Network engineering tools and software play a crucial role in network troubleshooting and analysis and are critical to maintaining a healthy and efficient network infrastructure
Effective network troubleshooting and analysis heavily rely on the type of software tools that network engineers utilize. These tools can significantly impact the outcome of the analysis, providing valuable insight into the underlying causes of network issues. These tools enable network engineers to identify and resolve issues in the network infrastructure quickly and efficiently, ensuring that the network remains operational and meets the organization’s requirements.
Here is our list of the best network engineer tools:
- ManageEngine OpManager EDITOR’S CHOICE A robust platform with a comprehensive network engineering toolset with monitoring and customizable alerts, ideal for detailed network management. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 Network Monitoring (FREE TRIAL) This cloud platform service provides both network device monitoring and traffic tracking with companion units that monitor servers and applications. Start a 30-day free trial.
- PRTG Network Monitor (FREE TRIAL) Get network discovery, inventory management, troubleshooting tools, and automated monitoring with this package. Offered as a SaaS package or as software for installation on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Nagios Offered in free and paid versions, this package of system monitoring tools can be extended by plug-ins. Rund on Linux or over a hypervisor.
- Wireshark This free tool captures packets from the network and displays them for filtering, searching, and analysis. Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset This package of more than 60 system administrator tools includes utilities, to discover, troubleshoot, and manage networks.
- Nmap Widely used for network investigation, this command line tool can be enhanced by a GUI add-on, called Zenmap.
- Faddom This discovery and mapping system can document networks, hardware, and applications. Runs as a virtual appliance.
- NetBrain This network monitoring and management service is able to automate typical network administration tasks. Based in the cloud.
- PingPlotter A Ping-based network discovery and performance monitoring system that can report on VoIP quality of service metrics. Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- PuTTY This terminal emulator can be used to test connections and probe port availability. Runs on Windows, Unix, Linux, and macOS.
One of the key advantages of these tools is that they allow engineers to monitor network performance and detect issues in real-time. They can monitor network traffic, identify bandwidth bottlenecks, and packet loss, and provide alerts when there are issues with network devices or connections. This real-time monitoring ensures that engineers can quickly respond to network issues before they impact users and cause downtime. Furthermore, these tools also provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, allowing engineers to analyze network performance over time and identify trends and patterns. This analysis can help engineers to identify potential issues before they become critical and proactively implement solutions to prevent them from occurring.
Another important feature of network engineering tools and software is their ability to automate network tasks and configurations. These tools can automate repetitive tasks such as device configurations and updates, freeing up engineer time to focus on more complex troubleshooting and analysis. In this article, we present the best Network engineering tools to help you have better control of your network and resolve issues effectively.
The Best Network Engineer Tools
Our methodology for selecting Network Engineer Tools
We’ve broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- Ability to troubleshoot and analyze complex networks
- Features for network discovery and performance monitoring
- Compatibility with various operating systems
- Real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities
- Integration and automation of network tasks
1. ManageEngine OpManager (FREE TRIAL)
Tested on: Windows, Linux
ManageEngine OpManager offers comprehensive network engineering tools that provide real-time network monitoring, robust fault management, and detailed network performance analysis.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Network Monitoring: Provides detailed monitoring of network devices and performance metrics.
- Intuitive Dashboard: Offers a user-friendly interface for real-time network status updates.
- Customizable Alerts: Allows users to set personalized thresholds for alerts and notifications.
- Automatic Device Discovery: Automatically detects and maps network devices, saving time and reducing manual effort.
- In-depth Reporting: Generates detailed reports on network performance and availability for analysis and troubleshooting.
- Multi-vendor Support: Compatible with devices from various vendors, ensuring flexibility in network management.
- Scalability: Supports both small and large networks, accommodating growth without compromising performance.
- Integrated Troubleshooting Tools: Includes tools for quick diagnosis and resolution of network issues.
- Performance Metrics: Provides comprehensive metrics for bandwidth, latency, and uptime.
- Security Features: Offers security protocols and encryption to safeguard network data.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine OpManager stands out due to its extensive network monitoring capabilities and user-friendly interface. The tool offers detailed insights into network performance, allowing administrators to quickly identify and resolve issues. Its customizable alerts and in-depth reporting features provide flexibility and precision in network management. Additionally, the tool’s scalability ensures it can accommodate growing network needs.
Its simple interface simplifies the management of complex network environments, ensuring swift identification and resolution of network issues. With advanced features like network mapping and traffic analysis, OpManager helps optimize network performance and ensures high availability. OpManager is great for sysadmins managing networks of any size and complexity, making it our top choice for network engineering tools.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for network administrators and IT professionals who require a comprehensive, scalable solution for managing diverse network environments. It is particularly suited for those overseeing large, complex networks with devices from multiple vendors. Its detailed monitoring and reporting capabilities make it a valuable asset for proactive network management and troubleshooting. Whether for small businesses or large enterprises, OpManager adapts to various network sizes and complexities.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: The intuitive dashboard makes network management straightforward and accessible.
- Flexible Customization: Customizable alerts and reports allow for tailored network monitoring.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Detailed monitoring capabilities ensure thorough oversight of network performance.
- Scalable Solution: Adapts to the needs of both small and large networks, making it a versatile choice.
- Multi-Vendor Compatibility: Supports a wide range of devices from different vendors, enhancing flexibility.
Cons:
- Complex Initial Setup: The initial configuration can be time-consuming and may require technical expertise.
Register for a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine OpManager is our top network engineering tool because of its robust monitoring capabilities and user-friendly interface. It provides a comprehensive view of network performance, allowing for detailed oversight and management. The customizable alerts and in-depth reporting features make it easy to tailor the tool to specific needs, while its scalability ensures it can grow with your network.
I found the automatic device discovery feature particularly useful, saving time and reducing manual effort. This tool is essential for any IT professional looking for an all-encompassing network management solution.
Download: Access a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/
OS: Windows, Linux
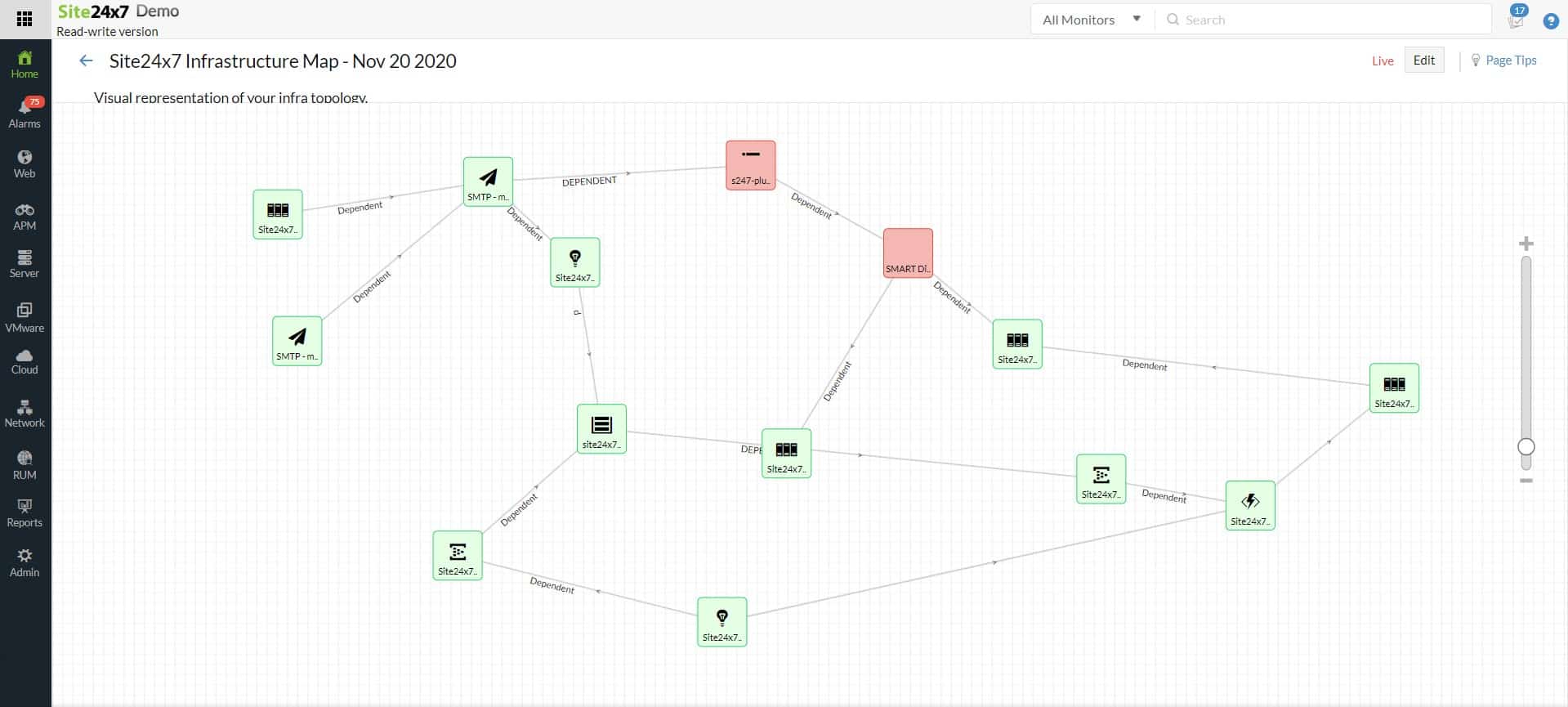
2. Site24x7 Network Monitoring (FREE TRIAL)
Site24x7 Network Monitoring is a cloud-based system that installs an agent on a host attached to the network that is to be monitored. The platform includes a network discovery service that identifies all equipment on the network, creates a network inventory, and draws up a network map. The package provides constant network device status polling with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Key Features:
- Integrated Network Management: Combines device and traffic monitoring.
- Automated Inventory Updates: Keeps network device records current.
- Alert System: Notifies about device faults and traffic issues.
Why do we recommend it?
Site24x7 Network Monitoring provides network device monitoring and traffic analysis. The network monitoring service is complemented by server and application monitoring modules. This system automatically adjusts the network inventory if a device is added to the network, moved, or removed. The package will raise an alert if a device has a fault or if traffic slows.
The Site24x7 package combines two types of network monitoring that are usually delivered as two separate purchases. The device and traffic monitoring tools are bundled together into plans that also provide server and application monitoring, so there is only one single purchase to get every type of network monitoring service.
The Network Monitoring service includes a series of performance thresholds that will trigger alerts if traffic speeds drop or if network devices report component problems. The alert thresholds can be adjusted and it is possible to set up new alert conditions.
Alerts appear in the dashboard of Site24x7 and the system can be instructed to forward them as notifications to specific technicians via SMS, voice call, email, or Slack message. This feature means that technicians don’t need to watch the system dashboard all the time in order to catch performance issues and take evasive action.
Who is it recommended for?
The Site24x7 platform is available in subscription plans and all of them include the network monitoring features. The plans are accessible for small businesses and also cater to larger organizations. The service is very easy to onboard and run, and most of the administrative requirements for network monitoring are implemented automatically by the tool.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Covers various network aspects in one platform.
- Automated Network Adjustments: Simplifies network management tasks.
- Versatile Alerting Options: Enhances response to network incidents.
Cons:
- Bundled Plan Requirement: Must subscribe to a comprehensive plan, even if only network monitoring is needed.
Site24x7 provides plans that include all of the monitoring and management units on the platform. There is an edition for managed service providers. All of the plans include the Network Monitoring service. You can try out Site24x7 with a 30-day free trial.
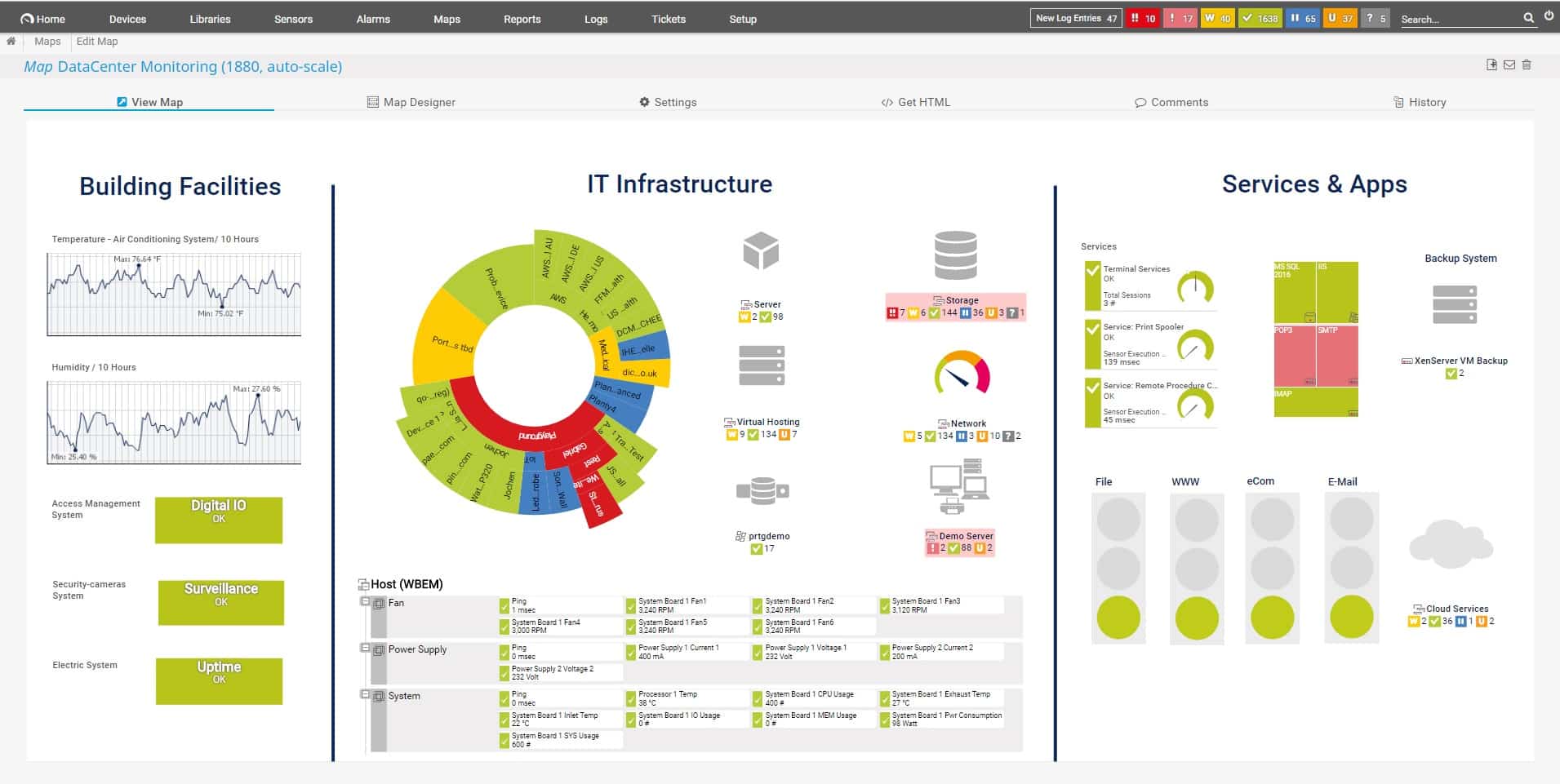
3. PRTG Network Monitor (FREE TRIAL)
PRTG Network Monitor is a user-friendly agentless Network engineering tool that is widely used for network troubleshooting and analysis. It provides real-time monitoring, alerting, and reporting capabilities, making it a popular choice among network engineers. One of the key features of PRTG Network Monitor is its ease of use. The tool is designed to be user-friendly, allowing engineers to quickly set up monitoring and alerts for their network infrastructure. It also provides a customizable dashboard, which allows engineers to monitor the health and performance of their network infrastructure in real-time.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies network monitoring for various users.
- Customizable Dashboard: Tailors monitoring views to specific needs.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Covers a wide range of network metrics.
Why do we recommend it?
PRTG is recommended for its user-friendly design and customizable dashboard, which simplify network monitoring and management, especially for real-time performance metrics.
PRTG Network Monitor provides real-time monitoring for a wide range of network devices and services, including servers, routers, switches, and applications. It allows engineers to monitor key performance metrics such as response time, packet loss, and bandwidth utilization. Additionally, PRTG Network Monitor provides historical data analysis, which allows engineers to analyze network performance trends over time. The tool also provides advanced reporting capabilities, allowing engineers to generate detailed reports on network performance metrics. These reports can be customized to meet the specific needs of the organization, providing valuable insights into network health and performance.
PRTG Network Monitor’s alerting capabilities are another key feature of the tool. It can send alerts when network issues are detected, allowing engineers to quickly identify and resolve issues before they cause downtime or impact users. These alerts can be customized, allowing engineers to set thresholds for specific performance metrics and configure the tool to alert them when those thresholds are exceeded.
Who is it recommended for?
It’s particularly suited for network engineers who prioritize ease of use and require a tool that provides comprehensive real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities.
Pros:
- Ease of Use: Accessible even to those with limited technical expertise.
- Real-Time Insights: Offers immediate visibility into network performance.
- Flexible Alerting Mechanisms: Allows customization of alert triggers.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: Some initial setup and customization may require extra effort.
PRTG Network Monitor also provides integrated network troubleshooting capabilities. It provides detailed visualizations of network topology, making it easy for engineers to identify the root cause of network issues quickly. Additionally, PRTG Network Monitor integrates with other tools, including Amazon CloudWatch and Microsoft Azure Monitor, providing a comprehensive network management solution.
4. Nagios
Nagios is a popular network tool used in IT infrastructure monitoring. It helps network engineers to identify and resolve problems before they get out of hand. Nagios alerts network engineers when critical components fail and when they recover after the problem has been resolved. It runs mainly on Linux operating systems. The product comes in two editions—Nagios Core and Nagios XI.
Key Features:
- Extensive Protocol Support: Monitors a wide array of network protocols.
- Customizable with Plugins: Offers tailored monitoring solutions.
- Free and Paid Versions: Accessible for different budget levels.
Why do we recommend it?
Nagios is recommended for its flexibility and extensibility, making it a robust solution for comprehensive IT infrastructure monitoring, particularly in Linux environments.
Some of the key network protocols and system resources monitored include:
- Network protocols include SMTP, POP3, HTTP, NNTP, ICMP, SNMP, FTP, SSH, and many more.
- Host resources such as processor load, disk usage, system logs, and more, using monitoring agents.
- Hardware conditions such as temperature, alarms, and more
Nagios Core is an agent-based free and open-source infrastructure monitoring application. On the other hand, Nagios XI is an easy-to-use agentless commercial edition that uses Nagios Core as its back-end alongside other technologies, including a built-in web configuration GUI, making it much easier to manage than Nagios Core.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators who need a customizable and scalable monitoring solution, especially those comfortable with Linux and seeking a tool with extensive plugin support.
Pros:
- High Customizability: Adaptable to diverse network environments.
- Wide Monitoring Scope: Ideal for comprehensive network surveillance.
- Flexibility in Pricing: Offers both open-source and premium solutions.
Cons:
- Complexity in Free Version: Nagios Core may be challenging for beginners.
Nagios XI monitors critical IT infrastructure components such as network devices, servers, and applications, including network protocols and system metrics, and resources.
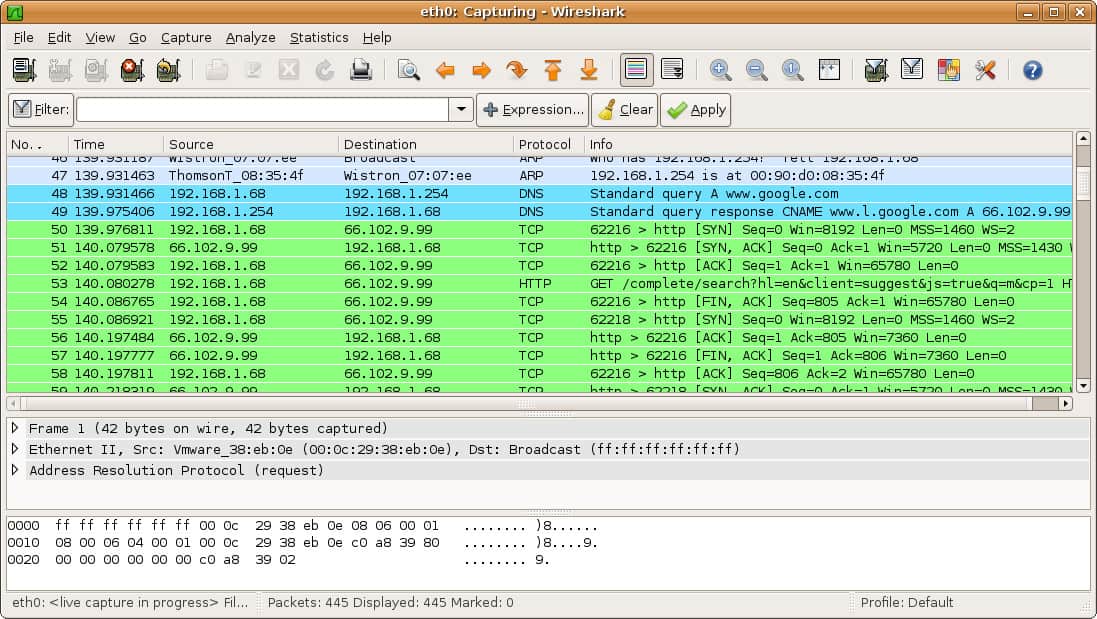
5. Wireshark
Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. Wireshark is a widely used Network engineering tool that is essential for network troubleshooting and protocol analysis. It provides a detailed packet-level analysis of network traffic, making it a valuable tool for identifying network issues and security threats.
Key Features:
- In-Depth Packet Analysis: Provides detailed insights into network traffic.
- Advanced Filtering Capabilities: Aids in pinpointing specific network issues.
- Free and Open Source: Accessible without cost and open for customization.
Why do we recommend it?
Wireshark is recommended for its unparalleled packet-level analysis capabilities, crucial for detailed network troubleshooting and security analysis.
One of the key features of Wireshark is its ability to capture and analyze network traffic in real-time. It allows network engineers to capture and inspect individual packets of data, providing detailed information about the contents of the packets and the devices and services involved in the transmission.
Wireshark’s advanced filtering and search capabilities allow engineers to quickly isolate specific packets and identify patterns in network traffic. It also provides real-time statistics on network performance metrics such as packet loss, latency, and bandwidth utilization.
Wireshark’s detailed analysis of network traffic makes it an essential tool for identifying security threats and vulnerabilities. It allows engineers to inspect network packets for malicious activity, including malware, viruses, and unauthorized access attempts. Additionally, Wireshark can be used to inspect network traffic for compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is a must-have for network engineers and security professionals who require in-depth analysis of network traffic and are interested in detailed packet inspection.
Pros:
- Detailed Network Insights: Ideal for thorough network analysis.
- Customizable Analysis: Filters and dissectors can be tailored.
- Universal Applicability: Supports a vast array of network protocols.
Cons:
- Technical Expertise Required: Best utilized by those with network analysis experience.
Wireshark’s versatility and flexibility are also key features of the tool. It can be used to analyze a wide range of network protocols and services, including HTTP, DNS, FTP, and VoIP. It is also compatible with a variety of operating systems and can be used on both wired and wireless networks.
6. SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset

SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset (ETS) is a commercial Network engineering tool that is designed to help network engineers troubleshoot and analyze complex networks. It is a comprehensive suite of network tools that provide a range of features for network engineers, including network discovery, device configuration management, network performance monitoring, and network troubleshooting.
Key Features:
- Versatile Tool Selection: Offers over 60 tools for diverse network tasks.
- Network Discovery & Mapping: Efficiently identifies and organizes network devices.
- Automated Device Management: Streamlines device configuration and maintenance.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds ETS stands out for its extensive range of tools, enabling comprehensive network monitoring, efficient device management, and effective troubleshooting – essential for any network engineer.
One of the key features of ETS is its network discovery tool, which allows engineers to identify and map out the devices on their network. This tool provides detailed information about each device, such as its IP address, MAC address, and manufacturer, which can be used to troubleshoot network issues and optimize network performance. ETS also includes device configuration management tools that allow engineers to automate routine configuration tasks and backup device configurations. This feature helps to streamline network management and ensures that devices are configured correctly and consistently across the network.

Another important feature of ETS is its network performance monitoring tools. These tools provide real-time visibility into network performance, allowing engineers to identify and resolve issues before they impact network availability or performance. The performance monitoring tools in ETS provide detailed information about network bandwidth usage, packet loss, latency, and other performance metrics, making it easier for engineers to optimize network performance and improve user experience.
Who is it recommended for?
ETS is highly recommended for network engineers and system administrators seeking a versatile, comprehensive toolset for efficient network management and troubleshooting in Windows-based environments.
Pros:
- Wide Range of Tools: Comprehensive suite enhances network management capabilities.
- Effective Network Visualization: Aids in quick identification and troubleshooting.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Offers immediate insights into network performance.
Cons:
- Windows Server Limitation: Not suitable for non-Windows environments.
ETS also includes network troubleshooting tools that help engineers identify and resolve network issues quickly. These tools provide real-time network diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities, enabling engineers to quickly pinpoint the root cause of network issues and take corrective action. A 14-day free trial is available on request.
7. Nmap
Nmap (Network Mapper) is a popular and free Network engineering tool that is essential for network troubleshooting and analysis. It is a network exploration and security auditing tool that is used to discover hosts and services on a network, as well as to identify security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
Key Features:
- Network Scanning Proficiency: Efficiently identifies network components.
- Security Auditing Capability: Highlights potential network vulnerabilities.
- Wide Protocol Range: Covers numerous network protocols for comprehensive scanning.
Why do we recommend it?
Nmap is a standout tool for network security due to its comprehensive scanning capabilities that efficiently identify devices and vulnerabilities within a network. Its adaptability and thorough security auditing make it indispensable for network professionals.
One of the key features of Nmap is its ability to scan large networks quickly and accurately. It can identify active hosts, open ports, and services running on those ports. Furthermore, Nmap can detect the operating system and software versions, providing valuable information for network troubleshooting and analysis.
Nmap’s advanced scanning capabilities make it an essential tool for network security analysis. It can be used to identify potential vulnerabilities in a network’s security posture, including open ports, unsecured services, and outdated software versions. It can also be used to identify devices that are connected to a network without authorization or that may be vulnerable to attacks. Another important feature of Nmap is its flexibility and customizability. It offers a range of scanning options, including TCP, UDP, and ICMP scans, as well as advanced options such as stealth scanning and OS detection.
Additionally, Nmap can be extended with custom scripts, allowing network engineers to perform complex scans and automate repetitive tasks. Nmap’s reporting capabilities are also an essential feature of the tool. It allows engineers to generate detailed reports on network discovery, security audits, and performance metrics. These reports can be customized to meet the specific needs of the organization, providing valuable insights into network health and security.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for network administrators and security professionals seeking an in-depth understanding of their network’s structure and security posture. Nmap is particularly useful for those needing detailed network analysis and security assessments.
Pros:
- Rapid Network Discovery: Quickly maps network structure.
- Security Analysis: Helps in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities.
- Customizable Scans: Adaptable to specific network environments.
Cons:
- Advanced Usage Complexity: May require technical knowledge for intricate scanning configurations.
8. Faddom
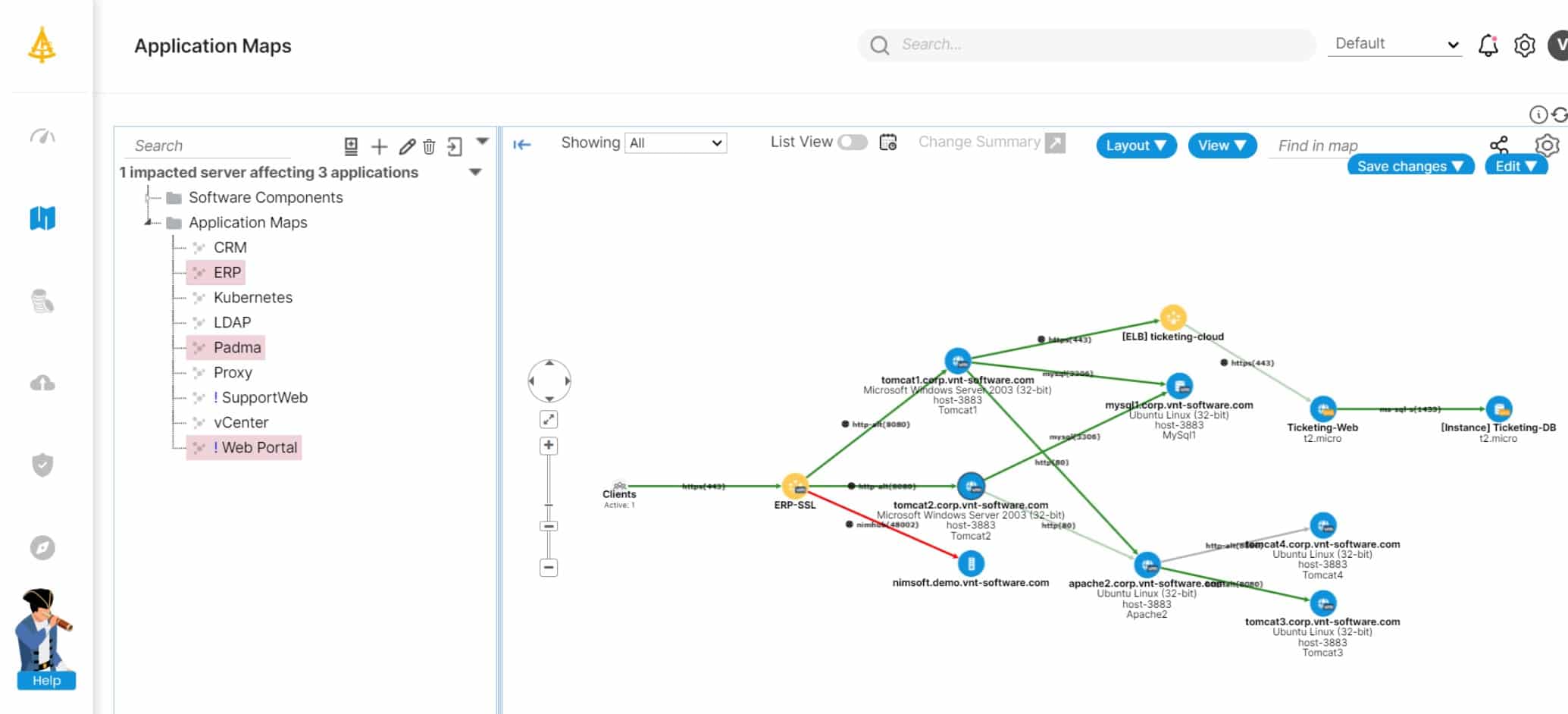
Faddom is an IT documentation tool that is able to discover all hardware on a network, including endpoints. This system scans each device to note all of its attributes, it generates an inventory, and a system map. The details of each device include the interfaces to which other devices are connected. This information appears on the connections shown on the created network map.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Network Discovery: Thoroughly documents network hardware.
- Detailed Application Mapping: Reveals interdependencies in network applications.
- Micro-Segmentation Aid: Supports intricate network segmentation planning.
Why do we recommend it?
Faddom is recommended for its thorough network discovery and mapping capabilities, which are crucial for effective network management and micro-segmentation planning.
Faddom advises that its network inventory and map are ideal for planning the Access Control Lists needed for micro-segmentation. This technique blocks or allows traffic from specific sources to specific destinations, filtering access at each switch on the network. Getting those allow and deny statements right relies on having a good understanding of the possible routes between two points on the network.
The Faddom system can also map applications and it isn’t limited to those that you host on your own servers. It also isn’t limited to identifying those applications that you know about. You don’t need to give the system a list of your software. Instead, it searches your servers and cloud accounts for running processes and then scans for spawned processes. It can also detect contributing modules in Web applications. Thus, it crawls through all of the systems that contribute to the applications that you know about and creates a map that shows their relationships.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for IT professionals who need detailed network documentation and are involved in planning and implementing network security measures like micro-segmentation.
Pros:
- Extensive Documentation: Provides detailed network and application insights.
- Access Control List Support: Aids in creating effective network traffic filters.
- Application-Centric Mapping: Identifies all contributing network components.
Cons:
- Limited Pricing Transparency: Requires consultation for pricing information.
There isn’t a price list available for Faddom. This system is an on-premises tool that you run over a hypervisor. That virtualization system is proprietary to Faddom and it is delivered with the software download. Book a demo and check out the pricing.
9. NetBrain
NetBrain is a cloud-based advanced commercial network tool that helps with network troubleshooting and analysis by providing network automation and visualization capabilities. It is designed to simplify and speed up the process of network problem resolution by automating time-consuming and complex tasks.
Key Features:
- Network Automation: Simplifies complex network tasks.
- Real-Time Topology Visualization: Offers a dynamic view of network architecture.
- Integration-Friendly: Seamlessly works with other network tools.
Why do we recommend it?
NetBrain is endorsed for its robust network automation and dynamic visualization features, which significantly streamline the troubleshooting and management of network systems. Its capacity to automate repetitive tasks and integrate seamlessly with other tools makes it a vital asset for efficient network operations.
One of the key features of NetBrain is its ability to automatically map network infrastructure and provide real-time visibility into the network. It allows network engineers to see the entire network topology, including devices, links, and services, providing a comprehensive view of the network environment. This helps engineers identify the root cause of network issues and troubleshoot them more efficiently.
NetBrain’s automation capabilities are also a key feature of the tool. It can automate tasks such as configuration changes, network device backups, and firmware updates, freeing up time for engineers to focus on more complex troubleshooting tasks. Additionally, NetBrain can integrate with other Network engineering tools and systems, such as ticketing systems and network monitoring tools, to provide a seamless workflow for network operations.
Another important feature of NetBrain is its ability to provide real-time network analytics and performance metrics. It can monitor network traffic, device performance, and service availability, providing real-time insights into network health and performance. This allows engineers to proactively identify and resolve potential issues before they impact network performance.
NetBrain’s collaboration and knowledge-sharing capabilities are also noteworthy. It provides a central platform for engineers to collaborate on network issues, share knowledge and expertise, and document network changes and configurations. This helps to improve network operations and reduce the risk of human error.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly beneficial for network engineers and IT professionals who face complex network environments daily. It is ideal for those looking to reduce the time spent on manual network tasks and improve problem resolution speed through automation and enhanced visibility.
Pros:
- Efficient Problem Resolution: Accelerates troubleshooting processes.
- Automated Network Operations: Reduces manual workload.
- Comprehensive Visibility: Provides clear insights into network performance.
Cons:
- Learning Curve for Advanced Features: May require training for full feature utilization.
10. PingPlotter
PingPlotter is a commercial network tool that helps with network troubleshooting and analysis by providing real-time monitoring and visualization of network performance. It is designed to help engineers quickly identify and resolve network issues by providing detailed insights into network behavior.
Key Features:
- Continuous Network Monitoring: Offers persistent oversight of network health.
- Graphical Performance Display: Visualizes network metrics effectively.
- Historical Data Analysis: Enables trend identification over time.
Why do we recommend it?
PingPlotter is highly recommended for its exceptional ability to monitor and visualize network performance in real-time. Its continuous monitoring capabilities and graphical displays help network engineers swiftly pinpoint and address issues, enhancing overall network reliability.
One of the key features of PingPlotter is its ability to perform continuous and real-time network monitoring. It sends out ping requests to target devices and monitors the response time and packet loss. This helps engineers quickly identify network connectivity issues, packet loss, and latency, which are all important metrics for network performance.
Another important feature of PingPlotter is its ability to provide a visual representation of network performance. It displays network data in the form of graphs, charts, and tables, making it easy for engineers to analyze and identify trends and patterns. This helps engineers quickly identify the root cause of network issues and make informed decisions about how to resolve them.
PingPlotter’s historical data analysis capabilities are also noteworthy. It allows engineers to view historical performance data, such as response time and packet loss, and identify trends and patterns over time. This helps to identify recurring network issues and make informed decisions about network optimization and troubleshooting.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly suitable for network engineers and IT specialists who require detailed and ongoing analysis of network health. PingPlotter is ideal for professionals seeking to optimize network performance through a deep understanding of data trends and immediate issue detection.
Pros:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Quickly identifies network performance issues.
- Intuitive Visualization: Simplifies understanding of complex network data.
- In-Depth Analysis: Facilitates thorough investigation of network problems.
Cons:
- May Require Technical Familiarity: Best used by those with some network background.
PingPlotter can be used on a range of platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, and can be integrated with other Network engineering tools and systems. PingPlotter Professional is available for a 14-day free trial.
11. PuTTY
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator that is widely used for network troubleshooting and analysis. It is open-source software that allows network engineers to access remote systems over a network connection. PuTTY is a lightweight application that is easy to install and use.
Key Features:
- Remote Access via SSH: Ensures secure connections to network devices.
- Supports Multiple Protocols: Versatile in handling different connection types.
- Free and Open Source: Widely accessible without cost constraints.
Why do we recommend it?
PuTTY is highly recommended for its robust security features and versatility in handling different types of network connections. As a free and open-source tool, it provides essential functionality for secure remote access to network devices, making it a staple in the toolkit of network professionals.
One of the primary uses of PuTTY is to establish secure shell (SSH) connections to remote devices. SSH is a protocol that provides secure communication between two devices over an unsecured network. PuTTY’s SSH client is designed to provide a secure and encrypted connection, preventing unauthorized access and data theft. This makes it an essential tool for network engineers who need to access devices in a secure way, such as routers, switches, and servers.
Another important feature of PuTTY is its ability to provide Telnet connections to remote devices. Telnet is an older protocol that is used for remote device access, but it is less secure than SSH. However, in some cases, network engineers may still need to use Telnet to connect to devices that do not support SSH. PuTTY’s Telnet client provides a secure way to use Telnet over the network, preventing unauthorized access and data theft.
PuTTY also supports other protocols such as rlogin, raw, and serial connections. This versatility makes it a valuable tool for network engineers who need to connect to a variety of devices. In addition to providing secure remote connections, PuTTY also has several features that aid in network troubleshooting and analysis. For example, PuTTY’s logging feature allows engineers to record their interactions with remote devices, which can be useful for debugging and auditing purposes. PuTTY also has a powerful terminal emulator that supports several terminal types, making it easier to work with different operating systems and devices.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for network engineers, system administrators, and IT professionals who need reliable and secure remote access to manage network devices. PuTTY is particularly useful for those who require a straightforward, command-line based interface for managing a variety of network protocols.
Pros:
- Secure Remote Management: Ideal for safe network device administration.
- Flexible and Lightweight: Adaptable to various network scenarios.
- Wide Protocol Compatibility: Supports SSH, Telnet, and more.
Cons:
- No Graphical User Interface: Primarily command-line based, which might deter some users.