup the WSUS database, whether it’s a Windows Internal Database (WID) or a Local SQL Server. Remote SQL Servers should have alternative backup solutions in place.
- Compress Update Revisions: This process identifies and compresses update revisions to optimize storage space and enhance efficiency.
- Database Maintenance: This helps improve database performance and ensures the smooth operation of the Patch & Asset Management system.
Why do we recommend it?
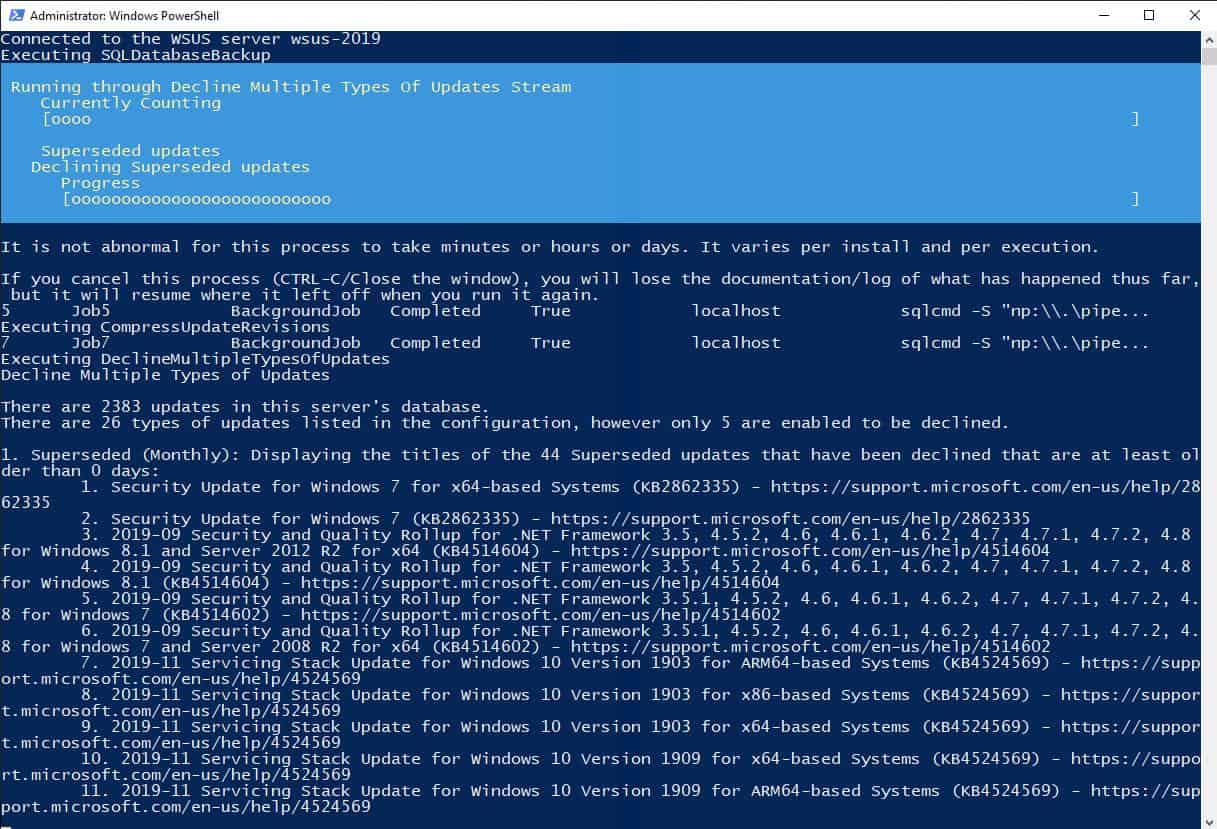
AJ Tek WSUS Automated Maintenance doesn’t replace the main functions of WSUS or augment its functions but it enables the WSUS system to work better. The tool is a package of PowerShell scripts and doesn’t have its own graphical user interface. Instead, this system works behind the scenes to clean up files and backup the WSUS system.
This system takes care of all of the maintenance tasks that you should be undertaking to keep WSUS and SCCM operating efficiently. WSUS Index Optimization in the package makes the database operations run faster. The tool also clears out unused drivers from the system. The system administrator is offered the option to remove certain types of updates and block them in the future, the options include expired, superseded, and preview updates.
With your WSUS system reduced in size and focused to only implement meaningful updates for your system, you free up space on your server and get to see a more manageable list of pending updates. The system also includes a method to manage the reports and synchronization logs that accumulate in WSUS. You can decide to keep the last 14 days of logs and choose to either delete or archive the rest.
The WSUS Automated Maintenance package makes your WSUS system more manageable and it frees up space on your server. It also frees up your time for other tasks. The system is available in a distributed format with modules for online, offline, and disconnected upstream servers, downstream servers used for replication, autonomous servers, and standalone WSUS servers.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool, like WSUS, is designed for use by businesses that use Windows on all of their endpoints. So, if you have any macOS workstations or Linux servers, you wouldn’t be interested in this package. The software installs on Windows.
Pros:
- Server Cleanup Wizard: it automatically runs the Server Cleanup Wizard (SCW) to remove unnecessary files from the file system, improving server performance and efficiency.
- Email the Report: You can easily receive reports via email in TXT, HTML, or PDF format, ensuring you stay informed about maintenance activities. If the report fails, it’s stored as a TXT log file for reference.
- Computer Object Cleanup: Automatically cleans up computer objects, deleting those that haven’t synced within a specified timeframe (default: 30 days), helping maintain a tidy Active Directory environment.
- Prune IIS Logs: This feature makes management easier by automatically deleting old log files from the WSUS IIS site’s logging folder, freeing up disk space and keeping the system running smoothly.
Cons:
- No Free Trial: AJ Tek WSUS Automated Maintenance does not offer a free trial, which means you cannot try out the software before making a purchase.
The interface for the system is a setup wizard and the actual processes run at the command line in PowerShell. Although the system doesn’t have its own GUI interface, you see the results of its actions in the WSUS system. AJ Tek doesn’t offer a free trial. However, the system is very cheap, starting at $60 per year.
6. AFDesign’s WSUS Tool for Spiceworks
Spiceworks’ user community produces add-ons and features for the free Spiceworks network management utility. One of the free tools available from the Spiceworks community is AFDesign’s WSUS Tool. The source code for the program is available at the utility’s page on the Spiceworks community website.
Key Features:
- Free Script: Users can access the tool for free without any cost or subscription required. This allows them to utilize the functionality without financial commitment.
- Works with Spiceworks Inventory: It can be easily integrated with Spiceworks Inventory to take advantage of additional functionality for managing Windows Server Update Services (WSUS).
- Written in Visual Basic: The tool is written in Visual Basic, a programming language; hence, it is easy to use whether you are a beginner or an expert.
- Execute Script from Remote Location: Utilize remote management software to install and execute the script from a central location. This allows for convenient management of WSUS tasks without the need to physically access each individual machine.
Why do we recommend it?
AFDesign’s WSUS Tool for Spiceworks is a lightweight free tool that is written in Visual Basic. It is available from the Spiceworks Community forum but you don’t need to be running any Spiceworks utilities in order to use it. The tool performs clean up and log management functions.
This is a script that automates the queries and actions that can be performed by the standard wuauclt.exe program, which ships with WSUS. This program runs on client terminals, so if you like this WSUS tool, you will need to install it on each endpoint. If you have remote management software, you can install and execute the script from your central location.
As the utility only employs standard Microsoft executables, you can be secure in the knowledge that you are not running third-party software that could damage your network or install malware. You can comb through the code yourself and see there is nothing malicious in there.
The program uses the standard WSUS detection procedure as a starting point. This gives you information on which services of the client agent are visible to the server. It will restart the client auditing software and run an audit check on it. This gets you a limited timeframe report rather than a tagged-on endless ongoing log file.
The process automation script checks each client. It is the type of utility you could probably write yourself. However, as someone has written this for you, the AFDesign WSUS Tool saves you some time running diagnostics.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is available on the Spiceworks Community forum for those who use Spiceworks Inventory. However, the tool works on WSUS rather than Spiceworks Inventory, so you can use it even if you don’t access any Spiceworks tools. You get access to the code and you are free to alter the program.
Pros:
- Track Activities: AFDesign’s WSUS Tool for Spiceworks allows you to keep track of who is doing what, helping you monitor and manage IT tasks effectively.
- User-Friendly: Spiceworks is a great starting point if you’re new to IT Help Desk tools. It’s easy to use, has a large support community, and integrates well with other tools, making it accessible for beginners.
- Full-Featured Monitoring Software: It offers extensive monitoring capabilities, including helpdesk and inventory support. The technical support is responsive, and there’s a supportive community to assist with any issues.
- Free and Effective: The tool is free and effective, with seamless integration with inventory and depreciation changes. It also provides a great dashboard for office ownership and management purposes.
Cons:
- Lacks Enterprise Features: Some users may find that AFDesign’s WSUS Tool for Spiceworks lacks certain features; hence, it might not be suitable for larger networks or enterprise-level use.
7. WSUS Offline Tool
Key Features:
- Client Integration with Windows Update: Networked clients can silently install patches without notifying end users, making the update process smooth and unobtrusive.
- Scalable Infrastructure: WSUS supports a scalable architecture; hence, you can install multiple WSUS servers. Remote WSUS servers can synchronize patches with the central server, improving performance and optimizing bandwidth utilization for remote updates.
- Web Management Interface: Manage WSUS through a user-friendly web interface accessible via a URL. The interface allows you to view patches, approve updates, classify systems into groups for easier management, and simplify patch deployments.
- Built-in Status Reports: WSUS provides built-in status reports with valuable insights into patch management activities. These reports are powered by a Microsoft SQL Server backend, so they can be used to analyze and inform decision-making.
Why do we recommend it?
The WSUS Offline Tool is a free utility that provides more thorough updates for offline computers than the standard Microsoft WSUS Offline Update system. The tool also updates the central records of WSUS to record its actions. The system relies on a copy of the tool being installed manually on each endpoint.
This tool schedules all available patches for the endpoint device type and delivers them from a central download server. Anoop C Nair, who wrote the tool, recommends it only for development and sandbox environments, not for live systems. Essentially, the tool will flag offline machines for all updates to be installed, not just the higher-status ones.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is free to use and so it is a good program to have to hand. If you have endpoints that never connect to the network, you won’t be able to rely on the standard WSUS system to keep them up to date. So, instead, you would copy all the update files onto a disk or USB stick and copy them over manually.
Pros:
- Automatic Update Downloads: it has automatic update downloads so you can configure specific updates with critical patches that are promptly acquired and available for deployment.
- Targeting: Administrators can deploy updates to specific computers or groups of computers, providing flexibility in patch management and ensuring that updates are applied where they are needed most.
- Database Options: you can effectively manage a database with extensive database options to store information about updates, events, and server settings.
- Reporting: Administrators can assess update compliance using detailed reports to monitor update approval and deployment status across computers and groups.
Cons:
- Lacks Advanced Troubleshooting Options: A few users find it lacking advanced troubleshooting options, which limits its effectiveness in diagnosing and resolving complex update-related issues.
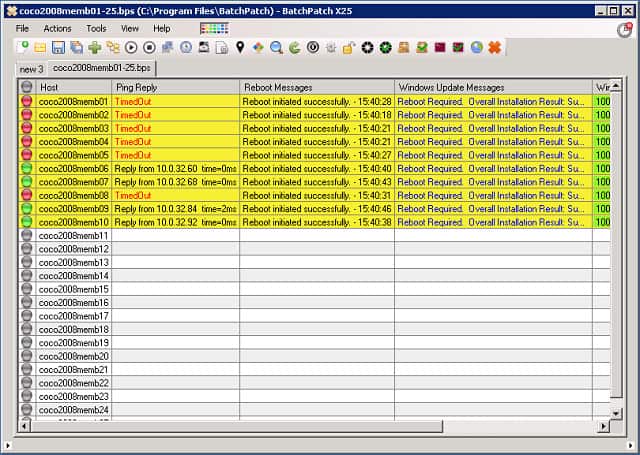
8. BatchPatch
BatchPatch adds a cheery and colorful GUI interface to your WSUS server. BatchPatch sits on top of the underlying WSUS service to provide better management and reporting functions than the bare WSUS facility. This utility is not free — the price for the tool is $399 for a one-user license with one year of support included. Prices go up to $2,999 for a 15-user license and increase to $3,745 if you buy a two-year support package with it.
Key Features:
- Flexible Update Installation: You can choose to install all available updates or select specific updates by name or classification groupings, such as Critical Updates or Security Updates. You can also opt to install only Important and/or Recommended updates, similar to Microsoft Windows Update.
- Use of Managed WSUS Server or BatchPatch: You can use your own managed WSUS server or BatchPatch along with Windows Update or Microsoft Update as a WSUS alternative, providing flexibility in update management.
- Offline Mode for Computers Without Internet Access: Users can also apply Windows Updates security updates to computers without Internet access using Offline Mode to ensure that offline systems remain secure.
- Deployment of Standalone Patches: Deploy standalone Microsoft or third-party patches, including updates for Adobe or Java, registry keys, scripts, and more, to remote hosts, providing comprehensive patch management capabilities.
Why do we recommend it?
BatchPatch is a very similar tool to the SolarWinds Patch Manager and ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus. It provides a new interface for software patches that communicates behind the scenes with the actual WSUS system. This system is able to install and update non-Microsoft software as well as Microsoft tools.
BatchPatch works on the central server and includes a client querying section, which enables you to remotely access each client terminal and run custom scripts for diagnostic purposes. Those remote functions let you manually reboot or shut down individual endpoints and employ Wake on LAN. Offline installs to clients can also be managed through BatchPatch. So, the functionality of this tool combines both server and client elements, although there won’t be any BatchPatch programs installed on any of the client computers.
First of all, this utility gives you all the functionality that the standard WSUS package includes; it just makes the commands easier to see. It makes a better effort of querying the statuses of each endpoint than the standard WSUS system. A range of pre-written report formats helps you view network device statuses. A rollup reporting system is available for networks with multiple WSUS servers.
BatchPatch goes beyond WSUS because it manages updates from other systems service producers, such as Adobe and Oracle. The scripting language of BatchPatch lets you sequence updates to manage software dependencies better. That extends across providers, so you can install required supporting software for each update, no matter where that software comes from.
BatchPatch is a step up from the straightforward WSUS system because it offers a full-blown patch management system for all service software. However, it isn’t advertised as a patch management tool for all software, i.e., applications and operating system software and services. The tool’s capabilities include downloading, transferring, and installing updates, diagnosing problem clients, and reporting on activities.
Who is it recommended for?
BatchPatch runs on Windows and will manage all of your endpoints from one server. As it isn’t a well-known brand like SolarWinds and ManageEngine, this tool has to compete on function and price. Both the better-known rivals are able to manage a longer list of software packages than BatchPatch.
Pros:
- No Remote Agent Installation Required: BatchPatch does not require remote agent installation, simplifying deployment and usage. You can simply launch BatchPatch and start patching without any additional setup.
- Integrated Job Queues: It creates sets of actions to execute in sequence on remote hosts. Users can automate tasks like running scripts before or after reboot or conducting multiple patch and reboot cycles.
- Advanced Multi-Host Custom Sequencing: BatchPatch offers advanced options for handling complex update and reboot tasks across numerous computers with online/offline dependencies, all configurable for single-click execution.
- Custom Script Execution: Depending on the patch management process, users can also execute custom scripts locally or remotely or add them to job queues for full automation.
Cons:
- High Price and Not Cloud-Based: BatchPatch is relatively expensive and not cloud-based. Hence, users didn’t find this flexible option for executing software deployments.
You can get a free trial version of BatchPatch. This does not have a time limit, but it is restricted to covering just four endpoints.
Choosing a WSUS server tool
The definition of “WSUS server tool” is very broad, so this review has covered the whole spectrum. If you just want to get a grip with error reporting on failed downloads, then NinjaOne Patch Manager would serve you well.
ManageEngine offers two routes to patch management. Patch Manager Plus manages updates for devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux as well as Windows Server. Patch Connect Plus integrates into SCCM to feed through patches available from software houses other than Microsoft onto a Windows Server machine.
Surprisingly few tools on the market just focus on enhancing WSUS. You are much more likely to get WSUS support with patch management systems such as BatchPatch or the Atera. It may be worthwhile to look into network device management systems and endpoint user managers. Many of these integrate well with patch management to improve the security of your network.
The importance of WSUS and patch management
Keeping all of your software up to date is an essential guard against viruses and network intrusions. Hackers discover new exploits in software all of the time and as soon as their new attacks are discovered software producers race to close off the loophole. Those exploit shutdowns are issued as patches and updates.
Keeping up to the latest version of your operating system is particularly important. An exploit in the operating system can give hackers access to the underlying firmware of your computer and give them unrestricted access to all software and data stored on your equipment. Therefore, WSUS is an essential tool for any business running the Windows Server environment.
WSUS functions
WSUS periodically checks the Microsoft servers for software updates and downloads them into a central repository. As an administrator, you have the option to approve or block specific updates. You can also specify the date on which the software will be distributed. It is also possible to pre-configure the distribution function to define automatic procedures for different classes of updates. So, you can specify that critical and security updates get installed automatically, while service packs and driver updates are held pending manual approval.
A detection function in WSUS creates a report on the updates available for each machine. This provides an inventory of the Microsoft software on each endpoint with the version status of each program. Other settings in WSUS block manual changes to Microsoft products operating on each computer.
WSUS and SCCM tools
Although a WSUS server works well as a patch management service, it only deals with Microsoft products, so you have to look elsewhere for more general patch management software. SCCM, the System Server Configuration Management tool, is another critical patch management service that operates in the Windows environment. It is common to encounter tools that can interact with both WSUS and SCCM to produce a more comprehensive patch management service.
WSUS Server FAQs
How do I use WSUSutil.exe?
WSUSutil.exe will give you a library of command-line controls to manage a WSUS server implementation. You don’t need to install the WSUSutil.exe program separately because it is part of the WSUS software package. The program is resident in the Program FilesUpdate ServicesTools directory of the drive that holds the WSUS server. You need to be in that drive to issue WSUS utility commands. All WSUS commands start with wsusutil followed by a keyword and parameters. For example, wsusutil reset.
How do I push WSUS updates immediately?
The WSUS administration settings enable you to specify that all updates are applied immediately so you don’t need to intervene for every single update. In order to set up an automatic push of WSUS updates immediately:
- Go to the Group Policy Object Editor
- Expand Computer Configuration and then expand Administrative Templates
- Expand Windows Components and click on Windows Update
- A details pane will open. Click on Allow Automatic Update Immediate to set it
- Click OK.
What is the latest version of WSUS server?
The latest version of WSUS server is 5.0. This is part of Windows Server 2016.
What is the difference between WSUS and SCCM?
WSUS only updates Microsoft products whereas SCCM is a much broader patch management system that can update software and firmware from other producers.
How do you audit a patch management process?
A patch management audit retrospectively checks that all necessary patches have been applied. Each patch changes the version number of the software. In order to perform this check, you need to have a list of all of the software that you have, including firmware and operating systems. You also need to look at the current version numbers and reconcile those against the version numbers that should be expected if the latest patch had been applied.
It is almost impossible to perform a patch management audit manually. In some cases, you might have intentionally refused an update. The reasons for those rejections need to be recorded so that you are aware of them later when you check on version numbers.