
Some governments, Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and network administrators aim to detect (and often block) VPN traffic for various reasons. VPN obfuscation refers to masking VPN traffic so that it isn’t easily identified as such. Related terms in VPN provider literature include “obfsproxy servers,” “traffic obfuscation,” “stealth VPN,” and “cloaking technology.” But what do these really mean?
In this post, we help you make sense of this confusing terminology. We discuss what obfuscation is and why you need it. We also explain the different methods used for traffic obfuscation and recommend a few VPNs that do it very well.
Best VPNs offering obfuscation
While many VPNs claim to offer superior obfuscation methods, many of them don’t work to bypass government blocks. And of those that do work, there’s a great deal of variation in the quality of the service in terms of speed, security, and support. Below is a look at the best VPNs on the market that offer obfuscation.
Best VPNs with obfuscation:
- NordVPN: NordVPN is a top provider that makes bypassing VPN blocks in China possible. Simply connect to one of the many obfuscated servers, and you’ll be good to go. NordVPN comes with a 30-day risk-free money-back guarantee.
TIP In our testing we found that the cheapest NordVPN plan (Standard) works perfectly. - Surfshark: Surfshark is great for unblocking and lets you connect an unlimited number of devices. It offers an advanced settings feature called NoBorders mode that obfuscates your VPN traffic when enabled.
- ExpressVPN: ExpressVPN is an extremely fast and reliable VPN known for its ability to bypass restrictions in China and other countries where blocks are imposed. It is easy to get started with, even in China, with no special setup required.
- AtlasVPN: Ultrafast VPN servers in 40+ countries capable of accessing the free web. Your data is secured with 256-bit encryption and a unique SafeSwap feature.
- Private Internet Access: PIA uses the Shadowsocks protocol to hide your VPN traffic from prying eyes. It includes 256-bit encryption and 24/7 support.
- PrivateVPN: This is another speedy VPN with excellent unblocking abilities. You can use the software in “Stealth VPN” mode to obfuscate your traffic.
VPNs often claim to keep you safe and private online but many VPNs (especially free ones) leak information.
We regularly test the top 70 VPNs for security and this list only includes VPNs which keep you anonymous and don't track your activity. Plus we only recommend VPNs which offer a full-money back guarantee allowing you to try them risk free.
WANT TO TRY THE TOP VPN RISK FREE?
NordVPN is offering a fully-featured risk-free 30-day trial if you sign up on this page. You can use the VPN we rate #1, with no restrictions for a month—great if you want to test out the provider before making a commitment.
There are no hidden terms—just contact support within 30 days if you decide NordVPN isn't right for you, and you'll get a full refund. Start your NordVPN trial here.
Best VPNs for obfuscation – at a glance
We’ve compared the most important features of the top VPNs here. Would you prefer to read the in-depth reviews? Start with NordVPN – our #1 choice for obfuscation.
| No value | NordVPN | Surfshark | ExpressVPN | AtlasVPN | Private Internet Access | PrivateVPN |
| Website | NordVPN.com | Surfshark.com | ExpressVPN.com | AtlasVPN.com | PrivateInternetAccess.com | PrivateVPN.com | Ranking for Obfuscation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | OpenVPN data encryption | 256-bit AES | 256-bit AES | 256-bit AES | AES-256-bit | 256-bit AES | AES-256 (with 128-bit option) | Activity logs | No identifying data | No logs stored | Avg Speed (Mbps) | 100+ Mbps | 100+ Mbps | 100+ Mbps | 100+ Mbps | 100+ Mbps | 74 Mbps | Total number of servers | 7,425 | 3,200 | Undisclosed | 1000+ | 1,000+ | 200+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best deal (per month) | $3.39 Up to 76% off 2 year plans + free eSIM data | $2.19 86% OFF + 3 months free | $4.99 SAVE: 61% + 4 months free on 2 year plans | $1.64 SAVE 86% on a 2 year plan + 6 months free | $2.19 SAVE 82% on the 2 yr plan + 2 months free | $2.00 Save 85% on a one year plan + 24-months free |
What is VPN obfuscation?
The dictionary definition of “obfuscation” is:
the action of making something obscure, unclear, or unintelligible
VPN obfuscation disguises VPN traffic such that it no longer looks like VPN traffic. This way, it can be hidden from anyone trying to detect it. Obfuscation techniques don’t change the traffic itself but rather create a mask that hides recognizable patterns.
OpenVPN is the default protocol used by most VPNs. It secures data by encrypting it, but it also adds a distinctive signature. Some detection techniques, in particular, advanced deep packet inspection (discussed below), can detect this signature.
The purpose of VPN obfuscation is to continue to transfer the data in a secure (encrypted) manner but to hide the nature of the traffic so that it can circumvent blocks.
There are various methods used to obscure VPN traffic, but they generally involve adding a layer of encryption that disguises the traffic as regular traffic. We’ll discuss these below, but first, we’ll take a look at why we need to mask VPN traffic in the first place.
Are obfuscated servers safe to use?
Yes, using obfuscated servers from a reputable VPN supplier is safe. The magic of obfuscated servers lies in their ability to enhance security and privacy by preventing ISPs, governments, and companies from detecting that a VPN is being used. They can significantly benefit users in countries with strict internet censorship or those who want to bypass VPN-blocking firewalls. However, the effectiveness of obfuscated servers may vary over time as censors and authorities adapt to new technologies.
It’s important to note that using obfuscated servers may have legal implications in some countries with strict laws against VPNs. Overall, obfuscated servers can provide an additional layer of security and privacy for VPN users.
Why do you need VPN obfuscation?
There are several major reasons you might need to hide the fact that you’re using a VPN:
- Bypass government censorship
- Evade network blocks
- Improve privacy and anonymity
- Prevent ISP throttling
Let’s look at these in more detail:
1. Bypass government censorship
In some countries, such as China, Egypt, Iran, North Korea, and Pakistan, the government heavily restricts access to the internet. They often block select destination websites by stopping traffic that’s traveling to those sites. For example, in China, the “Great Firewall” comprises various methods to prevent users from accessing blocked sites and apps such as Facebook, WhatsApp, and Twitter.
To bypass these blocks, many users employ the use of a VPN. When connected to a VPN, the user’s traffic is encrypted, so the contents are unreadable. A VPN also sends traffic through a secondary server, so inspection of the traffic would reveal that it’s going to the VPN server, not the banned destination website.
Of course, the Chinese government has caught on to the fact that people use VPNs to bypass blocks. In response, they attempt to block VPN traffic. This can be done in several ways. For example, if the VPN server is known to the government, they can block traffic going to that server. This happens frequently, even to top VPNs, which is why providers have to stay on their toes and be ready to send traffic through different servers that aren’t known to the government.
Another method used to block VPN traffic is to block the port that OpenVPN traffic usually enters through (port 1194). Sending OpenVPN traffic through a different port can sometimes bypass this type of blocking.
More advanced blocking methods involve the detection of the nature of the traffic itself. Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) can detect the unique signature that OpenVPN bears. If VPN traffic is detected, it’s blocked. This is where obfuscation comes in. By disguising the VPN traffic as something else, some VPNs manage to bypass advanced DPI methods.
2. Evade network blocks
If you’re using a VPN in your office or school to bypass blocks, it may not always work. Some network administrators put methods in place to detect VPN traffic. Obfuscation will help circumvent these detection measures and bypass blocks as normal.
3. Improve privacy and anonymity
Most obfuscation methods serve as an additional layer of security, privacy, and anonymity for your data. With an extra layer of encryption, it’s difficult for any snoopers to detect that you’re using a VPN. This includes your ISP, government agencies, and cybercriminals.
Whether you’re security-conscious and want to keep hackers at bay, or you’re a journalist or activist looking for extra online privacy, obfuscation can help.
4. Prevent ISP throttling
Many ISPs throttle your internet speed if they see you’re streaming, downloading, or visiting certain websites. A VPN should prevent this from happening, as your ISP can no longer see the contents or destination of your traffic.
However, your ISP may be able to detect that you’re using a VPN, and some users report that their ISPs throttle VPN traffic. While it’s more likely that slowdowns are due to the VPN itself (encryption slows down connections), it is plausible that some ISPs might indiscriminately throttle VPN traffic. If this is the case, then obfuscation should help to prevent this practice.
See also: How to stop ISP throttling with a VPN
How does VPN obfuscation work?
When reading about the features of various VPNs, you may come across terms related to VPN obfuscation. There are lots of “buzzwords” related to this topic, but many of them mean roughly the same thing. Some examples are “stealth VPN” or “stealth mode,” “cloaking technology,” “scramble,” and “obfuscated servers.” These all mean that the VPN is using some method of obfuscation to disguise your traffic when you use the appropriate settings. Some providers come up with novel names for their obfuscation methods, for example, Surfshark’s “NoBorders mode” and VyprVPN’s “Chameleon protocol.”
So, what are they actually doing to your VPN traffic? Below are some of the methods VPN providers may use for obfuscation. Note that for any sort of obfuscation to work, both the client and the server need to be set up to use it. For example, Obfsproxy needs to be configured on both the VPN app and the server to work.
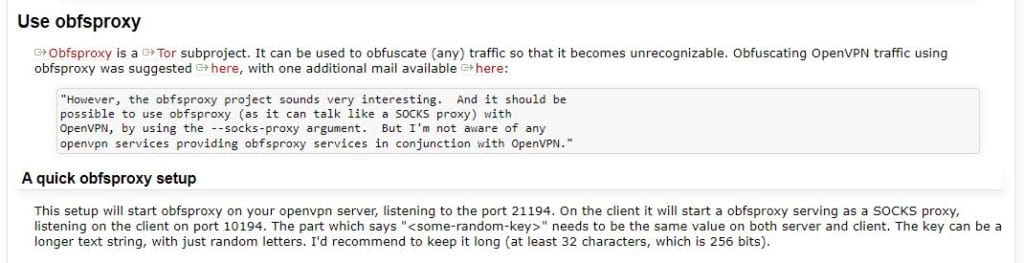
Obfsproxy
Obfsproxy is a subproject of the Tor project (responsible for the anonymous Tor browser). It was created in response to the blocking of Tor traffic in some countries, such as China. It obfuscates Tor traffic such that it is no longer recognized. Although Obfsproxy was developed for use with Tor, it can also be used with OpenVPN.
Obfsproxy runs various pluggable transports that work in different ways to hide OpenVPN traffic. The pluggable transport used depends on the type of block that is being circumvented. Currently, the most common pluggable transport used for OpenVPN traffic is obfs4, which works by scrambling traffic to make it look, essentially, like nothing.
Stunnel
Stunnel is open-source software that masks OpenVPN traffic as TLS/SSL traffic. TLS/SSL is a type of encryption that’s used by HTTPS. The VPN traffic is routed through a TLS/SSL tunnel, adding another layer of encryption and making it appear to any snoopers that it’s regular HTTPS traffic.
Shadowsocks
Shadowsocks is a type of proxy that’s often used to bypass censorship in countries like China. Although Shadowsocks is usually used alone, it can also be paired with a VPN to mask the encryption used in the VPN protocol. Notably, Shadowsocks works with Wireguard, a newer and lighter VPN protocol that’s being adopted by many VPN providers.
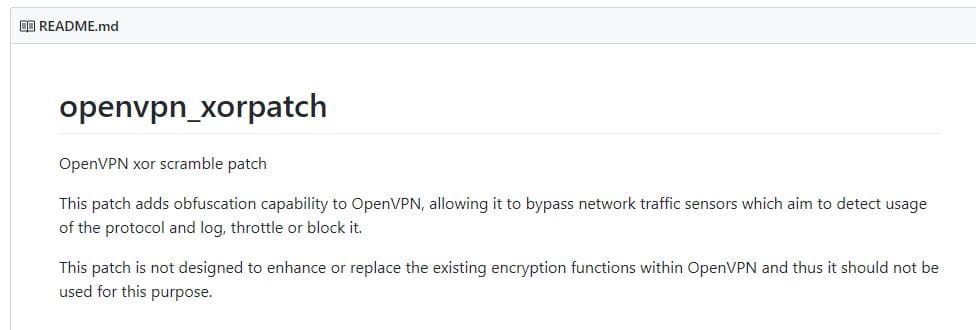
OpenVPN XOR scramble
OpenVPN XOR scramble uses the XOR cipher to disguise OpenVPN traffic. This is a simple cipher that involves the replacement of the value of each bit of data with another value. This is enough to ensure that some DPI methods can no longer detect the OpenVPN signature. However, the simplicity of XOR means it isn’t always effective against government blocks.
It’s worth noting that XOR has gained notoriety as a popular tool used by malware developers to hide their code from detection.
How do you know if a VPN server is obfuscated?
Normally, these VPN servers are labeled as such, or you can toggle this option on or off. Obfuscated servers are specialized VPN servers that hide the fact that you’re using a VPN to reroute. They allow users to connect to a VPN even in heavily restrictive environments.
When you connect to a regular VPN server, your ISP can’t see where you go online. But it may know you’re using a VPN from how your data looks. However, if you connect to an obfuscated server, it changes your data packets. Therefore, tools that are meant to block VPN traffic let it pass.








Call of Duty Mobile will permanently ban players for using a VPN. If I’m using an obfuscated vpn to find a game, then once it starts, switch to a device without Nord on it… will it still prevent CoD from knowing I’m using one? My free trial is on my phone, but I need to play on my superior iPad. But since I owe $10 to apple for another day (free trial expires the following day) I can’t download Nord on the iPad
Obfuscation prevents middlemen from scanning traffic for signs of VPN encryption. CoD is the endpoint, not a middleman, so I don’t think this would work. It’s more likely that CoD is blacklisting traffic from known VPN IP addresses rather than inspecting incoming traffic for VPN encryption.