Every country is impacted by cyber crime to some extent, not least Germany. Citizens and organizations operating in Germany feel the wrath of ransomware attacks, malicious hacks, phishing schemes, and more. There is strong awareness of cyber crime in the country and businesses are making efforts to stay ahead of the game, but it’s difficult to sidestep the advancing technologies employed by cyber criminals.
Below, we summarize some of the findings of the latest studies and reports with respect to cybercrime and cyber security in Germany.
1. Over 70% of German companies were the subject of a successful attack within 12 months
The 2022 Cyberthreat Defense Report (CDR) by CyberEdge Group revealed that over 70% of German organizations experienced a successful cyberattack.
The 2024 update of the report states that an alarming 52% of German businesses suffered six or more successful cyberattacks. This puts it in the top three most attacked countries globally, behind Mexico and Australia.
2. Germany saw the first death by ransomware
CyberEdge reported in 2021 that a woman from Düsseldorf was rushed to a hospital 19 miles away in Wuppertal because her local hospital in Düsseldorf was targeted by a ransomware attack. 30 of the hospital’s servers were compromised as part of the attack which prevented new patients from being processed. Sadly, the woman died.
3. German companies spend nearly 11% of their IT budget on security
So how much are companies spending to combat cybercrime? In 2022, CyberEdge found that German firms spend 10.8 percent of their IT budget on security. This is on the lower end of the scale with the UK (11.3 percent), Japan (11.2 percent), Australia (10.9 percent), and France (10.7 percent) rounding out the bottom five. Brazil topped the list at 15.6 percent followed by Turkey at 15.3 percent.
4. The security budgets of German organizations increased 3% in 2021
German organizations saw the lowest increase in security spending at 3.2 percent. Indeed, the average increase in security budgets over the last five years has been between 4 and 5 percent. CyberEdge found that Brazilian businesses increased security spending the most at 6.7 percent.
According to the 2023 report, German organizations are planning to increase their budget for cybersecurity by 4.8%. This would bring Germany in line with the top spenders.
5. Over 70% of German companies indicate a preference for machine learning and AI
CyberEdge also sought to find out how companies feel about the place of advancing technologies such as AI and machine learning in security products. 71.6 percent of German organizations have a moderate to strong preference for security products that have these types of features. This is the lowest percentage of all countries listed. France and Canada (73.6 percent) were also less bullish. Saudi Arabia (98 percent), Turkey (96.6 percent), and South Africa (91.8 percent) make up the top three.
CyberEdge’s latest report indicates that companies incorporating machine learning into their cybersecurity strategies have seen a marked reduction in drive-by downloads and zero-day attacks. The report by CyberEdge highlights the effectiveness of machine learning in enhancing cyber defense mechanisms. This is what CyberEdge had to say:
“We think this is the result of improvements in security tools that monitor activities on networks and endpoints, and use machine learning and AI to identify malicious actions early enough so that security teams can respond to and contain exploitation.”
6. 58% of organizations attacked by ransomware in 2023
The Sophos State of Ransomware Report 2023 indicates a slight reduction in ransomware incidents from 2022. In 2023, 58% of organizations were hit by malware, down from 67% the year before. Singapore topped the chart with 84% of organizations hit with attacks and the UK was at the bottom with just 44% of companies reporting a ransomware attack.
7. 39% of companies stopped attacks before data was encrypted
Germany did quite well at stopping ransomware in its tracks. Sophos found that well over one-third of attacks (39 percent) were stopped before data was encrypted. This put it above the average of 35 percent. India was the country that struggled the most, preventing encryption in just 20 percent of cases. At the other end of the scale was Saudi Arabia in which cybercriminals failed to encrypt the data of organizations in 62 percent of cases.
The latest report does not detail country-specific statistics. However, it offers an average across all surveyed countries. This data suggests a worsening scenario: the rate of successfully thwarting attacks before data encryption has decreased, falling from 31% in 2022 to 21% in 2023.
8. 44% of organizations paid the ransom to get their data back
The 2023 Sophos report reveals that 44% of German companies decided to pay a ransom to receive their data. All of the companies that paid a ransom successfully regained access to their data.
9. The average cost of ransomware attacks in Germany was more than $1.73 million
The 2022 Sophos report also took into consideration the cost of remediation for a ransomware attack. In Germany, the average cost was $1.73 million in 2021, a 48 percent increase from 2020 ($1.17 million). This worked out above the global average of $1.40 million. Belgian firms faced the largest costs to remediate ransomware attacks, shelling out an average of $3.71 million.
Although the latest report doesn’t specify costs for individual countries, the research reveals that the average cost has risen to around $1.82 million per incident. It is worth noting, however, that companies with an annual revenue of less than $10 million had recovery costs of around $165,520. Larger companies face substantially bigger costs to recover from cyberattacks.
10. 81% of companies hold cyber security insurance
In its 2022 report, Sophos revealed that well over three-quarters of German companies (81 percent) have cyber security included in their policies. While this sounds quite high, it actually puts the country just below average (82 percent) of all countries studied. Half of companies that hold cyber insurance have ransomware included in their insurance policy.
11. 27% of companies pay for standalone cyber insurance
Delving a little further into cyber insurance, the Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2022 looked specifically at standalone cyber insurance. This is often more comprehensive than combined coverage so is viewed as a better indicator of a firm’s cyber readiness. 27 percent of German companies have a standalone cyber insurance policy in 2022, a slight decrease on the 28 percent of 2021.
12. Germany dealt with increasing cyber attacks
According to the Hiscox report, the number of German firms that reported attacks increased from 46% in 2021 to 85% in 2023. To make things worse, the average number of attacks experienced by companies in Germany jumped from six to ten.
13. 63% of ransomware attacks occurred through phishing emails
In 2023, phishing continued to be the most prevalent attack vector for ransomware attacks. The latest Hiscox report found that 63 percent of ransomware attacks occur via phishing emails. The second most prevalent attack vector was credential theft.
14. Germans received the 5th highest share of malicious mailshots in 2021
A spam and phishing study conducted by Kaspersky revealed the frequency of malicious correspondence in various regions. It uncovered that in 2021, Germany was the fifth most targeted country by malicious emails, having previously been the most popular target for several years until 2020. It received a 4.83 percent share of malicious email campaigns. This year, Spain was the biggest target, receiving 9.32 percent.

15. Germany was the source of over 5.19% of spam in 2022
In terms of where spam originates, Germany saw an improvement compared to 2021. It switched places with China going from 14% to just over 5% (the opposite happened to China’s stats). As was the case for the last few years, Russia came out as the main culprit, accounting for 29.82% of spam.
16. German .de domains no longer scam website hotspots
In 2020, 1.23 percent of scam websites had a .de domain. This put it in fourth place behind .com (24.36 percent), .ru (2.12 percent), and .com.br (1.31 percent). In 2021 however, .de domains didn’t make the list of domains to watch, highlighting a decrease in scam websites on these top-level domains.
17. Out of 75 countries studied, Germany ranks 44th for overall cyber security
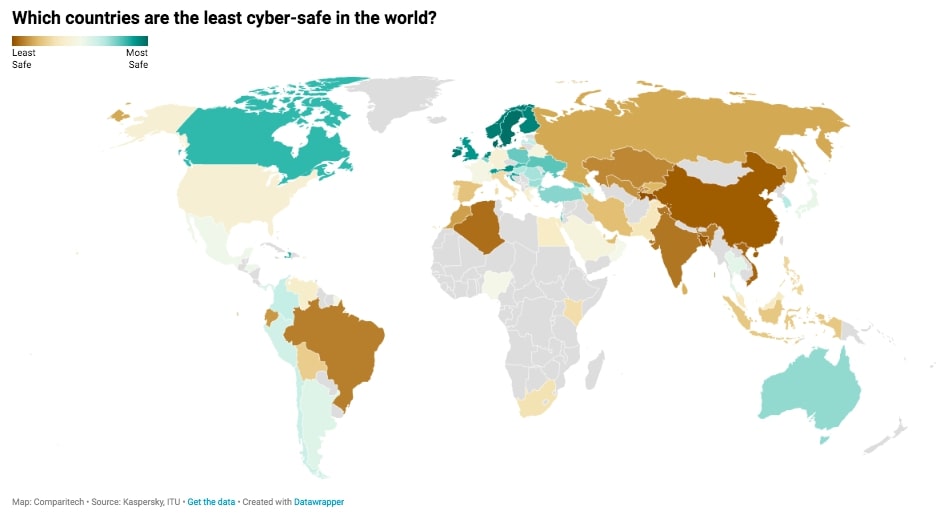
A Comparitech study analyzed a range of cyber security statistics to paint a holistic view of the state of cyber security in 75 countries. Germany fared okay, but featured in the lower half of the sample in 44th place. It received a score of 19.57, where a low score is better. The top-performing country was Denmark with 3.56, while the country that seems to be most lacking in terms of cyber security was Tajikistan with 35.54.
18. Germany has dished out €78 million worth of GDPR fines
A 2024 data breach report by DLA Piper provides information about GDPR fines. It found that since 2018 Germany has paid out €78,078,833 in fines. This makes it the 6th most fined country. Ireland still tops the list with 2.8 billion in fines issues, largely due to massive fines handed to Meta.
19. The fourth-largest GDPR fine to date was issued in Germany
A big contributor to the above figure was the fact that Germany issued one of the largest GDPR fine to date. The Hamburg data protection supervisory authority fined global retailer H&M €32,258,708.
20. Germany experienced the highest number of data breach notifications
Another area DLA Piper dove into was the number of personal data breach notifications issued in each country. It found that Germans experienced the largest number of personal data breach notifications since the GDPR came into effect. 32,030 companies reported data breaches to consumers whose data was affected.
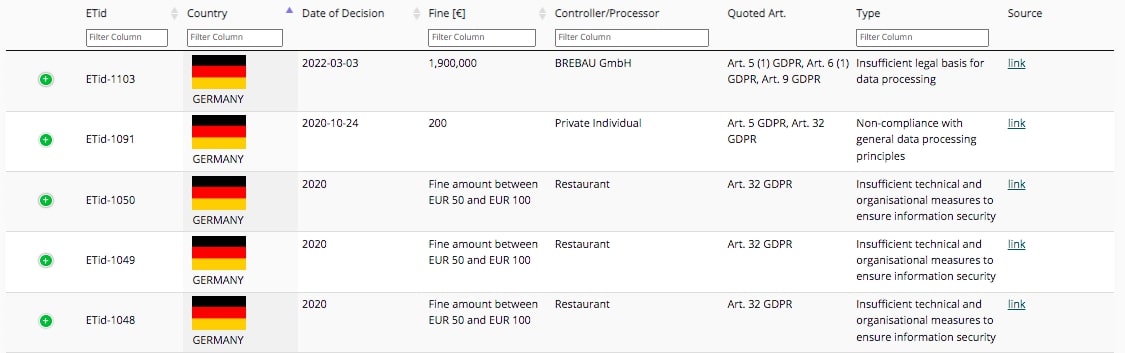
21. 163 GDPR fines have been issued in Germany so far
Enforcement Tracker has been keeping tabs on all GDPR fines for which information is made publicly available. Of 2,213 entries in its database, 163 (7.37 percent) were issued in Germany.
22. The average cost of a data breach in Germany was $4.67 million
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 provides a wealth of information about how breaches impact organizations. One key area of study is the overall cost of a data breach, which can be extremely high for some firms. In Germany, the average cost of a breach was $4.67 million (down from $4.85 million the year before).
23. 57% of breaches are caused by malicious attacks
So what causes these expensive data breaches? IBM revealed in its Cost of a Data Breach Report 2020 that the majority (57 percent) of data breaches in Germany result from malicious attacks. The only region with a higher percentage is the Middle East where 59 percent of breaches stem from malicious attacks. In Germany, 24 percent of breaches occur due to system glitches and 19 percent as a result of human error.
24. Germany has the highest rate of organizations with fully deployed security automation
With high breach costs and a significant portion of breaches resulting from malicious attacks, it’s perhaps not surprising that German organizations are the most likely to have fully deployed security automation, with 30 percent of organizations falling under this category. A further 45 percent have partially deployed security automation. The global averages for these figures are 21 percent and 38 percent respectively.
25. Germany has the shortest data breach identification and containment time
The popularity of security automation could be a reason that German companies are the quickest to identify and contain a breach. Identification occurs within 128 days, well below the global average of 207 days. Containment takes 32 days compared to the average of 73.
According to IBM’s latest report, companies that use automation benefit from a 108-day shorter average time to identify and contain a breach. This is a testament to the efficacy of automated security systems.
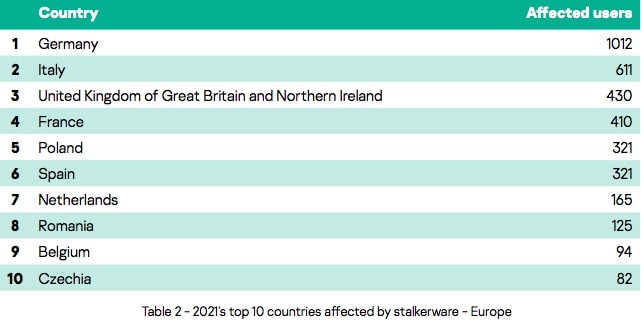
26. Germany is the country most affected by stalkerware in Europe
A stalkerware study by Kaspersky in 2021 found that Germany saw the highest number of incidents of stalkerware of all European countries investigated (some 1,012 incidents). This was despite a 34.5 percent reduction on the previous year (1,546 incidents recorded in 2020).
On a global scale, there were four countries with higher rates than Germany, starting with Russia, followed by Brazil, the US, and India.
27. Employees use an average of 70 passwords
The LastPass 3rd Annual Global Password Security Report offers useful information about how employees use passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). The study found that German employees use an average of 70 passwords each. This sounds quite high but it’s still far fewer than the number of passwords Belgian employees have to juggle (112). LastPass also found that German employees reuse an average of 13 passwords. This was about average, but really, even one reused password is a big no-no when it comes to password security.
28. 32% of businesses use MFA
MFA adds an extra step to login processes, enhancing account security. LastPass discovered that 32 percent of German organizations have employees that use MFA, putting it sixth behind Denmark, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, and the UK.
29. Newly discovered malware variants are up by 20% on the previous year
BSI Germany reported in 2021 that it had discovered 144million new types of malware, up 20% from 2020. This equates to an average of 394,000 malware attacks each day.
30. Revenue from the cyber security market is estimated to reach US$6.44bn in 2022.
A recent report from Statista found that revenue in the cyber security market is expected to reach a record high of almost $6.5bn in 2022. By 2027 this figure is projected to reach a market volume of US$11.73bn.
FAQs about cyber security and cyber crime in Germany
What is the punishment for cyber crime in Germany?
Anyone found guilty of breaching rule 263a of the German Criminal Code can receive up to five years in prison or a fine as punishment for their crimes, depending on the severity.
How do I report a scammer online in Germany?
People who have been affected by online fraud, a scam, or are a victim of a cybercrime in Germany can report the crime to their local police station. You can file a report online or visit your local police station to report it to a police officer in person.
See also: