Flash drives are an easy target for data theft or loss, whether through physical theft or accidental exposure. This makes it essential for businesses to ensure that any sensitive information stored on these devices is properly secured. Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys offers a comprehensive solution to this problem, providing businesses with the ability to lock flash drives and protect valuable data from unauthorized access.
Endpoint Protector is an efficient data loss prevention (DLP) solution designed to secure data on endpoints such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. With its advanced encryption and access control features, Endpoint Protector allows businesses to lock flash drives, preventing unauthorized users from accessing, copying, or modifying data. This level of protection is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive customer information, intellectual property, or confidential company data.
Businesses can implement granular policies to manage access to flash drives, allowing them to restrict data transfers based on specific users, locations, or devices. Additionally, the software enables the encryption of flash drives to ensure that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains secure.
In this article, we will explore how Endpoint Protector helps businesses lock flash drives and prevent data leakage, highlighting its key features and benefits. By understanding how this tool works, companies can better protect their data, mitigate security risks, and maintain compliance with data protection regulations.
The evolution of Endpoint Protector
The flash drive security system that is included in Endpoint Protector was derived from two pre-existing systems:
- EasyLock
- Enforced Encryption
These two units have been discontinued as independent products since their functionality was integrated into the Endpoint Protector package.
EasyLock
EasyLock was a software solution that offered 256bit AES Military Strength Data Encryption that can turn any storage device into a data vault by password protecting it and encrypting the data stored on it.
Before it was discontinued, EasyLock offered technology to make sure all data transfers were seamless. As a result, users wouldn’t have to worry about the encryption and decryption process as they moved their back and forth to their drives and among different operating systems.
Enforced Encryption
An enforced encryption solution is an encryption and decryption program that runs automatically when a USB storage device is plugged in. It installs a program to ensure the security of the data written to or read from it by encrypting or decrypting it accordingly.
The first time a USB drive is plugged in, the client part of the application is installed. This makes the drive ready for the encryption and decryption processes as data is being stored and retrieved after authentication has been confirmed.
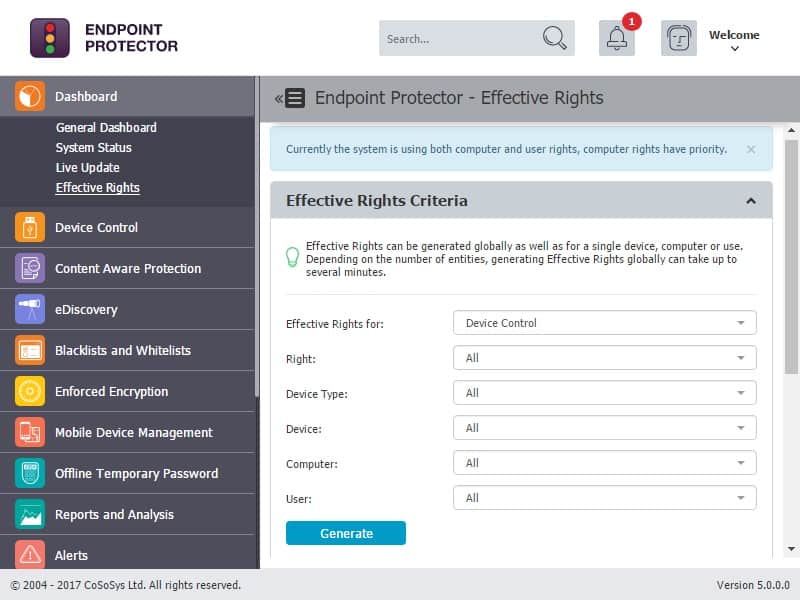
Endpoint Protector Device Control
Using Enforced Encryption, users will be authorized to transfer confidential data only on encrypted USB portable storage devices. In addition, the data will be safe even if a device is lost or stolen due to the password-protected encrypted area.
Now, EasyLock USB Enforced Encryption is combined with Endpoint Protector to allow administrators to extend their Device Control policy, ensuring all data transferred to USB storage devices is automatically encrypted.
It is an industry best-practice
Enforced Encryption is a best practice for IT security and covers USB devices, e-mails, internal hard drives, communications protocols, to name a few assets.
Enforced Encryption for USB devices can be remotely deployed, which means it is the ideal tool for networks of any architecture – on-premises, cloud, or hybrid.
Why choose Endpoint Protector?
Advantages of using Endpoint Protector include:
- Simplified user experience, fast and easy installation – the tool uses a web interface for centralized management and is easy to use once deployed, which only takes minutes.
- Security and compliance – apart from ensuring that data is kept safe, this tool can meet data security compliance requirements.
- It offers computer-based policies and also user-based policies that can lock individual devices or users, respectively.
- It can also trace and monitor movements of content – using this tool results in increased control of data that is moving around a corporate network and creating increased awareness among employees as they share their data on USB drives.
- It sends alerts out in case of security incidents and full logging and tracking capabilities to troubleshoot trigger causes occurring in a network environment.
- Convenient licensing also means individuals and large businesses alike can use this tool to secure their data.
What else does Endpoint Protector offer?
Endpoint Protector has a handful of modules to help secure corporate data, including Device Control, Content Aware Protection, eDiscovery, and Enforced Encryption.
The tool controls all device activity at the endpoints and monitors and scans all possible exit points to prevent the exiting of sensitive content. In other words, it ensures sensitive data does not leave the internal network either by being copied on a device or by being sent out via email without the proper authorization. Instead, it reports all such sensitive data movements.
Moreover, data at rest on endpoints can also be scanned for sensitivity so remedial action can be taken if an alert is triggered. And then, of course, there is the enforced encryption of the data USB devices.
Devices covered
Endpoint Protector is designed around three major entities:
- Users – the employees and guests handling computers and the other devices that connect to them.
- Computers – all the Windows, Mac, and Linux computers with the Endpoint Protector Client installed.
- Other devices – all the other devices which connect to these computers or directly to the network and are supported by Endpoint Protector like USB hard disk drives, digital cameras, and USB sticks.
Step by step installation and management of Endpoint Protector
Endpoint Protector makes sure that its users know how to use its products and have put enough information out there to help anyone:
Knowledgebase
Users can simply go to the company’s knowledgebase page and get all the information they need about everything from installation to the management of Endpoint Protector.
A user manual
Alternatively, they can download the Endpoint Protector users’ manual [Ver. 5.4.0.0, PDF].
YouTube videos
And, finally, they can go to YouTube and watch videos of how the tool can be used to create a secure environment:
How does Endpoint Protector work?
There are a few steps involved in how Endpoint Protector works:
- Deploy the Device Control module – the Device Control module is the first layer of security provided by Endpoint Protector. By defining granular access rights for USB and peripheral ports, device security is enforced while maintaining productivity. In addition, as a cross-platform solution, it protects the entire network, regardless of if the computers are running on Windows, Mac OS X, or Linux.
- The Endpoint Protector Client is the application installed on client computers. It communicates with the Endpoint Protector Server to block or allow devices to function and sends out notifications in case of policy breaches.
- Data is encrypted automatically when files are transferred to and from devices and is even moved securely when shared between computers.
- A lightweight agent allows for the remote monitoring of USB – and peripheral – ports from a simple web-based interface that has no impact on the protected computers’ user experience (UX).
- Administrators can remotely manage accesses by granting or denying USB usage – even when the computers are offline – while keeping track of activity with the help of log reports.
- The administrator can also configure several security settings such as setting a client to uninstall password, restricting access to sensitive information only to Super-Admin roles, fixed password protection on any sensitive data, enforce administrators’ password security by requesting change during the next login and setting password expiration options.
- Furthermore, they have precise and granular control – they can assign permissions depending on departments’ requests and specify which device can or can’t be used. They can create device white- and blacklists and define policies per user, computer, or group.
How can Endpoint Protector help businesses?
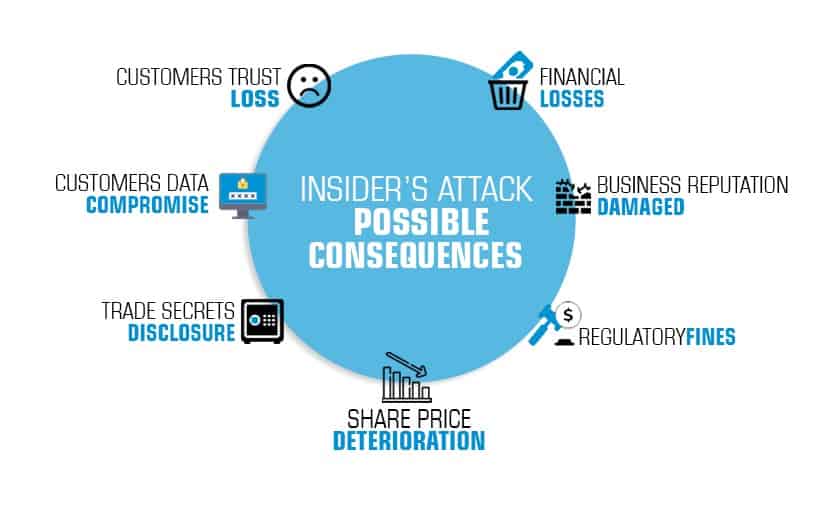
Let’s look at it from a corporate angle; using Endpoint Protector comes with advantages like:
- An additional layer of security – using Enforced Encryption, authorized users will be permitted to transfer confidential data using encrypted USB portable storage devices. As a result, corporate data will always be safe; even if the USB drives are lost or stolen, the data remains secure due to the password-protected and encrypted area.
- Compliance with regulations – many IT industry regulations now ask for confidential data to always be encrypted, regardless of where it resides. And, Enforced Encryption helps companies become compliant with HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX, and other regulations.
- Better Data Leakage Prevention (DLP) – businesses that opt for the flagship Endpoint Protector DLP solution can rest assured that their security is further enhanced with the use of Enforced Encryption; thus, making sure sensitive data is secured even more, and data leakages are additionally
- Ensuring business continuity – installing this tool minimizes the risks of data loss that can affect the image, performance, and even survival due to fines and lawsuits; it is better to protect data instead of trying to manage data loss consequences.
The threats involved
Some threats that can be prevented by using Endpoint Protector include:
USB phishing scams
Hackers scatter USB drives near a company they want to break into with the hopes that an employee will be curious enough to pick one up and plug it into a device that is on the corporate network. These USB drives have malicious programs stored on them that start running as soon as the drives are connected to a port.
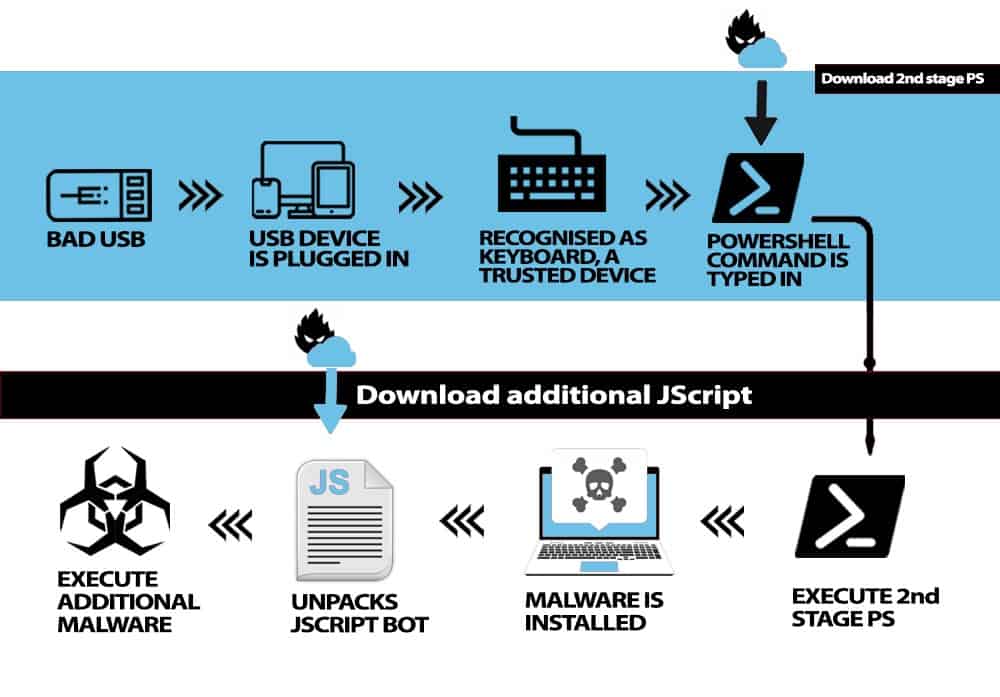
BadUSB and Rubber Ducky attacks
In these attacks, USB drives are programmed to mimic Human Interface Devices (HID), like keyboards, to trick the computers into responding to typed-in commands that unleash malware.
Insider threats
Employees and authorized users can let sensitive information out intentionally or otherwise as they store data on USB drives that could be lost, stolen, or simply handed over to unauthorized users with malicious intentions.
Injection of virus and malware
Alternatively, malicious and authorized users can willingly plug in an infected USB or simply steal data by making illegal copies of it.
What are other Endpoint Protector features?
Let’s have a look at some of the features of this tool:
- This tool offers military-grade encryption – it protects data with government-approved 256bit AES CBC-mode encryption.
- It has an Offline Temporary Access Administrator that generates passwords and grants temporary access to an entire computer, a specific device connected to it, or enables Content Aware Protection feature on the computer; this feature can be used even when there is no network connection between the computer and the Endpoint Protector Server.
- It has a Logs Report that allows the administrator to see exactly what activity has taken place and at what time; the information provided contains computer names, users, and devices used – along with the action taken and the files accessed.
- The Statistics module shows system activity regarding data traffic and device connections that can be filtered to get deeper insights.
- File Tracing displays information about files that are being traced – when they have been transferred from a protected computer to a portable device or another device on the network, for example. It also displays the original location of the shared files, as a Detect Source Copy feature is activated by default.
- The File Shadowing section lists information about shadowed files that have been transferred from a protected computer to a portable device so the files may be protected by an additional password set by the administrator; the shadowed files can be saved locally on the Server by the Endpoint Protector administrator for safekeeping.
- Endpoint Protector Alerts sends alerts for Sensitive Content Transfers, Devices, Computers, Groups, and Users depending on the required subject; an Alert will trigger an email sent to administrators before being logged as history for easier troubleshooting.
- A File Maintenance module that allows administrators to organize and clean up files that are no longer needed.
- A Transparent Mode is used when administrators want to block all devices but don’t want users to see and know anything about Endpoint Pointer’s enforcing policy activity.
- The Stealth Mode is similar to the Transparent Mode. However, it allows the administrator to monitor all user and computer activities and actions by permitted devices without alerting the user.
- It has a Password Length and Security Parameters Management to require users to use a password with specific formats, like include numbers, special characters, etc., to encrypt data securely; the password is never saved and is even erased from RAM immediately after it has been entered.
One other Endpoint Protector tool
Finally, administrators can shut it all down by using the Endpoint Protector USB Blocker. They can lock all USB ports on every device on the network with this security tool. This step will stop data from being leaked via flash drives.
It helps prevent confidential data from being copied to unauthorized removable storage devices while also protecting against the spread of USB malware and potential data breaches.
An administrator can ensure that absolutely no weak point is exposed via a USB port – there is no transfer of sensitive data, no theft, no leaks, no transmission of viruses, and no installation of malware – by simply battering down all the hatches.
We would like to hear from you. Please, let us know of any experience you have had with Endpoint Protector; leave us a comment below.