The ability to collect, analyze, and utilize publicly available information has become a crucial aspect of cybersecurity, threat intelligence, and investigative work. Open-source intelligence (OSINT) tools enable professionals to gather data from publicly accessible sources across the internet, helping them uncover valuable insights related to individuals, organizations, and threats. These tools are widely used by cybersecurity experts, law enforcement agencies, private investigators, and even businesses aiming to protect their digital assets.
For security operations centers (SOCs), threat analysts, and risk management teams, OSINT tools provide an invaluable resource for identifying vulnerabilities, monitoring for data breaches, tracking cybercriminal activities, and conducting background checks.
The primary pain points faced by these professionals include the overwhelming volume of online information, the complexity of sifting through data to find relevant insights, and the time-consuming nature of manual research. OSINT tools are designed to address these challenges by automating data collection, streamlining analysis, and helping users focus on the most pertinent threats or risks.
OSINT tools can address the following pain points in any organization
- Gathering data from multiple sources using manual methods can take too much time and effort.
- Limited visibility into external information increases the risk of threats.
- Limited ability to connect data across different points, like social media, forums, and public databases. As a result, the picture you get can be inaccurate or distorted.
- Incompatible data formats can make any analysis slow and unreliable.
- There is no centralized platform to monitor and manage all the data collected from different sources.
These tools offer cybersecurity professionals a means to proactively identify potential threats before they escalate, while investigators can leverage them to track leads and build evidence-based cases. Ultimately, OSINT tools help mitigate the challenges of information overload, improve the accuracy of threat detection, and enhance overall efficiency, enabling professionals to make informed decisions in real-time.
Let’s now explore why OSINT tools have become essential in today’s information-driven world.
Open Source Intelligence Tools – or OSINT tools – are not as intimidating as they sound. You see, we live in an age where the value of information, which is a commodity in its own rights, has continued to increase over time. Everyone, it seems, needs to have it.
And yet, surprisingly, the amount of information – about almost anything under the sun – that is available, to anyone who can be bothered to look, has also grown immensely. This is where the best OSINT tools we will soon see come into play as we learn to dig deep to uncover all this data.
Here’s our list of the best OSINT tools:
Based on our independent research, selection requirements, and rating methodologies, these are the best OSINT tools on the market today:
- Maltego EDITOR’S CHOICE This is a powerful open-source intelligence (OSINT) and link analysis tool, enabling users to map out complex relationships between people, organizations, websites, and more. It excels in visualizing data, conducting investigations, and gathering intelligence for cybersecurity, fraud detection, and digital forensics. Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- OSINT Framework A website directory of data discovery and gathering tools for almost any kind of source or platform. This is a free index to a wide range of free and paid online systems that range from dating platforms to data analysis tools.
- Babel Street Insights This international search system uses AI to cross language barriers for any search term. This is a cloud-based service.
- Google Dorks OSINT data gathering method using clever Google search queries with advanced arguments.
- Shodan A search engine for online devices and a way to get insights into any weaknesses they may have.
- Metasploit An advanced open-source framework used for penetration testing and security auditing, offering tools to discover and exploit vulnerabilities in systems.
- Recon-ng An open-source web reconnaissance tool developed in Python and continues to grow as developers contribute to its capabilities.
- Aircrack-ng A wifi network security testing and cracking tool that can be used both defensively and offensively to find compromised networks.
If you need to know more, explore our vendor highlight section just below, or skip to our detailed vendor reviews.
Best OSINT Tools highlights
Top Feature
Powerful link analysis and data visualization for mapping complex relationships
Price
Three editions: Free Community, Professional, and Organization; contact vendor for pricing
Target Market
Cybersecurity teams, investigators and analysts seeking visual intelligence tools
Free Trial Length
Free Community edition available (registration required)
Additional Benefits:
- Uncovers hidden links between individuals, organizations and assets
- Supports complex OSINT workflows and multi-source intelligence
- Integrates with APIs and external data providers
- Trusted by investigative journalists and professionals globally
Features:
- Visual link analysis through interactive graphing (Maltego Graph)
- Automates data collection with customizable transforms
- Works across Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Collaborative tools for team-based investigations
- Real-time querying and data enrichment from multiple sources
Top Feature
Comprehensive directory of categorized open-source intelligence tools and resources
Price
Free to use; some linked tools may require registration or offer premium features
Target Market
Cybersecurity professionals, investigators, journalists, and researchers seeking structured OSINT resources
Free Trial Length
Not applicable; the framework itself is freely accessible
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Real-time multilingual monitoring of public, deep, and dark web data
Price
Negotiated pricing: contact the vendor for details
Target Market
Government agencies, defense, intelligence, and large enterprises
Free Trial Length
Free demo available upon request
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Advanced search queries that reveal sensitive or hidden public data
Price
Free
Target Market
Penetration testers, researchers, and OSINT analysts needing fast reconnaissance
Free Trial Length
Not applicable
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Real-time visibility into internet-connected devices
Price
Freelancer: $69/mo, Small Business: $359/mo, Corporate: $1,099/mo
Target Market
Cybersecurity analysts and network administrators
Free Trial Length
Free version
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Automated penetration testing and exploitation
Price
Free (Metasploit Framework); Contact sales for Metasploit Pro
Target Market
Security professionals and penetration testers
Free Trial Length
Free version
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Modular command-line OSINT framework
Price
Free
Target Market
Cybersecurity researchers and Linux users
Free Trial Length
Free version
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Wireless encryption cracking and auditing
Price
Free
Target Market
Penetration testers and wireless security analysts
Free Trial Length
Free version
Read more ▼
Key points to consider before selecting an OSINT tool
When choosing an OSINT tool, it’s essential to evaluate your organization’s specific needs and the unique features that can help address the challenges faced in gathering and analyzing open-source intelligence. Here are several key points to consider before selecting an OSINT tool:
1. Purpose and Use Case
Different OSINT tools serve various purposes, from monitoring social media activity to gathering data on potential threats. Before purchasing, clearly define your primary use case. Identify whether you’re focused on threat intelligence, risk management, background checks, or investigating cybercriminal activity. Choose a tool that is tailored to the specific data types and sources relevant to your needs.
2. Ease of Use and User Interface
The effectiveness of an OSINT tool depends not only on its features but also on how easy it is for users to navigate and operate. Look for a tool with an intuitive user interface (UI) and robust reporting capabilities. A well-designed UI can drastically reduce training time and enhance your team’s productivity.
3. Data Sources and Coverage
Ensure the OSINT tool can access a wide range of public data sources, including social media platforms, dark web sites, forums, news outlets, and more. The depth and breadth of the data collected directly impact the quality and accuracy of the insights you can gather.
4. Automation and Customization
Many OSINT tools offer automation capabilities that allow users to schedule searches or create alerts for specific keywords or data patterns. Evaluate whether the tool supports the level of automation you need. Additionally, customization options for data extraction and analysis can save time and ensure more relevant results.
5. Integration with Other Tools
If your organization relies on other security tools or data management platforms, it’s important to choose an OSINT tool that integrates smoothly with your existing software stack. Integration can streamline your workflows, ensuring that the OSINT tool complements and enhances the performance of your other systems.
6. Scalability
As your organization grows or as your OSINT needs evolve, you may require more advanced features or a tool that can handle a larger volume of data. Make sure the OSINT tool you select is scalable and can grow with your needs, whether you’re expanding your team or monitoring new sources.
7. Support and Training
OSINT tools often have a steep learning curve, especially for beginners. It’s essential to choose a tool that offers excellent customer support and training resources, such as documentation, tutorials, and user communities. Access to responsive support can minimize downtime and ensure a smoother implementation process.
8. Cost and Licensing
Finally, assess the total cost of ownership for the OSINT tool. Some tools are subscription-based, while others require a one-time purchase. Consider your budget and the long-term financial commitment required. Additionally, check the licensing model to ensure it aligns with your team size and usage expectations.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select an OSINT tool that best meets your organization’s needs, enhances your security capabilities, and supports informed decision-making.
To dive deeper into how we incorporate these into our research and review methodology, skip to our detailed methodology section.
How to calculate ROI for OSINT tools
Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) for OSINT (Open Source Intelligence) tools involves assessing the financial and non-financial benefits of using these tools compared to their costs. Here’s a general framework you can follow:
Identify Costs
These are the direct and indirect expenses associated with using the OSINT tools.
Direct Costs:
- Subscription fees – monthly/yearly charges for using the tool
- Training – if required for employees to get up to speed with the tool
- Licensing – if any
- Infrastructure costs – if the tool requires any additional hardware or software
Indirect Costs:
- Employee time spent learning or using the tool
- Operational costs (e.g., any downtime due to new tool implementation)
Identify Benefits
Define the value or benefits you gain from the OSINT tool. These may be financial or non-financial.
Financial Benefits:
- Cost savings – e.g., reduced need for hiring external agencies or private investigators
- Increased efficiency – e.g., faster intelligence gathering, reducing man-hours
- Improved decision-making – leading to cost savings or revenue generation
Non-financial Benefits:
- Enhanced security – e.g., early detection of potential risks, which prevents costly breaches
- Improved compliance – e.g., better regulatory adherence
- Risk mitigation – e.g., avoiding financial losses from fraudulent activities or cyberattacks
Calculate ROI
ROI can be calculated using the formula:
Where:
- Total Costs = the sum of all costs associated with the OSINT tool.
- Total Benefits = the tangible and intangible benefits derived from using the tool.
Example:
- Suppose you purchase an OSINT tool with the following costs:
- Subscription fee: $10,000 per year
- Training costs: $2,000
- Infrastructure costs: $1,000
- Employee time: $3,000 (time spent by employees using and learning the tool)
So, the total cost is:
$10,000 + $2,000 + $1,000 + $3,000 = $16,000
For the benefits:
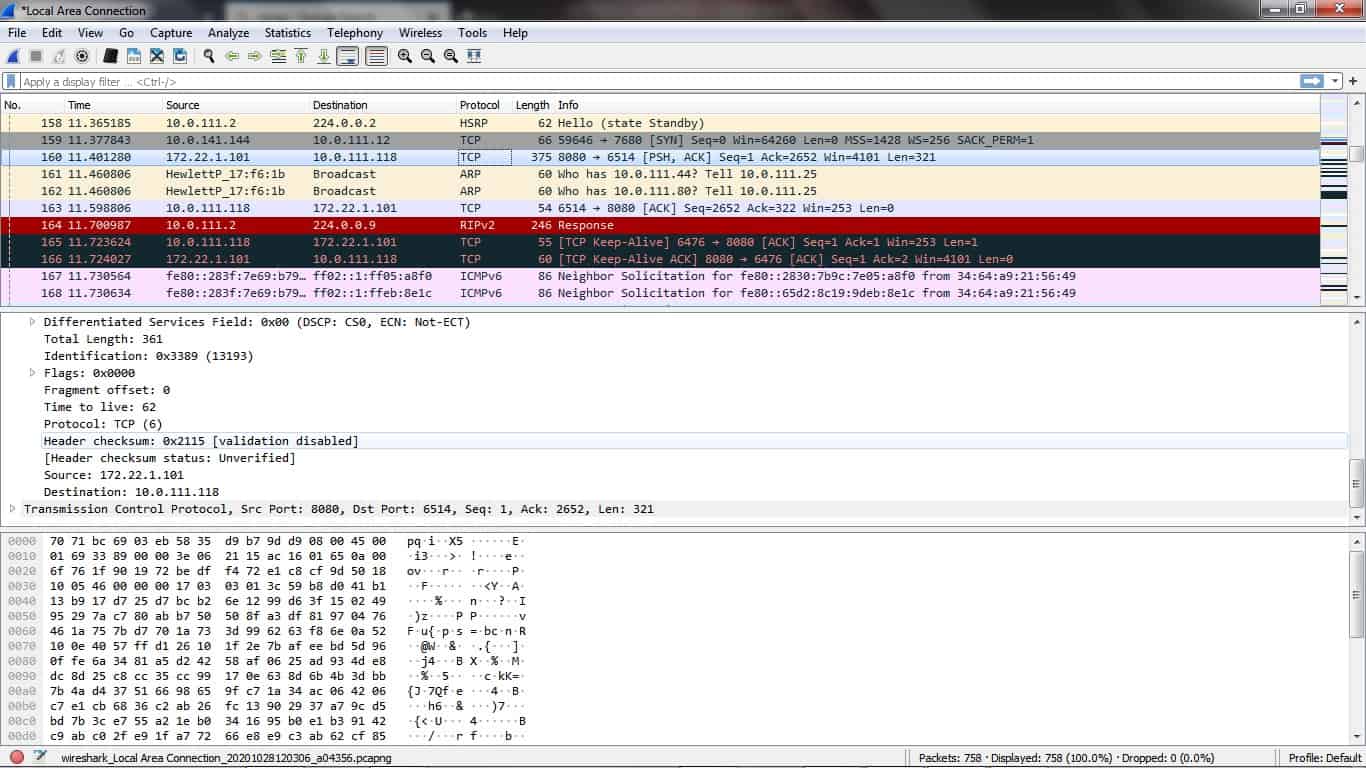
- The tool reduces the need for external investigation services, saving you $20,000 per year.
- It helps you identify and mitigate risks, saving $10,000 annually in avoided losses.
- It improves employee productivity, saving 100 hours of work, equivalent to $5,000 in wages.
So, the total benefit is:
$20,000 + $10,000 + $5,000 = $35,000
Now, using the ROI formula:
In this case, the ROI for using the OSINT tool is 118.75%, which means for every dollar spent, you are receiving an additional $1.18 in value.
Track ROI over time
Since OSINT tools are often part of long-term investments, it’s important to track ROI over a longer period. The benefits may increase as the team becomes more proficient with the tool or as the organization gains more intelligence that can be leveraged for decision-making.
ROI calculation summary
The ROI for OSINT tools can be calculated by comparing the total costs (both direct and indirect) with the benefits (both financial and non-financial) derived from using the tools.
What is OSINT?
OSINT – short for Open Source Intelligence – is the art of searching for, collecting, and summarizing information that is freely, and publicly, available on the Internet for the purpose of using it as a source of intelligence.
This public information can be about an individual, a business or corporate entity, a network, a nation, or any other source of relevant data. And, as the “open source” part of OSINT indicates, there is no need to employ sneaky or illegal tactics to obtain it.
After all, why would anyone want to resort to illegal activities when the data they need is freely available from Internet sources like websites, blog posts, social media platforms, search engine result pages (SERPs), and other public-facing digital assets, just to name a few?
Why would we need OSINT for business?
The scope of this article will be limited to a business and its network. The person doing the research is assumed to be an administrator trying to protect the network.
And so, as an administrator of a business network, the main reasons for using OSINT would be:
- Penetration testing: a great use for OSINT would be to gather all the information that is available out there and see if any of it can lead to an indication that your network has been compromised.
- Breach detection: if there is data out on the Internet that you didn’t share it could mean you have been hacked and have had data stolen. Monitoring the Internet using OSINT could give you an early start in damage control and even catch the people behind the data theft. Alternatively, it could simply be that a public-facing (or peripheral) device hasn’t been secured well enough and could be leaking data. Either way, an OSINT tool will give you a heads-up.
- Ethical hacking: turn the table and gather information on a source-target; find out everything you can about competitors and use it to gain an insight into their way of doing things. Remember, as long as you abide by the OSINT ethical hacking rules, you will be on the right side of the law. Never cross that line – no matter how strong the temptation is.
- Chatter monitoring: use OSINT to listen to what is being said about you and yours. Perhaps you have a reputation to maintain, a brand to protect, or a network to secure. Monitor traffic and packets to see what is being directed your way; use the tools to find out all you can before an attack happens.
Finally; remember it isn’t just businesses that use OSINT. Governments and their agencies also use it to gather data on undeclared assets that belong to persons or organizations of interest, for example. With the right tools, a business can find out if there are any such probes aimed their way by simply looking at the searches, queries, and any network penetration attempts that are being made.
What types of OSINT do we have?
OSINT tools can be divided into three main categories:
- Discovery tools: are used to search for the information that is out there. A great example would be Google. Although it may seem like it is a simple search engine, there is really nothing simple about the information it can discover when an OSINT expert has a go at it, as we will soon see.
- Scraping tools: once discovered, the data must be “scraped” and collected somewhere safe. These tools make sure only the required data is filtered for extraction to avoid bulky transfers (which could alert the source) and also avoid unnecessary data that could muck up the information that is to be extracted from it.
- Aggregation tools: once the data has been stored safely, it needs to be mined and sifted through to convert it into usable These tools are used to combine related data bits into a larger picture and present it in a way that will show relations and connections between datasets and bring it all together in a consumable format.
Of course, there are tools that have all three functionalities included in one package.
OSINT gathering tactics
There are three methods of OSINT intelligence gathering:
- Passive: this is the “normal” way of digging for information; usually done by scouring the web with applications like Google search, Bing Maps, and Yandex images. This method is hard to detect as no probing is involved and only archived information is collected.
- Semi-Passive: here too, scouring the Internet is involved, to find the data; but software solutions are also involved to non-intrusively gather information about a network, for example, and send the data off to collection servers. No brute force attacks or in-depth querying is involved.
- Active: in this scenario, the information is collected by directly extracting it from the target; although no malicious software is involved in breaching their security. Remember, although it is publicly available, just sitting unprotected on their servers and networks, it could still be perceived as hacking. This type of probing can be detected because it involves scanning of networks to find open ports, for example. Once the data has been discovered, the next step involves getting it into storage servers for further analysis.
This brings us to the point where we have to warn you about using OSINT tools without hiding your identity. Always assume that your target will find out about the intelligence probe and might even try to go after you – legally or otherwise. Learn how to hide your identity by using VPNs, fake accounts, and TOR, and other anonymity tactics.
What kind of information can you gather with OSINT?
To be honest, you could probably extract any information that is in digital format. There is no such thing as a secure online presence. Once a device is exposed to the Internet, someone, somewhere, could probably find a way to it.
The only truly secure system is one that is powered off, cast in a block of concrete, and sealed in a lead-lined room with armed guards – and even then I have my doubts. – Gene Spafford
Search engines like Google can give you insights into data that is not only shared on the web but also, with the help of advanced arguments, allow you to delve deeper to find files and information that hasn’t been shared intentionally.
Then again, using tools like Google Earth, you can see some of the remotest parts of the planet and even accidentally uncover state secrets. On the other hand, you can also catch live events with the help of unsecured security cameras, unprotected CCTVs, and even a Google mapping car.
To put it all in perspective: all that is needed to start finding information on a person is a single phone number. Once we have that, it is easy for anyone to build an OSINT tool – from scratch – that can extract information like name, location, and social media account details which can then be used to dig further for even more personal or financial information.
The Best OSINT tools
Before we begin, we need to remind you: the information provided in this post is for informational purposes only; you – and only you – will be held responsible for any misuse of said information.
We looked for OSINT tools that can collect, collate, visualize, and store pertinent research.
Feature Comparison Table:
| Product/Features | OSINT Framework | Babel Street Insights | Google Dorks | Shodan | Maltego | Metasploit | Recon-ng | Aircrack-ng |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network mapping | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Vulnerability detection | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Data harvesting | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Social Media Intelligence (SOCMINT) | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| API availability | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Data visualization | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Customizable scripts | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Platform compatibility | Web-based | Web-based | Web-based | Web-based | Windows, Linux, macOS | Windows, Linux, macOS | Linux | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| User interface (CLI/GUI) | Web UI | Web UI | Web UI | Web UI | GUI | CLI | CLI | CLI/GUI |
| Free version available | Yes | No | Yes | Yes (Limited features) | Yes (Community version) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
1. Maltego
Best for: Identifying links between data points
Price: Three editions: Community, which is free to use; Professional; Organization – Maltego doesn’t publish a price list.

This OSINT tool is helpful in finding information on individuals as well as organizations. It can run on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
Maltego’s key features
Maltego is a unique system for discovering links between people and events. Here are its most important features:
- Relationships Visualization: Maltego identifies and visualizes relationships between various data points, facilitating network analysis.
- Visual Data Map: It generates a visual data map, depicting connections and relationships between different entities.
- Multi OS Support: Maltego is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, ensuring accessibility across different platforms.
- Data Gathering Automation: Pre-built algorithms that gather data from external sources and automate information collection.
- Data Integration: Integrates with a wide range of external data sources, including DNS records, social media, and WHOIS databases.
Unique buying proposition
Maltego’s unique buying proposition lies in its powerful data mining and link analysis capabilities. I tried this tool for an afternoon and you really need to put in a lot more time to learn the system in order to get useful information out of it. The investigative journalists at Bellingcat regularly use this tool for their projects, and they also give courses on how to use Maltego effectively. So, if you are interested in Maltego, it would be worth investing in a training program, so you know how to use it properly.
Feature-in-focus: Maltego’s Maltego Graph
Maltego Graph allows users to visually explore relationships between various data points, uncover hidden connections, and map out intricate networks. This makes it ideal for investigators, cybersecurity professionals, and OSINT specialists seeking comprehensive intelligence insights. This visual representation of data can also help investigators notice patterns in data.
Comparitech SupportScore
Maltego gets a good SupportScore because it lies in the sweet spot between enthusiast-driven technology and an established enterprise. The staff of the company are very motivated to the product, which means they have high job satisfaction. The age of the business and its profitability give Maltego stability, which improves the points awarded in the SupportScore calculation.
The tool gets a SupportScore or 8.1 out of 10, which is respectable. The presence of extensive in-app guides as well as a competent Customer Support team win this tool its high score.
Why do we recommend it?
Maltego is a truly unique tool but you would need to take a course in how to use it in order to even know how to start with an investigation. Those who have mastered the use of the tool get stunning results by tracking the links between identities to reveal the presence of an individual in different arenas and then track other people related to that person and identify their activities.
Although you need to register with Maltego Community to start digging for information, which is a mighty tool as it is, you can also buy the premium version for even more advanced features.

Once signed in, you get a “Graph” window where you do your research. The query results are displayed in the form of a bubble graph that shows the relations of each “transform” results – as Maltego query scripts are known.
To start the information-gathering process, you first enter the main entity you are researching – an individual, organization, phone number, etc. – and run the available transforms to see the results. For example, it can be used to map networks to see how the servers on it are linked and if, perhaps, they have been compromised. The resulting information can be filtered or further “transformed” for even more in-depth data analysis.
Who is it recommended for?
Maltego is a useful tool for private investigators and journalists. It can also be used by hackers to profile individuals and track their activities. Bellingcat uses Maltego extensively, for example, to reveal the identities of the Russian secret service agents behind the poisoning of Alexei Navalny.
Pros:
- Great for Mapping Complex Networks and Relationships: Maltego offers a highly visual interface, making it ideal for mapping complex networks and relationships.
- User-Friendly Interface: The interface of Maltego is detailed, providing in-depth information, yet it remains easy to learn and use for users of varying technical expertise.
- API Data Source: Maltego users can add new data sources via API, enhancing its flexibility and utility.
- Collaborative Features: Allow teams to share investigative results, workflows, and analyses.
- Real-time Data Access: Supports real-time data queries for manual investigations.
Cons:
- Cost-Prohibitive for SMBs: The paid versions of Maltego can be expensive, which may deter smaller organizations with limited budgets from accessing its full range of features and capabilities.
Although this tool is very easy to use, as you simply start from one piece of information and start to progressively build on it, it is also very powerful and never disappoints in its result delivery.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Maltego is our top pick for an OSINT tool because this innovative system uses link analysis and personal or corporate associations to spot collaborations and clandestine activities. The tool is designed for cybersecurity professionals, investigators, and researchers. It enables users to gather, analyze, and visualize information from a wide variety of sources, such as social media, DNS records, domain names, and public databases. Maltego has a unique ability to map and visualize complex relationships between entities, such as people, organizations, websites, and other networked assets. This makes it an invaluable tool for digital forensics, threat intelligence, and fraud detection. The technology operates by leveraging pre-built algorithms that automate the process of extracting data from different sources. These transforms can be customized or extended to integrate with external APIs and data sets, allowing for deep, context-rich intelligence gathering. Maltego presents findings in an intuitive graphical format, making it easy to spot connections, patterns, and potential threats across large volumes of data. Maltego is particularly well-suited for investigations related to cybercrime, malware analysis, social engineering, and penetration testing. Its flexible, scalable platform offers both free and paid versions, suitable for individuals and enterprises alike.
OS: Windows, Linux, and macOS
2. OSINT Framework
Tested on: The Web
Best for: Discovering open-source data
Price: Free

This is perhaps one of the most popular OSINT tools out there. The thing is that OSINT Framework is more of a website with a directory of tools rather than just one single tool. And, it is perhaps this ability to find all the tools you may need to dig up all the information on a target, in one place, that makes it the go-to option for information gathering.
OSINT Framework’s key features
OSINT Framework isn’t a tool as much as a list of links in a website. Here are its main features:
- Online Tool: OSINT Framework is an online platform, accessible via web browsers, facilitating easy access for users.
- Directory of Information Sources: It provides a directory of various information sources, aiding users in conducting open-source intelligence (OSINT) research.
- Search Facilities: OSINT Framework offers search facilities, enabling users to quickly find relevant tools and resources.
- Data Collation: Users can collate data from various sources using the tools and resources available within the framework.
Unique buying proposition
As it is a free resource, the concept of “buying” isn’t really relevant here. However, OSINT Framework’s unique buying proposition lies in its comprehensive, organized collection of open-source intelligence tools and resources. It offers users an extensive directory of categorized links and resources for data gathering, making it an invaluable tool for investigators, cybersecurity experts, and researchers looking for structured and efficient intelligence gathering.
Feature-in-focus: OSINT Framework’s library of links
OSINT Framework’s library of links offers a curated collection of open-source intelligence tools and resources, categorized for easy access. It includes links for gathering data from various sources such as social media, domain information, and public records. This comprehensive library helps investigators streamline their research and enhance efficiency.
Comparitech SupportScore
OSINT isn’t a commercial product; it is an infrequently updated list of links. So, it doesn’t really have a team of any kind, let alone a support team. In fact, it is run by one person and has no revenue. Thus, most of the points categories for the SupportScore calculation are zero.
The OSINT Framework gets a SupportScore value of 0.5. However, as this is a static resource, the concept of support is irrelevant.
Why do we recommend it?
OSINT Framework is a directory of data sources and links through to handy tools for data discovery and sorting. This is a great resource but there are a lot of tools linked to in this list. You need to establish a search strategy that focuses on a particular type of data, such as vehicle registration or email addresses.
Another reason this is a popular collection is that many of the best OSINT tools are written or created for a Linux environment. This directory, meanwhile, has many tools that can be run from a browser and, even when the installation is needed, there are options for most major operating systems.
The collection of OSINT tools can help dig up information using anything from a simple telephone number, IP address, or email addresses. There are even options for venturing into the Dark Web or the ability to analyze malicious files. So, proceed with caution.

There are tutorials and games included to get beginners started with the digging-for-information game. Need a VM for a research campaign? You can find a list of software solutions under “Virtual Machines”.
Who is it recommended for?
OSINT Framework is a good starting point for anyone who has never performed a search of public data before because it has a training section. The guides explain methods to implement when conducting research. You can then use that knowledge to scan through a large number of tools and data sources in the list to perform a targeted research project.
Pros:
- Widely Recognized: OSINT Framework is widely recognized as a leading platform in the OSINT community, offering valuable resources and tools.
- New Tools Discovery: It serves as an excellent resource for discovering new tools and techniques for collecting open-source intelligence.
- Tools Sorting by Category: Users can sort tools by category, facilitating easy navigation and discovery of relevant tools.
- Completely Free: OSINT Framework is entirely free to use, eliminating any barriers to access for users.
Cons:
- Overwhelming for New Users: The vast array of tools and resources available within OSINT Framework can be overwhelming for new users who are not familiar with open-source intelligence techniques and methodologies.
Almost all of the tools that are linked to an OSINT Framework are free while the few remaining ones might ask for a small subscription fee.
3. Babel Street Insights
Best for: Identifying similar data across languages
Price: No price list

There are a number of social media scanning OSINT tools available now but probably the most successful of these is a system that most of its userbase doesn’t want to admit to having and that’s Babel Street Insights. For example, the FBI uses Babel Street Insights extensively but doesn’t shout about it.
Babel Street’s key features
Insights is the data visualization unit of a stack of OSINT gathering tools. Here are the main features of the suite:
- Social Media Search: Wnables users to conduct searches across various social media platforms, allowing for comprehensive social media monitoring.
- Thousands of Public Data Sources: It provides access to thousands of public data sources, allowing users to gather information from diverse sources.
- Multi-National Searches: Supports multi-national searches, enabling users to gather information from different countries and regions.
Unique buying proposition
Babel Street Insights’ unique buying proposition lies in its ability to aggregate and analyze vast amounts of publicly available data across multiple sources, including social media, news, and deep web content. It provides powerful search, monitoring, and visualization tools, helping organizations gain actionable intelligence for risk management, threat detection, and investigations.
Feature-in-focus: Babel Street’s social media scanning
Babel Street’s social media scanning allows users to monitor and analyze real-time data across various platforms, including Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. It helps track trends, sentiments, and emerging threats by identifying key discussions, influencers, and patterns. This feature is vital for cybersecurity, risk management, and public sentiment analysis.
Comparitech SupportScore
Babel Street is a mid-sized company with 291 employees and a respectable but not spectacular turnover. These two factors, together with a surprisingly low employee job satisfaction rating brings down the SupportScore of the business.
The company gets a SupportScore of 8.1 out of 10 even though its Customer Support team and online documentation each get the full 10 out or 10.
Why do we recommend it?
Thanks to the internet, threats are now global, even when targeted at small businesses. There are several applications of this search system that crosses into 200 different languages in its data gathering. The Babel Street system can be used to track the movements of terrorists or even armies – the system is currently tracking the movements of Russia’s army in Ukraine. Right down to the small business level, data breaches put email addresses and other business personnel identifiers in the hands of miscreants who could be anywhere in the world. Tracking those hackers can help prevent an attack.

The Babel Street system uses AI to link together events and postings on the internet and also skillfully translates statements between languages where words don’t always have a one-to-one mapping.
The system can be used to examine insider threats, pressure group campaigns, reputational damage attempts, and competitor slurs as well as international hacker campaigns. Once a suggestion of a threat to you or your business has been identified, the system can be used to map out associates and possible commissioners of hostile actions.
Forewarned is forearmed and so keeping constant track of threats and the people who are known to oppose you or your business helps you to strategize blocking tactics to get ahead of any gathering threat. You might be targeted by a rival but actually hit by an unknown overseas attacker. Drawing links between an attack and the true origin of that action can help you alert law enforcement to your opponents and support legal action to ensure the right people get punished.
Who is it recommended for?
Despite our mention of small businesses above, this tool isn’t affordable and so will probably only be used by government agencies and large enterprises. Babel Street doesn’t publish a price list but a report in Vice about the service, which was published in April 2017 noted that the US Army National Guard was paying $18,500 at that time for a one-year subscription.
Pros:
- Builds and Depicts Networks of Attackers: Assists in building and depicting networks of attackers, aiding in threat intelligence analysis and investigation.
- Links Unrelated Events: Links together seemingly unrelated events, facilitating the identification of patterns and connections.
- AI Translation: Search capabilities in 200 languages, utilizing AI for translation, ensuring comprehensive coverage and analysis.
Cons:
- Not Free: Not available for free, requiring users to pay for access to its features and capabilities.
Babel Street is a cloud-based system and you can investigate it by accessing a demo.
4. Google Dorks
Best for: Ad-hoc queries
Price: Free
Anyone who takes Google’s search capability for granted, or underestimates the power that lies behind this search engine’s capability to dig deep and come up with some interesting information, is a fool.
Google Dorks’ key features
Google Dorks is a query language rather than a tool. Here are its main features:
- Google Syntax: It utilizes simple Google search syntax to filter and refine search engine data, enabling users to find specific information efficiently.
- Not Produced by Google: Despite the name, Google Dorks is not produced or endorsed by Google; it’s a term used by the online community for certain search techniques.
- Utilize Advanced Search Queries: Google Dorks refers to a category of websites or online tools that utilize advanced search queries to extract specific information from search engine results.
Unique buying proposition
Google Dorks is a free system. Its appeal lies in its ability to leverage advanced Google search operators to uncover hidden, publicly accessible information on the web. By using specialized search queries, it allows security professionals and researchers to quickly identify sensitive data, security vulnerabilities, and valuable intelligence for investigations and cybersecurity assessments.
Feature-in-focus: Google Dorks’ search operators
Google Dorks’ search operators enable advanced search techniques to uncover hidden or sensitive information on the web. By using specific commands like “site:”, “intitle:”, or “filetype:”, users can refine searches to access confidential data, vulnerabilities, or files. This powerful tool is invaluable for cybersecurity, OSINT, and investigative purposes.
Comparitech SupportScore
As Google Dorks isn’t a product, there is no support system for it. Therefore, we were unable to calculate a SupportScore here.
Why do we recommend it?
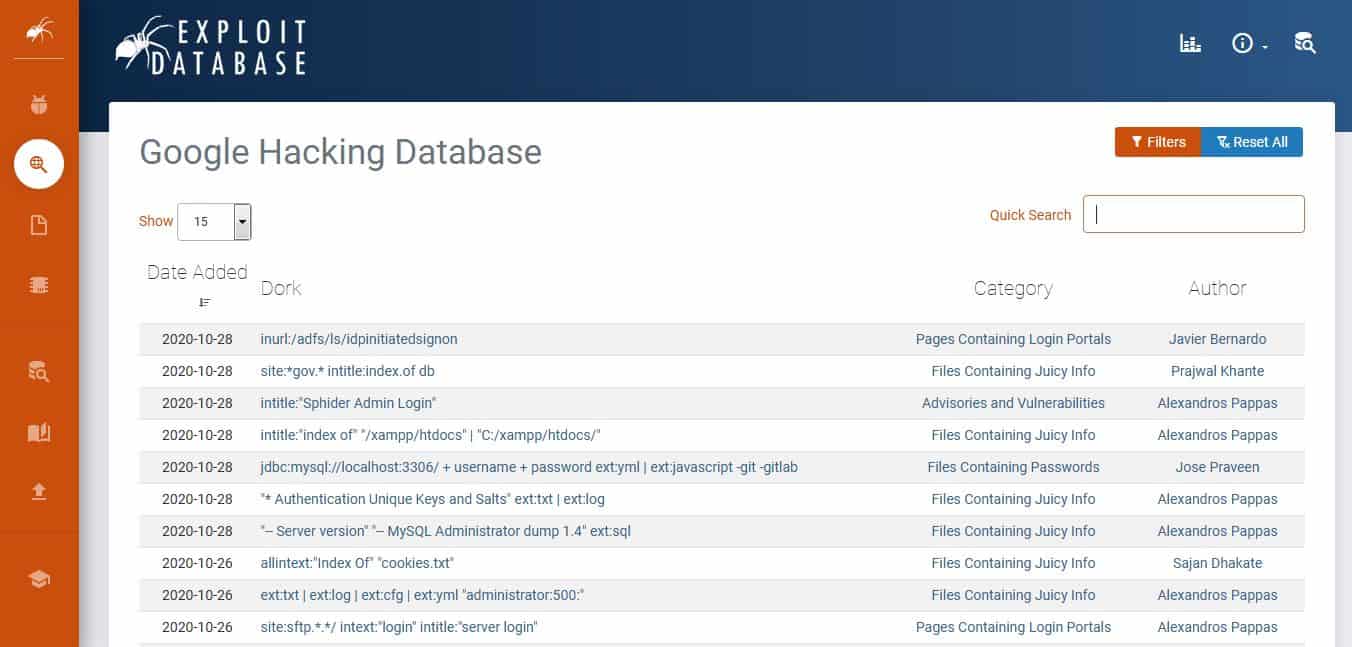
Google Dorks are advanced search techniques that can be used in the Google search engine to perform research into vulnerabilities on a website or discover information about businesses that are not immediately apparent from surface searches. You can discover tips on good Google Dorks to try by looking through the Exploit Database.
With the right arguments, anyone can find files or documents that may seem securely stored. In fact, one of the first things to do during a penetration test is to use Google Dorks to see what can already be accessed without any data mining tools.

As you may have understood, Google Dorks is not a tool, per se. It is a data querying method that involves querying for information using advanced – and clever – search arguments in Google Search.
Here’s how it works: websites are automatically indexed when Google bots crawl them. Now, unless sites with sensitive data or folders specifically block the bots (using noindex meta tags), their contents will be made available as search results for specific Google queries.
The concept here is to enable any user to delve deep into a server’s annals to come up with data corresponding to various arguments. The beauty of it is that Google has a large list of arguments that can address queries for almost any type of data including usernames and passwords.
There is no one website to go for the ultimate compilation of clever Google syntaxes; that means you will need to do a Google search for that too. But, for your reference, we have one of the most popular Google Dorks sites: Google Hacking Database on Exploit Database. Enthusiasts from all over the world update this registry daily.
Again, be aware that this is a powerful OSINT tool that can uncover sensitive information that could get you in trouble simply because you downloaded, or even looked at it.
Who is it recommended for?
Google Dorks can be used for many purposes and therefore there are many different types of people who use them. They can be used by penetration testers to reveal security weaknesses in a website and hackers can use them, too, for the same purpose. Researchers can discover interesting information about a company on the back pages of a website that might have been left there in the belief that the public wouldn’t be able to access them.
Pros:
- Completely Free: Google Dorks is entirely free to use, eliminating any financial barriers for users.
- Great for OSINT Beginners: Google Dorks can serve as a useful starting point for beginners in open-source intelligence (OSINT), offering simple yet effective techniques for information gathering.
Cons:
-
- Limited to Google Search Engine: Google Dorks is limited to the Google search engine, restricting its scope compared to more comprehensive OSINT tools that can access multiple search engines and data sources.
5. Shodan
Best for: Private OSINT searches
Price: The plans: Freelancer = $69 per month; Small Business = $359 per month; Corporate = $1,099 per month

Shodan is a querying digital intelligence gathering tool. It is a search engine that can be used to find information on IP addresses, ports, and any Internet-connected devices. It can be used to gather information on servers belonging to businesses or even cities, for example.
Shodan’s key features
Shodan specifically searches for details of the technology used by each company. Its main features are:
- Proprietary Query Language: It utilizes a proprietary query language for searching and retrieving information from its database.
- Export and Reporting Feature: Shodan allows users to export search results and build reports directly within the tool, facilitating further analysis and documentation.
- Great User Interface: It features a great user interface, displaying metrics alongside a geographical map, enhancing data visualization and analysis.
Unique buying proposition
Shodan’s unique buying proposition lies in its ability to search and analyze internet-connected devices, including servers, routers, and IoT devices. It provides real-time visibility into global networks, uncovering vulnerabilities, security risks, and configuration details. This makes it an essential tool for cybersecurity professionals and network administrators to monitor and secure digital infrastructure.
Feature-in-focus: Shodan’s network scanner
Shodan’s network scanner allows users to discover and analyze internet-connected devices across the globe. It identifies device types, IP addresses, and vulnerabilities, providing detailed insights into network configurations and security risks. This powerful tool is invaluable for cybersecurity professionals seeking to monitor, assess, and secure digital infrastructure from potential threats.
Comparitech SupportScore
Shodan is a search engine, and so much of its operations are automated. Although this is a subscription service, users are pretty much expected to know what they are doing – there are no modules to install or maintain. Thus, Shodan’s Customer Success team is more or less non-existent. The online help documentation, however, is excellent, and that category gets top marks in our SupportScore formula.
Overall, Shodan gets a SupportScore of 3.4 out of 10.
Why do we recommend it?
Shodan is a search tool that details the equipment and other technologies, such as SSL certificates, used by a business. The company currently highlights its ability to list the IoT devices used by a company, including their locations and details about their configurations and other attributes.
To start using it, simply type in any business and you get information on the devices that the business uses including honeypot ICS, location, services (HTTP, etc.), and even any vulnerabilities the devices might have.
The results are grouped by network names or IP addresses. Host information includes what operating systems are being used, open ports, type of Internet server, website design language, and much more. Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), or IP range, network scanning for bulk information is also possible.
Some queries may only work for the US – but, there are plenty more tools that help search for information from the rest of the world. You can start by typing in a query for a country to get the number of unique IP addresses they have registered.

Using this tool becomes a breeze once you have learned the Shodan syntax which is similar to Google Search. For example, querying for “Org: Organization_Name” gives you the information related to the devices that belong to an organization.
With such commands, users can run a query to list open surveillance or web cameras and even grab snapshots from them.
Although the main purpose of this tool is for reconnaissance, some commands can be actually used to perform penetration testing. In the right hands, this is a powerful tool that can lay bare the weaknesses of a network.
Who is it recommended for?
Shodan is an essential tool for security professionals – both physical security consultants and cybersecurity analysts. This service lets you see what information is available about your systems. Naturally, hackers would benefit from this tool as well.
Pros:
- User-Friendly: Shodan is designed to be user-friendly, catering to both technical and non-technical users, enabling easy navigation and utilization.
- Web-based Service: Shodan operates as a web-based service, accessible through web browsers, providing ease of access for users.
- Free Edition: Shodan offers a free edition, allowing users to access certain features without any cost.
Cons:
- Paid Tool: Shodan is primarily a paid tool, with pricing starting at $59, which may be a barrier for some users.
- Offered as a Service: Shodan is offered as a service, similar to Google, meaning users cannot tinker with its inner workings or access its backend infrastructure, potentially limiting customization options.
6. Metasploit
Best for: Penetration testing
Price: Open-source is free; Contact Sales for the Metasploit Pro price

There is nothing shy about this tool; on the contrary, it is a bold weapon that can be used to get all the required information on a target – be it a host or a network – and then exploit any vulnerability that may have been discovered. This is usually done by sending out a payload that executes commands.
Metasploit’s key features
Having used Metasploit framework, I can attest to its powerful features. Here are its best attributes:
- Penetration Testing Tool: Metasploit is primarily designed for penetration testing, allowing security professionals to assess the vulnerabilities of a system or network.
- Free and Commercial Use: Metasploit offers both free and commercial versions, providing flexibility for users with varying needs and budgets.
- Ethical Hacking Tools: Metasploit includes a wide range of hacking systems, tools, and payloads that can be used to exploit vulnerabilities in target systems.
Unique buying proposition
Metasploit Pro’s unique buying proposition lies in its advanced capabilities for automated penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and exploit development. It streamlines the process of identifying security weaknesses, providing actionable insights for remediation. With robust reporting and collaboration tools, Metasploit Pro helps organizations improve security posture while saving time and resources.
Feature-in-focus: Metasploit Pro’s user interface
Metasploit Framework has a terrible user interface, however, Metasploit Pro’s user interface is intuitive and user-friendly. This paid tool is designed for use by experienced security professionals. It features a streamlined dashboard for easy navigation, with drag-and-drop functionalities, detailed reporting, and simplified exploit execution. The interface enhances workflow efficiency, enabling users to perform penetration tests and vulnerability assessments seamlessly.
Comparitech SupportScore
Metasploit is a product of Rapid7. The company lets users download Metasploit Framework for free but it charges for Metasploit Pro. So, the company provides customer support for Metasploit Pro, but users of Metasploit Framework have to rely on community support.
Rapid7 gets an excellent SupportScore of 9.4 out of 10. However, remember that this high-quality support is only available to buyers of Metasploit Pro and not the users of Metasploit Framework.
Why do we recommend it?
Metasploit is a vulnerability scanner and penetration testing tool. The importance of this system is that it provides tools to probe a system and discover information about security components and possible ways into a network and then it automatically copies that data over to attack tools to implement a system breach.
With Metasploit, users can upload, download, listen to, or alter files they have found. In the case of mobile devices, they can even capture screenshots and activate the camera and microphone for remote eavesdropping.

This is a no-nonsense tool that can cause real damage – and get you in trouble – if abused. It has seven modules that can be used for different intelligence gathering campaigns: auxiliary, payloads, evasion, encoders, exploits, post, and NOP.
These modules tackle specific issues like getting past defenses (encoders), running scripts, and code by exploiting buffer overflows (NOP), or performing tasks after compromising a system (post), for example.
Once someone has access to a system, they can practically own every single device on it. The scary thing about this OSINT tool is that it can deliver payloads to devices running almost any type of operating system out there: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and many more.
Who is it recommended for?
Metasploit is one of the most highly-recommended hacker tools – both for white hat and black hat hackers.
Pros:
- Security Framework: Metasploit is one of the most widely used security frameworks, trusted by security professionals globally.
- Community Support: It boasts one of the largest communities in the cybersecurity domain, ensuring continuous support and frequent updates to keep up with emerging threats.
- Highly Customizable: Metasploit is highly customizable, allowing users to tailor it to their specific requirements by integrating various open-source applications and modules.
- Free Version: Metasploit offers a free version that provides essential functionality for security testing purposes.
Cons:
- Technical Complexity: Metasploit caters to more technical users, which may pose a steep learning curve for beginners in the security field.
Metasploit, itself, can be run from Linux, macOS, and Windows.
7. Recon-ng
Best for: Scanning the Web for OSINT
Price: Free
Here is another tool that is great at getting information from open, public records. Although the interface could appear to be a bit daunting at first – because of the CLI – it really is an easy tool to master after spending a few days playing around with it.

On the contrary, anyone that is proficient at working in a Unix/Linux environment will find this to be a familiar tool.
Recon-ng’s key features
I found Recon-ng difficult to use but it can produce powerful results. Its best features are:
- Linux Command-line Tool: Recon-ng is a command-line tool specifically designed for Linux operating systems, providing a platform for reconnaissance activities.
- Free to Use: Recon-ng is freely available for use, making it accessible to a wide range of users without any cost barriers.
- Community Plug-ins: It supports community-supplied plug-ins, allowing users to extend its functionality by integrating additional modules and tools.
Unique buying proposition
Recon-ng is a free tool, so you don’t have to buy it. However, its “unique buying proposition” lies in its modular framework, offering customizable tools for automated OSINT gathering. It allows users to collect, process, and analyze data from multiple online sources efficiently. With a user-friendly interface and powerful reporting features, Recon-ng is ideal for cybersecurity professionals seeking comprehensive intelligence in one platform.
Feature-in-focus: Recon-ng’s Web scans
Recon-ng’s web scans enable users to automate the collection of valuable OSINT from websites and online resources. With its range of modules, users can gather domain information, subdomains, IP addresses, and other publicly available data. These scans help cybersecurity professionals identify vulnerabilities and track digital footprints for security assessments.
Comparitech SupportScore
As it is a free tool, there is no organized support team for Recon-ng. Users will have to register with community forums to get tips on usage.
Why do we recommend it?
Recon-ng is good at crawling the Web for specific information – whatever word/name/address you give it to search for. All discovered records are inserted into a database. This is a command line tool and Linux expert users will find it easy to use.

Recon-ng has default modules that are also open source, and then there is a marketplace to add even more features. And because it is an open-source tool, it continues to evolve and grow as the developer community continues to contribute to it. Written in Python, Recon-ng is designed exclusively for web-based open source reconnaissance. Therefore, it can’t be used for exploits.
But, still, once the information has been collected, it is stored in a database which can then be used to generate insightful custom reports.
Who is it recommended for?
Recon-ng is a research tool. Anyone who is good at investigating but not so good at using the Linux command line will struggle with this tool. You would need to partner up with a technician to use this utility. You also need to export the data from the database and import it into some other data visualization tool in order to analyze it, which isn’t an easy task.
Pros:
- Open Source and Free: Recon-ng is open-source software, providing users with complete freedom to modify, distribute, and use it without any licensing costs.
- Strong Community Support: It benefits from a robust community of users and developers, making it one of the most popular OSINT (Open Source Intelligence) tools available.
- User-Friendly Interface: Recon-ng offers a user-friendly interface that is reminiscent of Metasploit, enhancing user experience and ease of navigation.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Due to its highly detailed nature, Recon-ng may require significant time and effort to fully explore and utilize all its features and capabilities.
8. Aircrack-ng
Best for: WiFi hacking
Price: Free

Aircrack-ng is a wireless network security penetration testing tool that has four main functions:
- Packet monitoring – capturing of frames and collecting WEP IVs (Initialization Vectors); if a GPS is added, it can log the position of APs (access points).
- Penetration testing – by performing packet injection attacks, fake access points, replay attacks, and more to test a network’s security.
- Performance analysis – testing wifi and driver capabilities.
- Password security testing – password cracking on WEP and WPA PSK (WPA 1 and 2).
Although the tool was developed primarily for Linux, there are versions for Windows, OS X, and FreeBSD. The fact that it is a fully CLI tool means that it can be easily tweaked to meet unique requirements using custom scripts.
Aircrack-ng’s key features
Famously, Aircrack-ng is able to crack WEP security, but no WiFi system uses that standard anymore. The main benefits of the tool are:
- Wi-Fi Security: Aircrack-ng is capable of auditing Wi-Fi security configurations and can also be used to crack weak wireless encryption, providing comprehensive security assessment capabilities.
- Cross-platform Compatibility: It runs on various operating systems including Linux, FreeBSD, macOS, and Windows, ensuring flexibility and accessibility for users across different platforms.
Unique buying proposition
Aircrack-ng’s is a free tool, but its “unique buying proposition” lies in its comprehensive suite of tools for wireless network security testing. It specializes in packet capturing, cracking WEP and WPA-PSK keys, and analyzing Wi-Fi networks. With robust features for network auditing, Aircrack-ng is essential for cybersecurity professionals focused on securing wireless environments and detecting vulnerabilities.
Feature-in-focus: Aircrack-ng’s attack capabilities
Aircrack-ng offers powerful attack capabilities, including packet injection, deauthentication, and WEP/WPA-PSK cracking. It allows users to perform various attacks on wireless networks, such as capturing handshake data and exploiting weak encryption. These features make it an essential tool for penetration testers and security professionals assessing Wi-Fi network vulnerabilities.
Comparitech SupportScore
Aircrack-ng is an open-source project, so there is no business behind the tool and no organized Customer Support team. Thus, we are unable to calculate a Supportscore for the product.
Why do we recommend it?
Aircrack-ng is a very well-known hacker tool that can scan wireless systems and, theoretically crack captured data. So, this is a snooping tool rather than a scanner of open source intelligence.
Who is it recommended for?
Hackers use Aircrack-ng a lot. However, its power is greatly diminished by effective transmission encryption. Although you will find it difficult to reap the contents of transmissions, if information about which devices are connected to the wireless network is of use, you will find a benefit from this tool. Penetration testers and system security managers can use this tool to confirm that transmission security is adequate.
Pros:
- Huge Community Support: It is one of the most widely supported wireless security tools, benefiting from a large community of users and developers who contribute to its development and maintenance.
- Free to Use: Aircrack-ng is freely available for use, enabling users to perform wireless security assessments without any cost barriers.
Cons:
- Not an AIO Tool: Aircrack-ng may not be the best option for users seeking an all-in-one security tool that encompasses a wide range of security assessment functionalities beyond wireless security.
Honorable mentions
Here are a selection of tools that can further enhance the performance and reach of the tools we have seen above:
1. Wireshark
Wireshark – this popular free, open source packet sniffing tool is one of the best penetration testing applications that lets you see if there are any unprotected protocols like FTP, Telnet, and SSH travelling in a network.
2. Nmap
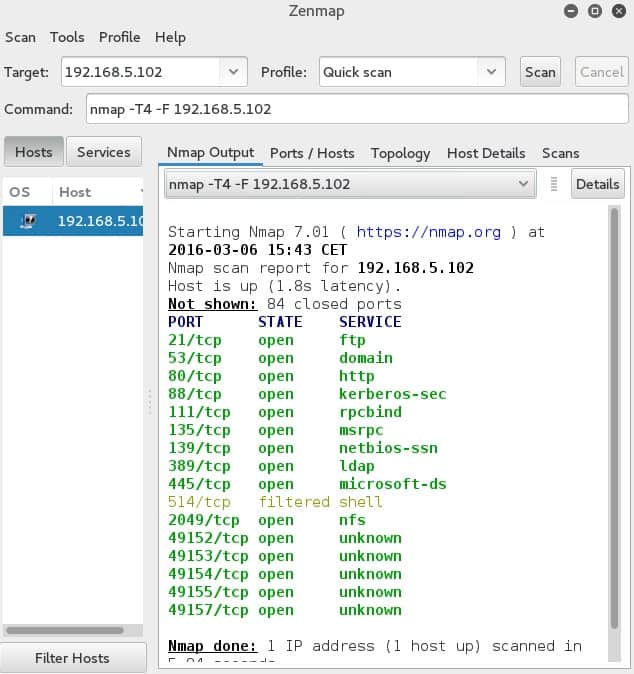
Nmap – this is another popular “old-timer” that is still used to keep an eye on network security; it can be used for discovery or testing purposes to see host statuses and gather information like shared data, operating systems, and much more to uncover vulnerabilities. As time goes by, it has gotten more powerful and now has a GUI (Zenmap).
3. PhoneInfoga
PhoneInfoga – squeeze as much information as possible from a phone number; this tool works globally, for phone numbers from across the world. The only catch: it needs Python.
4. TinEye
TinEye – in a world where the problem of fake news is being exacerbated with expert Photoshop manipulations, this reverse search engine uses image identification instead of keywords or metadata. It is a simple, browser-based tool.
We would like to hear about other OSINT tools you use or think should be on this list. Tell us about them; leave a comment below.
Why trust us?
At Comparitech.com, our team of experts brings years of experience in technology, cybersecurity, and data privacy to deliver accurate, insightful reviews and analysis. We prioritize transparency, rigorously testing products and services to provide unbiased recommendations. Our staff is dedicated to helping consumers make informed decisions by combining technical expertise with in-depth research, ensuring you receive reliable and trustworthy information on the latest tech solutions.
Our methodology for choosing OSINT tools
When selecting OSINT (Open Source Intelligence) tools, we follow a rigorous methodology to ensure we provide accurate and reliable recommendations:
1. Features and Capabilities
We thoroughly evaluate each tool’s core functionalities, including its ability to collect and analyze data from multiple open sources such as social media, websites, and public databases. The tools must offer advanced features like real-time monitoring, keyword tracking, and comprehensive reporting to ensure efficient intelligence gathering.
2. Ease of Use
A user-friendly interface is essential for both beginners and experienced users. We assess the overall design, setup process, and accessibility of each tool. The learning curve should be minimal, allowing users to start gathering and analyzing data quickly. Additionally, we consider the quality of available user support resources.
3. Integration and Compatibility
OSINT tools should seamlessly integrate with existing systems like cybersecurity platforms or data analytics solutions. We review how well each tool works with different operating environments, APIs, and data formats, ensuring it fits into varied workflows and can be adapted to an organization’s specific needs for intelligence gathering.
4. Accuracy and Reliability
The integrity of data is critical in OSINT. We conduct tests to measure the accuracy of the tool’s data collection and analysis. The tools must produce reliable and consistent results, ensuring that the intelligence gathered is relevant, valid, and actionable in real-world scenarios for informed decision-making.
5. Security and Compliance
Given the sensitive nature of OSINT data, security is a top priority. We evaluate each tool for its adherence to best practices in data protection, including encryption and secure storage. Additionally, we verify compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and other regional or industry-specific standards to protect user data.
6. Cost-effectiveness
We analyze the pricing structure of each OSINT tool in relation to its features and performance. A high-quality tool must offer a balance of price and value. We consider subscription models, licensing fees, and potential hidden costs, ensuring that organizations receive tangible benefits from the tool’s investment.
7. User Reviews and Feedback
User feedback is invaluable in assessing real-world performance. We gather reviews from industry professionals, security experts, and businesses that actively use the tools. This helps us understand user satisfaction, support quality, and tool effectiveness in practical, everyday applications, providing a more comprehensive view of the tool’s value.
By applying this methodology, we ensure that the OSINT tools we recommend are well-rounded, effective, and provide maximum value for both individual and organizational needs.
Broader B2B software selection methodology
When selecting B2B software solutions, we use a comprehensive and structured methodology to ensure that the chosen tools meet the specific needs of businesses while delivering optimal performance, scalability, and value. Our approach involves assessing a range of critical factors to make well-informed decisions.
1. Business Requirements and Objectives
We begin by understanding the unique needs and objectives of the business. This involves engaging with key stakeholders to determine the software’s role in improving operational efficiency, enhancing productivity, and addressing pain points. Software must align with both short-term and long-term business goals to drive success.
2. Feature Set and Customization
We evaluate the core features of each software solution to ensure they align with the business’s functional requirements. In addition to evaluating standard features, we also look for customization options, flexibility, and scalability to ensure the software can adapt as the business grows and evolves.
3. Usability and User Experience
The ease of use is a critical factor in software adoption. We assess how intuitive the interface is, how easy it is to set up, and whether it provides an efficient user experience for both technical and non-technical users. A user-friendly platform encourages higher engagement and minimizes the learning curve for employees.
4. Integration and Compatibility
Seamless integration with existing business systems is essential for efficient workflow. We evaluate how well the software integrates with other tools such as CRMs, ERP systems, or marketing platforms. Compatibility with existing infrastructure ensures that businesses can leverage the software without disrupting their operations or incurring additional costs.
5. Security and Compliance
In a business environment, data security and regulatory compliance are paramount. We assess the software’s security features, including encryption, access control, and data protection protocols. Additionally, we verify that the software complies with relevant industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other local or global data privacy laws.
6. Performance and Scalability
We conduct thorough tests to evaluate how well the software performs under varying loads and its ability to scale as the business grows. Software solutions must be able to handle increasing data volumes and user traffic while maintaining high performance and reliability without compromising speed or functionality.
7. Vendor Reputation and Support
The reputation of the software vendor is a key consideration. We look at factors such as vendor stability, customer satisfaction, and overall market standing. Additionally, we assess the quality of customer support, including the availability of help resources, response times, and the vendor’s history of addressing issues promptly.
8. Cost-effectiveness
A thorough analysis of the software’s pricing structure is essential. We review subscription models, licensing fees, and potential hidden costs. The total cost of ownership must provide a strong return on investment by delivering substantial value in terms of performance, time savings, and operational improvements.
9. User Feedback and Industry Reviews
We also consider feedback from current users to understand real-world experiences with the software. By reviewing testimonials, case studies, and third-party reviews, we gain insights into the software’s strengths and weaknesses, allowing us to make a more informed recommendation.
By applying this comprehensive B2B software selection methodology, we ensure that businesses can choose solutions that effectively meet their needs, support growth, and offer a high ROI. Our approach considers all aspects of the software’s functionality, performance, and overall value to ensure the right fit for any organization.
Read more about our methodology at the B2B software methodology page.
OSINT FAQs
What are OSINT tools?
OSINT is short for Open Systems Intelligence and OSINT tools are utilities that either seek out information from public sources or organize that data into a meaningful format that identifies deeper information in the form of a collection than can be gleaned from individual data instances. OSINT can be used for academic research, for stalking and profiling in a phishing campaign, or for an investigation into criminal activity, political intrigue, or cybersecurity threats.
Do hackers use OSINT?
OSINT is a research strategy and anyone can use it for good or revil. So, OSINT can be used by hackers and it can also be used to track the activity of hackers.
Is OSINT free?
OSINT mines public sources of information, which usually means the Web, where most information is free. Some data collections and news sources might require a subscription for access. The tools used for OSINT range from a straightforward Web search to complicated data mapping tools. Most tools are free to use. Some have both free and paid versions.
Are OSINT tools Legal?
OSINT accesses data that is accessible by the public. There is no snooping or data theft involved. Therefore, it is not illegal to search through this data. If you are a company and you work with personally identifiable information on members of the public, storage of the data that you gather might be subject to data protection rules, such as GDPR.