A network protocol analyzer (or packet sniffer) is a tool used to capture, analyze, and troubleshoot network traffic. It intercepts data packets as they travel across the network, allowing administrators to examine details such as source, destination, protocol, and packet content. Wireshark is this type of tool and it helps diagnose network issues, monitor performance, and detect security vulnerabilities by providing deep visibility into network communications at various protocol layers.
About Wireshark
Wireshark is a widely used open-source network protocol analyzer that allows users to capture and interactively browse the traffic running on a computer network. It provides a detailed, real-time view of network activity by capturing data packets as they travel across the network, which can then be analyzed in depth.
Wireshark supports hundreds of network protocols and media types, making it an invaluable tool for network administrators, security professionals, and developers. It helps diagnose network issues, troubleshoot performance problems, analyze security breaches, and ensure compliance with network protocols. The captured packets can be examined in a human-readable format, with detailed information on each protocol layer, such as Ethernet, IP, TCP, and application-layer protocols like HTTP, DNS, and FTP.
Wireshark offers powerful filtering and search capabilities to focus on specific traffic patterns, allowing users to zoom in on the relevant data. It also supports both live packet capture and offline analysis from saved capture files. Additionally, Wireshark is available for multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, and it is often used in combination with other network monitoring tools for comprehensive network management and troubleshooting.
What is an IP address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves two main purposes: identifying the host (device) on the network and specifying its location in the network.
There are two versions of IP addresses commonly in use:
- IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4): The most widely used version, consisting of a 32-bit number, typically written as four decimal numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1). It allows for approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses.
- IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6): Developed to address the shortage of IPv4 addresses, IPv6 uses a 128-bit number, written as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). IPv6 offers an almost unlimited number of unique addresses.
IP addresses are used by routers and devices to route data packets to their correct destinations. They can be assigned dynamically (via DHCP) or statically (manually configured) depending on the network setup. An IP address is essential for all devices to communicate over the internet or local networks.
Finding an IP address with Wireshark using ARP requests
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests can be used by Wireshark to get the IP address of an unknown host on your network. ARP is a broadcast request that’s meant to help the client machine map out the entire host network.
ARP is slightly more foolproof than using a DHCP request – which I’ll cover below – because even hosts with a static IP address will generate ARP traffic upon startup.
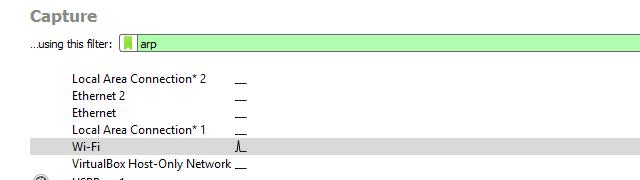
To pull an IP address of an unknown host via ARP, I started Wireshark and began a session with the Wireshark capture filter set to arp, as shown above.
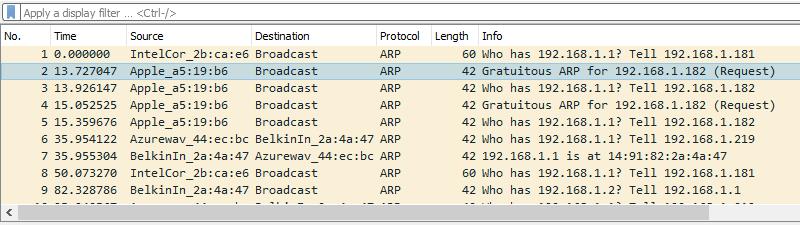
I then wait for the unknown host to come online. I used my cell phone and toggled the WiFi connection on and off. Regardless, when an unknown host comes online it will generate one or more ARP requests. Those are the frames you should look for.
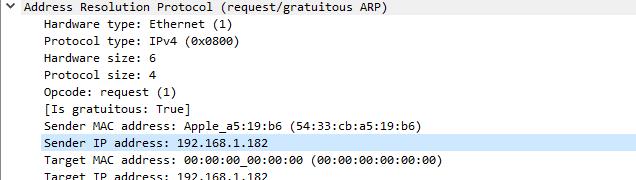
I spotted the request and clicked on it. I used Wireshark’s Packet details view to analyze the frame. I looked at the Address resolution protocol section of the frame, especially the Sender IP address and Sender MAC address.
In this case, you can see my phone received an IP address of 192.168.1.182 from the router, and you can identify the device as an Apple phone by looking at the vendor OUI.
Quick Guide Recap
Finding IP Address with Wireshark using ARP Requests:
- Initiate a Wireshark session with ‘arp’ as the capture filter.
- Wait for the target device to come online and generate ARP requests.
- Click on an ARP request to analyze it.
- In ‘Packet details’ view, focus on ‘Sender IP address’ and ‘Sender MAC address’ in the ‘Address resolution protocol’ section.
Wireshark IP address puller using DHCP requests
Another easy way to determine the IP address of an unknown host on your network is to use DHCP traffic. This method only works if the host requests an IP address.
If you’re dealing with a situation where someone has put a malicious physical network device on your corporate network; this method isn’t recommended – they’ve likely set a static address. But for normal use, it works just as well as ARP.
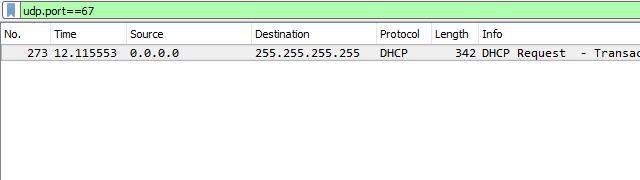
To capture DHCP traffic, I like to start a new session with no capture filter and set the Wireshark display filter to udp.port==67 as shown above. Then I waited for the unknown host to come online and requested an IP address from my DHCP server.
You can also force every host on your network to request a new IP address by setting the lease time to an hour or two and capturing network traffic. In this case, you’d want to browse through hostnames until you find the target client.
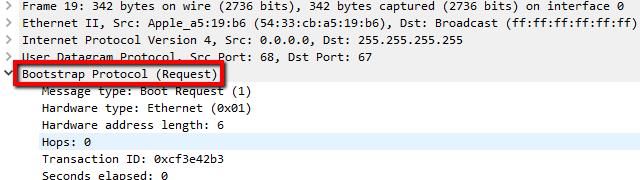
Note that the frame I captured has a source IP address of 0.0.0.0. This is normal until the host is assigned a valid IP address by the DHCP server.
I clicked on the captured frame, and looked at the Packet details view. I browsed until I found the entry for Bootstrap protocol and clicked the arrow to expand it
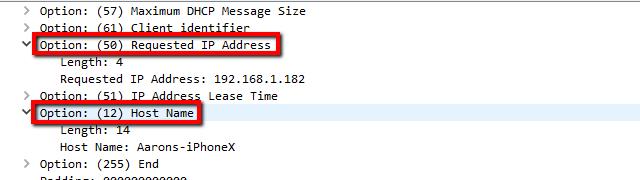
I scrolled through the list of options until I found the Requested IP address, which showed what the DHCP server attempted to assign. In just about every case this correlates to the IP address of the host machine, despite the fact it’s phrased as a request.
You can also find a handful of other useful options like the IP address lease time and Host name of the unknown client requesting an address.
Quick Guide Recap
Wireshark IP Address Puller Using DHCP Requests:
- Start a new Wireshark session without a capture filter and set the display filter to ‘udp.port==67’.
- Wait for the target device to come online and request an IP address from the DHCP server.
- Optionally, to force all hosts to request a new IP, set the lease time to a short duration and capture network traffic. Look for the target client among the hostnames.
- Click on the captured frame with a source IP address of 0.0.0.0 (normal until the host is assigned a valid IP address).
- In ‘Packet details’ view, find and expand the ‘Bootstrap protocol’ entry.
- Scroll to ‘Requested IP address’, showing the IP address the DHCP server attempts to assign (usually correlates to the host’s IP).
- Other useful options to note include ‘IP address lease time’ and ‘Host name’ of the unknown client requesting an address.
Getting the IP address of an unknown host with Wireshark
Those two methods are sure-fire ways to find the IP address of an unknown host. Depending on your network, there may be others. For instance, sending out a broadcast ping will work in some situations when you share a collision domain with the host. But especially for home networking, where all devices are more or less directly connected to a switch, analyzing ARP and DHCP requests are the best choices for discovering an IP address.
Wireshark IP Puller FAQs
Is it illegal to run Wireshark on a public network?
It isn’t illegal to run Wireshark on a public network. However, pay attention to the Terms and Conditions of the network you want to use Wireshark on. It may prohibit the use of Wireshark, in which case you could be banned from the network or even sued for using it.
How do I view the MAC address of a received packet in Wireshark?
To view all of the MAC addresses in a captured packet stream:
- Open a packet capture file in Wireshark
- Go to Statistics and then Conversations.
- Click on the Ethernet tab.
You will see all of the MAC addresses from the captured packets.
Can you pull OPs with Wireshark over wifi?
Yes. Wireshark can capture packets off of a WiFi network as long as the computer it is installed on has a WiFi transceiver and is in promiscuous mode. Wireshark uses the Airpcap standard for wireless packet capture.
What devices can Wireshark use to capture packets?
Wireshark captures packets through the network interface of the computer that it is installed on. It can run on Windows, Linux, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, and Unix.
How do I trace a specific IP address in Wireshark?
If you only want to see the traffic to and from Wireshark in a trace file, load it into Wireshark and then apply a filter to the packet data. You enter this filter in the bar across the top of the packet display pane where you will see the words Apply a display filter. For example, if you want to trace the activity of 192.168.0.12 you should type in:
ip.addr == 192.168.0.12
This will filter the records in the display panel so that you only see the packet going to or coming from that address.
How do I get the IP address of a hostname in Wireshark?
You don’t need to open up Wireshark to get the IP address of a hostname or a domain.
- Open a Command Prompt window and type in:
nslookup <hostname> - Type in the name of the host that you want to get the IP address for instead of <hostname>.
- If you already have Wireshark open and you want to look in passing packets for the IP address of a known hostname, open a packet stream in Wireshark then enter a display filter. This should be:
ip.host == <hostname> - Give the name of the host instead of <hostname>.